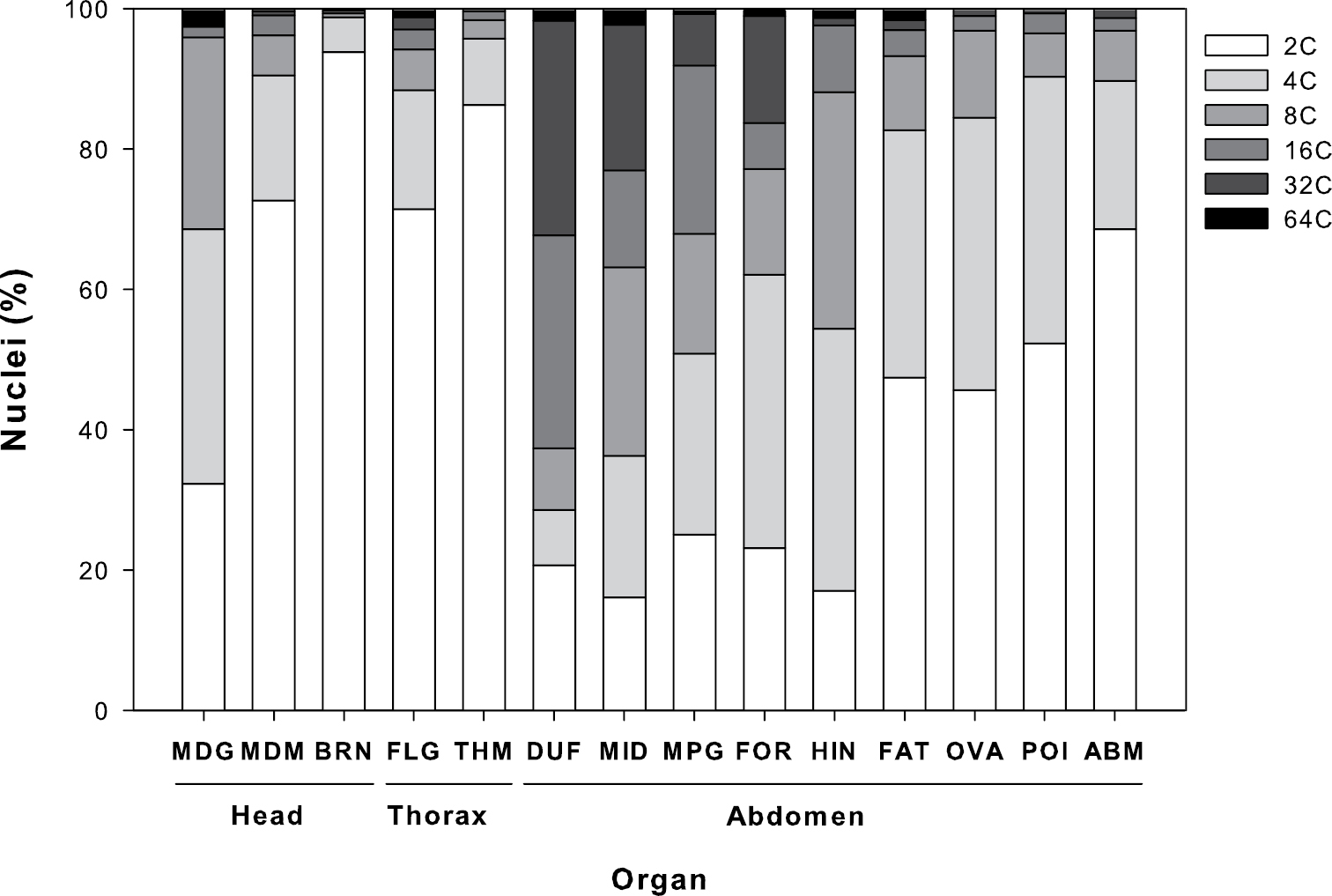
|
Dog Rose
''Rosa canina'', the dog rose, is a variable climbing, wild rose species native to Europe, northwest Africa, and western Asia. Description The dog rose is a deciduous shrub normally ranging in height from , though it can scramble higher into the crowns of taller trees. Its multiple arching stems are covered with small, sharp, hooked prickles, which aid it in climbing. The leaves are pinnate, with 5–7 leaflets, and have a delicious fragrance when bruised. The dog rose blooms from June to July, with sweet-scented flowers that are usually pale pink, but can vary between a deep pink and white. They are in diameter with five petals. Like other roses it has a quintuscial aestivation. Unusually though, of its five sepals, when viewed from underneath, two are whiskered (or 'bearded') on both sides, two are quite smooth and one is whiskered on one side only. It has usually 10 or more pistils, and multiple stamens. Flowers mature in September to October, into an oval, , red-orange h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was the son of a curate and was born in Råshult, in the countryside of Småland, southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosa Rubiginosa
''Rosa rubiginosa'' (sweet briar, sweetbriar rose, sweet brier or eglantine; synonym (taxonomy), syn. ''R. eglanteria'') is a species of rose native to Europe and western Asia. Description It is a dense deciduous shrub 2–3 meters high and across, with the stems bearing numerously hooked Spine (botany), prickles. The foliage has a strong apple-like fragrance. The leaf, leaves are pinnately compound, 5–9 cm long, with 5–9 rounded to oval leaflets with a serrated margin, and numerous glandular hairs. The flowers are 1.8–3 cm in diameter, the five petals being pink with a white base, and the numerous stamens yellow; the flowers are produced in clusters of 2–7 together, from late spring to mid-summer. The fruit is a globose to oblong red rose hip, hip 1–2 cm in diameter. Etymology Its name ''eglantine'' is from Middle English ''eglentyn'', from Old French ''aiglantin'' (adj.), from ''aiglent'' 'sweetbrier', from Vulgar Latin *''aculentus'' (with the endi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matthias De L'Obel
Mathias de l'Obel, Mathias de Lobel or Matthaeus Lobelius (1538 – 3 March 1616) was a Flemish physician and plant enthusiast who was born in Lille, Flanders, in what is now Hauts-de-France, France, and died at Highgate, London, England. He studied at the University of Montpellier and practiced medicine in the Low Countries and England, including positions as personal physicians to two monarchs. A member of the sixteenth-century Flemish School of Botany, he wrote a series of major treatises on plants in both Latin and Dutch. He was the first botanist to appreciate the distinction between monocotyledons and dicotyledons. The plant genus '' Lobelia'' is named after him, as is Lobel's maple '' Acer lobelii''. Life Mathias de l'Obel was born in Lille (Flemish ''Rijsel'') in the County of Flanders, Spanish Netherlands, now French Flanders in 1538, the son of Jean De l'Obel, a lawyer whose practice specialized in aristocrats in the army. Relatively little is known about his li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illustration Rosa Canina1
An illustration is a decoration, interpretation, or visual explanation of a text, concept, or process, designed for integration in print and digitally published media, such as posters, flyers, magazines, books, teaching materials, animations, video games and films. An illustration is typically created by an illustrator. Digital illustrations are often used to make websites and apps more user-friendly, such as the use of emojis to accompany digital type. Illustration also means providing an example; either in writing or in picture form. The origin of the word "illustration" is late Middle English (in the sense ‘illumination; spiritual or intellectual enlightenment’): via Old French from Latin">-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ... from Latin ''illustratio''(n-), from the verb ''illustrare''. Illustration styles Contemporary illustration uses a wide range of styles and techniqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexaploid
Polyploidy is a condition in which the cells of an organism have more than two paired sets of ( homologous) chromosomes. Most species whose cells have nuclei (eukaryotes) are diploid, meaning they have two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each of two parents; each set contains the same number of chromosomes, and the chromosomes are joined in pairs of homologous chromosomes. However, some organisms are polyploid. Polyploidy is especially common in plants. Most eukaryotes have diploid somatic cells, but produce haploid gametes (eggs and sperm) by meiosis. A monoploid has only one set of chromosomes, and the term is usually only applied to cells or organisms that are normally diploid. Males of bees and other Hymenoptera, for example, are monoploid. Unlike animals, plants and multicellular algae have life cycles with two alternating multicellular generations. The gametophyte generation is haploid, and produces gametes by mitosis; the sporophyte generation is diploid and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, respectively, in each homologous chromosome pair—the form in which chromosomes naturally exist. Somatic cells, tissues, and individual organisms can be described according to the number of sets of chromosomes present (the "ploidy level"): monoploid (1 set), diploid (2 sets), triploid (3 sets), tetraploid (4 sets), pentaploid (5 sets), hexaploid (6 sets), heptaploid or septaploid (7 sets), etc. The generic term polyploid is often used to describe cells with three or more sets of chromosomes. Virtually all sexually reproducing organisms are made up of somatic cells that are diploid or greater, but ploidy level may vary widely between different organisms, between different tissues within the same organism, and at different stages in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentaploid
Polyploidy is a condition in which the biological cell, cells of an organism have more than two paired sets of (Homologous chromosome, homologous) chromosomes. Most species whose cells have Cell nucleus, nuclei (eukaryotes) are diploid, meaning they have two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each of two parents; each set contains the same number of chromosomes, and the chromosomes are joined in pairs of homologous chromosomes. However, some organisms are polyploid. Polyploidy is especially common in plants. Most eukaryotes have diploid somatic cells, but produce haploid gametes (eggs and sperm) by meiosis. A Ploidy, monoploid has only one set of chromosomes, and the term is usually only applied to cells or organisms that are normally diploid. Males of bees and other Hymenoptera, for example, are monoploid. Unlike animals, plants and multicellular algae have Biological life cycle, life cycles with two alternation of generations, alternating multicellular generations. The gamet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosa Sect
Rosa or De Rosa may refer to: Plants and animals * ''Rosa'' (plant), the genus of roses * Rosa (sea otter), a sea otter that has become popular on the internet *Rosa (cow), a Spanish-born cow People * Rosa (given name) * Rosa (surname) * Santa Rosa (female given name from Latin-a latinized variant of Rose) Places * 223 Rosa, an asteroid * Rosa, Alabama, a town, United States * Rosa, Germany, in Thuringia, Germany *Rösa, a village and former municipality in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany * Rosà a town in the province of Vicenza, Veneto, Italy *Monte Rosa, the second highest mountain in the Alps and Western Europe *Republic of South Africa, a southernmost country in Africa. Film and television * ''Rosa'' (1986 film), a Hong Kong film released by Bo Ho Films *'' Rosa – A Horse Drama'', a 1993-94 opera by Louis Andriessen on a libretto by Peter Greenaway * "Rosa" (''Doctor Who''), an episode of the eleventh series of ''Doctor Who'' Music *"Rosa", a song by Pixinguinha *De Rosa (ban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by most types of flowers of seed plants for the purpose of sexual reproduction. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced Gametophyte#Heterospory, microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm cells). Pollen grains have a hard coat made of sporopollenin that protects the gametophytes during the process of their movement from the stamens to the pistil of flowering plants, or from the male Conifer cone, cone to the female cone of gymnosperms. If pollen lands on a compatible pistil or female cone, it Germination, germinates, producing a pollen tube that transfers the sperm to the ovule containing the female gametophyte. Individual pollen grains are small enough to require magnification to see detail. The study of pollen is called palynology and is highly useful in paleoecology, paleontology, archaeology, and Forensic science, forensics. Pollen in plants is used for transferring Ploidy#Haploid and monoploid, haploid male genetic ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egg Cell
The egg cell or ovum (: ova) is the female Reproduction, reproductive cell, or gamete, in most anisogamous organisms (organisms that reproduce sexually with a larger, female gamete and a smaller, male one). The term is used when the female gamete is not capable of movement (non-motile). If the male gamete (sperm) is capable of movement, the type of sexual reproduction is also classified as oogamous. A nonmotile female gamete formed in the oogonium of some algae, fungi, oomycetes, or bryophytes is an oosphere. When fertilized, the oosphere becomes the oospore. When egg and sperm fuse together during fertilisation, a diploid cell (the zygote) is formed, which rapidly grows into a new organism. History While the non-mammalian animal egg was obvious, the doctrine ''ex ovo omne vivum'' ("every living [animal comes from] an egg"), associated with William Harvey (1578–1657), was a rejection of spontaneous generation and preformationism as well as a bold assumption that mammals als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
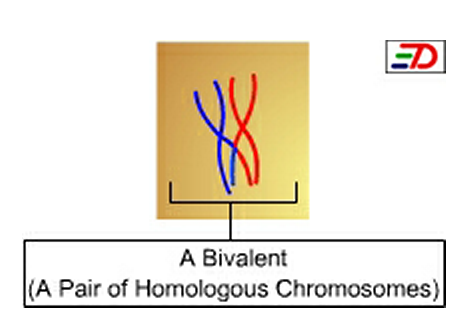
Bivalent (genetics)
In cellular biology, a bivalent is one pair of chromosomes (homologous chromosomes) in a tetrad. A tetrad is the association of a pair of homologous chromosomes (4 sister chromatids) physically held together by at least one DNA crossover. This physical attachment allows for alignment and segregation of the homologous chromosomes in the first meiotic division. In most organisms, each replicated chromosome (composed of two identical sisters chromatid) elicits formation of DNA double-strand breaks during the leptotene phase. These breaks are repaired by homologous recombination, that uses the homologous chromosome as a template for repair. The search for the homologous target, helped by numerous proteins collectively referred as the synaptonemal complex, cause the two homologs to pair, between the leptotene and the pachytene phases of meiosis I. Formation The formation of a bivalent occurs during the first division of meiosis (in the zygotene stage of meiotic prophase 1). In mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |