|
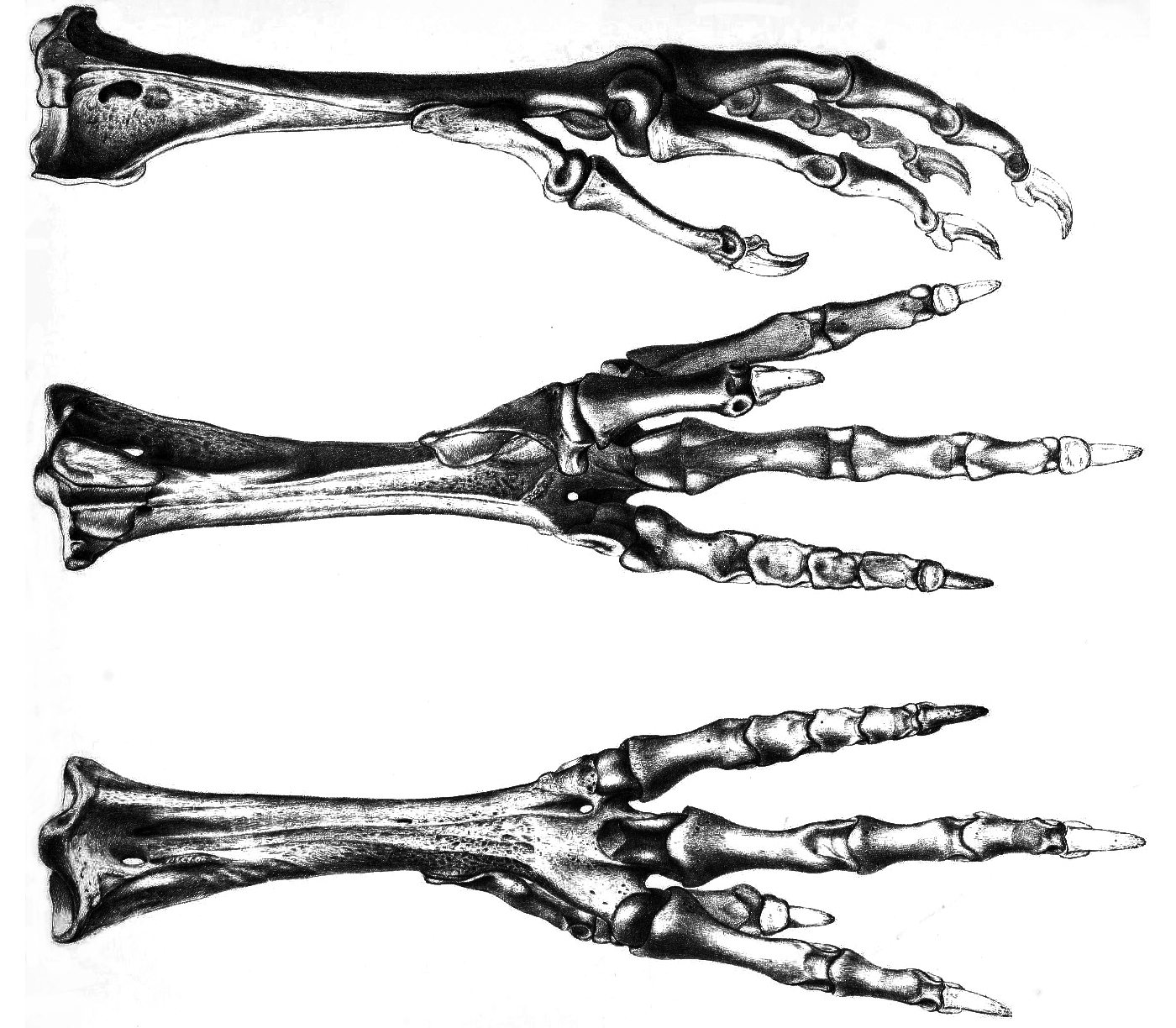
Dodos
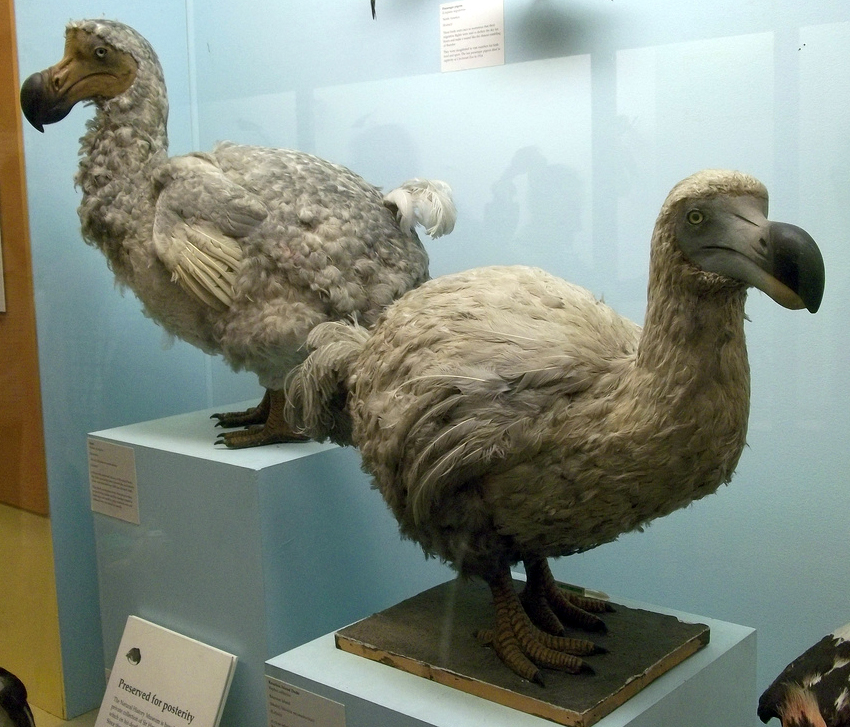
The dodo (''Raphus cucullatus'') is an extinct flightless bird that was endemic to the island of Mauritius, which is east of Madagascar in the Indian Ocean. The dodo's closest relative was the also-extinct and flightless Rodrigues solitaire. The two formed the subtribe Raphina, a clade of extinct flightless birds that are a part of the group that includes pigeons and doves (the family Columbidae). The closest living relative of the dodo is the Nicobar pigeon. A white dodo was once thought to have existed on the nearby island of Réunion, but it is now believed that this assumption was merely confusion based on the also-extinct Réunion ibis and paintings of white dodos. Subfossil remains show the dodo measured about in height and may have weighed in the wild. The dodo's appearance in life is evidenced only by drawings, paintings, and written accounts from the 17th century. Since these portraits vary considerably, and since only some of the illustrations are known to have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Réunion Ibis
The Réunion ibis or Réunion sacred ibis (''Threskiornis solitarius'') is an list of extinct birds, extinct species of ibis that was endemic to the volcanic island of Réunion in the Indian Ocean. The first subfossil remains were found in 1974, and the ibis was first scientifically described in 1987. Its closest relatives are the Malagasy sacred ibis, the African sacred ibis, and the straw-necked ibis. Travellers' accounts from the 17th and 18th centuries described a white bird on Réunion that flew with difficulty and preferred solitude, which was subsequently referred to as the "Réunion solitaire". In the mid 19th century, the old travellers' accounts were incorrectly assumed to refer to white relatives of the dodo, due to one account specifically mentioning dodos on the island, and because 17th-century paintings of white dodos had recently surfaced. However, no fossils referable to dodo-like birds were ever found on Réunion, and it was later questioned whether the painting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mare Aux Songes
The Mare aux Songes (English: "pond of taro"; ) swamp is a lagerstätte located close to the sea in south eastern Mauritius. Many subfossils of recently extinct animals have accumulated in the swamp, which was once a lake, and some of the first subfossil remains of dodos were found there. History In 1865, a British railway engineer working in south-east Mauritius noticed bones that had been disturbed by workers digging peat. He showed his findings to the government schoolmaster at Mahébourg, George Clark, who subsequently uncovered an abundance of subfossil dodo bones in the swamp. Clark had been searching for thirty years, having been inspired by Strickland & Melville's monograph about the bird. In 1866, Clark explained his procedure to The Ibis, an ornithology journal: Remains of over 300 dodos were found in the swamp, but only very few skull and wing bones among them, which may be explained by the upper bodies having been washed away or scavenged while the lower body was tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodrigues Solitaire
The Rodrigues solitaire (''Pezophaps solitaria'') is an extinct flightless bird that was endemism, endemic to the island of Rodrigues, east of Madagascar in the Indian Ocean. Genetically within the family of Columbidae, pigeons and doves, it was most closely related to the also extinct dodo of the nearby island Mauritius#Mauritius Island, Mauritius, the two forming the subfamily Raphinae. The Nicobar pigeon is their closest living genetic relative. Rodrigues solitaires grew to the size of swans, and demonstrated pronounced sexual dimorphism. Males were much larger than females and measured up to in height and in weight, contrasting with and for females. Its plumage was grey and brown; the female was paler than the male. It had a black band at the base of its slightly hooked beak, and its neck and legs were long. Both sexes were highly Territory (animal), territorial, with large bony knobs on their wings that were used in combat. The Rodrigues solitaire laid a single egg that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raphina
The Raphina are a clade of extinct flightless birds formerly called didines or didine birds. They inhabited the Mascarene Islands of Mauritius and Rodrigues, but became extinct through hunting by humans and predation by introduced non-native mammals following human colonisation in the 17th century. Historically, many different groups have been named for both the dodo and the Rodrigues solitaire, not all grouping them together. Most recently, it is considered that the two birds can be classified in Columbidae, often under the subfamily Raphinae. The first person to suggest a close affinity to the doves was Johannes Theodor Reinhardt, whose opinions were then supported by Hugh Edwin Strickland and Alexander Gordon Melville. Recent extractions of DNA from the dodo and Rodrigues solitaire, as well as 37 species of doves, has found where in Columbidae the raphines should be placed. Raphines are not the most primitive columbid, instead they are grouped with the Nicobar pigeon as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicobar Pigeon
The Nicobar pigeon or Nicobar dove (''Caloenas nicobarica'', Car: ') is a bird found on small islands and in coastal regions from the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India, east through the Indonesian Archipelago, to the Solomons and Palau. It is the only living member of the genus '' Caloenas'' alongside the extinct spotted green pigeon and Kanaka pigeon, and is the closest living relative of the extinct dodo and Rodrigues solitaire. Taxonomy In 1738, the English naturalist Eleazar Albin included a description and two illustrations of the Nicobar pigeon in his ''A Natural History of Birds''. When in 1758 the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus updated his ''Systema Naturae'' for the tenth edition, he placed the Nicobar pigeon with all the other pigeons in the genus ''Columba''. Linnaeus included a brief description, coined the binomial name ''Columba nicobarica'' and cited Albin's work. The species is now placed in the genus '' Caloenas'' erected by English zoologist George Rober ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1662
Events January–March * January 4 – Dziaddin Mukarram Shah becomes the new Sultan of Kedah, an independent kingdom on the Malay Peninsula, upon the death of his father, Sultan Muhyiddin Mansur. * January 10 – At the age of 19, Louis Grimaldi becomes the new Prince of Monaco upon the death of his grandfather, Honoré II. * January 14 – A Portuguese garrison invades Morocco and kidnaps 35 women and girls, then steals 400 head of cattle. The Moroccans counterattack and kill the garrison's commander, 12 knights and 38 other Portuguese soldiers before the surviving Portuguese are given sanctuary inside the English fortress at Tangier. A brief war ensues between England and Morocco. * January 22 – Former Chinese Emperor Yongli, who had surrendered to General Wu Sangui in December, is put on a boat along with his sons and grandsons at Sagaing in Burma (at the time, Burma), leaving under the promise that they will be given safe passage elsewher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columbidae
Columbidae is a bird Family (biology), family consisting of doves and pigeons. It is the only family in the Order (biology), order Columbiformes. These are stout-bodied birds with small heads, relatively short necks and slender bills that in some species feature fleshy ceres. They Herbivore, feed largely on plant matter, feeding on seeds (granivore, granivory), fruit (frugivore, frugivory), and foliage (folivore, folivory). In colloquial English, the smaller species tend to be called "doves", and the larger ones "pigeons", although the distinction is not consistent, and there is no scientific separation between them. Historically, the common names for these birds involve a great deal of variation. The bird most commonly referred to as "pigeon" is the domestic pigeon, descendant of the wild rock dove, which is a common Urban wildlife, inhabitant of cities as the feral pigeon. Columbidae contains 51 genera divided into 353 species. The family occurs worldwide, often in close p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northgrippian
In the geologic time scale, the Northgrippian is the middle one of three age (geology), ages or stage (stratigraphy), stages of the Holocene Epoch (geology), Epoch or series (stratigraphy), Series. It was officially ratified by the International Commission on Stratigraphy in June 2018 along with the earlier Greenlandian and later Meghalayan ages/stages. The age takes its name from the North Greenland Ice Core Project (NorthGRIP). The age began 8,276 Before Present, BP (6326 BCE or 3854 Holocene calendar, HE), near the 8.2-kiloyear event, and goes up to the start of the Meghalayan, which began 4,200 BP (2250 BCE or 7750 HE), near the 4.2-kiloyear event. See also * Geologic time scale * North Greenland Ice Core Project * 5th millennium BC References 7th millennium BC Cenozoic, *01 Geological epochs Holocene, * Quaternary geochronology, *03 Quaternary, * {{geochronology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subfossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Though the fossil record is incomplete, numerous studies have demonstrated that there is enough information available to give a good understanding of the pattern of diversification of life on Earth. In addition, the record can predict and fill gaps such as the discovery of ''Tiktaalik'' in the arctic of Canada. Paleontology includes the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are sometimes considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gizzard Stone
A gastrolith, also called a stomach stone or gizzard stone, is a rock held inside a gastrointestinal tract. Gastroliths in some species are retained in the muscular gizzard and used to grind food in animals lacking suitable grinding teeth. In other species the rocks are ingested and pass through the digestive system and are frequently replaced. The grain size depends upon the size of the animal and the gastrolith's role in digestion. Other species use gastroliths as ballast.Rondeau, et aLarval Anurans Adjust Buoyancy in Response to Substrate IngestionCopeia: February 2005, Vol. 2005, No. 1, pp. 188–195. Particles ranging in size from sand to cobble have been documented. Etymology Gastrolith comes from the Ancient Greek γαστήρ (''gastēr''), meaning "stomach", and λίθος (''lithos''), meaning "stone". Occurrence Among living vertebrates, gastroliths are common among crocodiles, alligators, herbivorous birds, seals and sea lions. Domestic fowl require access to ''grit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plumage
Plumage () is a layer of feathers that covers a bird and the pattern, colour, and arrangement of those feathers. The pattern and colours of plumage differ between species and subspecies and may vary with age classes. Within species, there can be different colour morph (zoology), morphs. The placement of feathers on a bird is not haphazard but rather emerges in organized, overlapping rows and groups, and these are known by standardized names. Most birds moult twice a year, resulting in a breeding or ''nuptial plumage'' and a ''basic plumage''. Many ducks and some other species such as the red junglefowl have males wearing a bright nuptial plumage while breeding and a drab ''eclipse plumage'' for some months afterward. The painted bunting's juveniles have two inserted moults in their first autumn, each yielding plumage like an adult female. The first starts a few days after fledging replacing the ''juvenile plumage'' with an ''auxiliary formative plumage''; the second a month o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digestion
Digestion is the breakdown of large insoluble food compounds into small water-soluble components so that they can be absorbed into the blood plasma. In certain organisms, these smaller substances are absorbed through the small intestine into the blood stream. Digestion is a form of catabolism that is often divided into two processes based on how food is broken down: mechanical and chemical digestion. The term mechanical digestion refers to the physical breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces which can subsequently be accessed by digestive enzymes. Mechanical digestion takes place in the mouth through Chewing, mastication and in the small intestine through segmentation contractions. In chemical digestion, enzymes break down food into the small compounds that the body can use. In the human digestive system, food enters the mouth and mechanical digestion of the food starts by the action of mastication (chewing), a form of mechanical digestion, and the wetting contact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |