|
Do (verb)
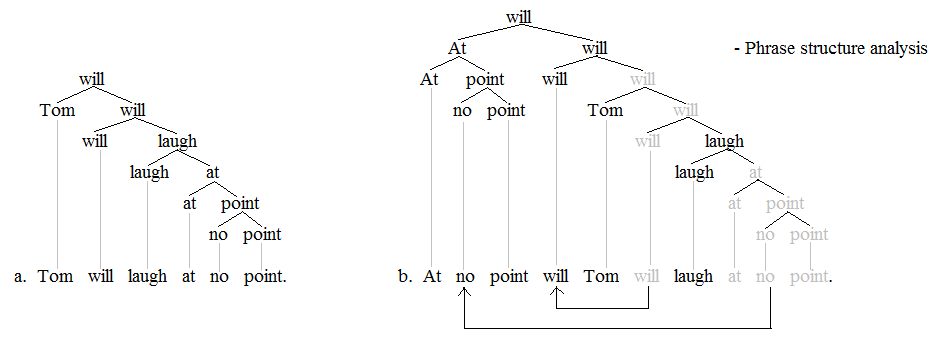
''Do''-support (sometimes referred to as ''do''-insertion or periphrastic ''do'') in English grammar is the use of the auxiliary verb ''do'' (or one of its inflected forms, e.g. does) to form negated clauses and constructions which require subject–auxiliary inversion, such as questions. The verb ''do'' can be used ''optionally'' as an auxiliary even in simple declarative sentences, usually as a means of adding emphasis (e.g. "I ''did'' shut the fridge."). However, in negated and inverted clauses, ''do'' is usually used in today's Modern English. For example, in idiomatic English, the negating word ''not'' cannot attach directly to just any finite lexical verb; rather, it can only attach to an auxiliary or copular verb. For example, the sentence ''I am not'' with the copula ''be'' is fully idiomatic, but ''I know not'' with the finite lexical verb ''know'', while grammatical, is archaic. If there is no other auxiliary present when negation is required, the auxiliary ''do'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periphrasis
In linguistics and literature, periphrasis () is the use of a larger number of words, with an implicit comparison to the possibility of using fewer. The comparison may be within a language or between languages. For example, "more happy" is periphrastic in comparison to "happier", and English "I will eat" is periphrastic in comparison to Spanish . The term originates from the Greek worπεριφράζομαι 'talking around', and was originally used for examples that came up in ancient Greek. In epic poetry, it was common to use periphrasis in examples such as "the sons of the Achaeans" (meaning the Achaeans), or "How did such words escape the fence of your teeth?" (adding a layer of poetic imagery to "your teeth"). Sometimes periphrastic forms were used for verbs that would otherwise be unpronounceable. For example, the verb δείκνυμι 'to show', has a hypothetical form * , which has the disallowed consonant cluster , so one would instead say , using a periphrasis with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interrogative Word
An interrogative word or question word is a function word used to ask a question, such as ''what, which'', ''when'', ''where'', '' who, whom, whose'', ''why'', ''whether'' and ''how''. They are sometimes called wh-words, because in English most of them start with '' wh-'' (compare Five Ws). Most may be used in both direct (''Where is he going?'') and in indirect questions (''I wonder where he is going''). In English and various other languages the same forms are also used as relative pronouns in certain relative clauses (''The country where he was born'') and certain adverb clauses (''I go where he goes''). It can also be used as a modal, since question words are more likely to appear in modal sentences, like (''Why was he walking?'') A particular type of interrogative word is the interrogative particle, which serves to convert a statement into a yes–no question, without having any other meaning. Examples include ''est-ce que'' in French, ли ''li'' in Russian, ''czy'' i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weak And Strong Forms In English
Stress (linguistics), Stress is a prominent feature of the English language, both at the level of the word ''(lexical stress)'' and at the level of the phrase or sentence ''(prosodic stress)''. Absence of stress on a syllable, or on a word in some cases, is frequently associated in English with vowel reduction – many such syllables are pronounced with a centralized vowel (schwa) or with certain other vowels that are described as being "reduced" (or sometimes with a syllabic consonant as the syllable nucleus rather than a vowel). Various contradictory phonology, phonological analyses exist for these phenomena. For example, in the following sentence, a speaker would typically pronounce ''have'' with a schwa, as or (homophonous with ''of''): : Alice and Bob have arrived. But in other contexts where the word carries stress, it would be pronounced in its "strong" (unreduced) form as (homophonous with ''halve''). For example: : Alice and Bob have three children. : [In response t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stress (linguistics)
In linguistics, and particularly phonology, stress or accent is the relative emphasis or prominence given to a certain syllable in a word or to a certain word in a phrase or Sentence (linguistics), sentence. That emphasis is typically caused by such properties as increased loudness and vowel length, full articulation of the vowel, and changes in Tone (linguistics), tone. The terms ''stress'' and ''accent'' are often used synonymously in that context but are sometimes distinguished. For example, when emphasis is produced through pitch alone, it is called ''Pitch-accent language, pitch accent'', and when produced through length alone, it is called ''quantitative accent''. When caused by a combination of various intensified properties, it is called ''stress accent'' or ''dynamic accent''; English uses what is called ''variable stress accent''. Since stress can be realised through a wide range of Phonetics, phonetic properties, such as loudness, vowel length, and pitch (which are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negative Inversion
In linguistics, negative inversion is one of many types of subject–auxiliary inversion in English language, English. A negation (e.g. ''not'', ''no'', ''never'', ''nothing'', etc.) or a word that implies negation (''only'', ''hardly'', ''scarcely'') or a phrase containing one of these words precedes the finite verb, finite auxiliary verb necessitating that the subject and finite verb undergo Inversion (linguistics), inversion. Negative inversion is a phenomenon of English syntax. Other Germanic languages have a more general V2 word order, which allows inversion to occur much more often than in English, so they may not acknowledge negative inversion as a specific phenomenon. While negative inversion is a common occurrence in English, a solid understanding of just what elicits the inversion has not yet been established. It is, namely, not entirely clear why certain fronted expressions containing a negation elicit negative inversion, but others do not. As with subject-auxiliary inver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellipsis (linguistics)
In linguistics, ellipsis () or an elliptical construction is the omission from a clause of one or more words that are nevertheless understood in the context of the remaining elements. There are numerous distinct types of ellipsis acknowledged in theoretical syntax. Theoretical accounts of ellipsis seek to explain its syntactic and semantic factors, the means by which the elided elements are recovered, and the status of the elided elements. Background Varieties of ellipsis have long formed a basis of linguistic theory that addresses basic questions of form–meaning correspondence: in particular, how the usual mechanisms of grasping a meaning from a form may be bypassed or supplanted via elliptical structures. In generative linguistics, the term ''ellipsis'' has been applied to a range of syntax in which a perceived interpretation is fuller than that which would be expected based solely on the presence of linguistic forms. One trait that many types and instances of ellipsis h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Questions
IN, In or in may refer to: Dans * India (country code IN) * Indiana, United States (postal code IN) * Ingolstadt, Germany (license plate code IN) * In, Russia, a town in the Jewish Autonomous Oblast Businesses and organizations * Independent Network, a UK-based political association * Indiana Northeastern Railroad (Association of American Railroads reporting mark) * Indian Navy, a part of the India military * Infantry, the branch of a military force that fights on foot * IN Groupe, the producer of French official documents * MAT Macedonian Airlines (IATA designator IN) * Nam Air (IATA designator IN) * Office of Intelligence and Counterintelligence, sometimes abbreviated IN Science and technology * .in, the internet top-level domain of India * Inch (in), a unit of length * Indium, symbol In, a chemical element * Intelligent Network, a telecommunication network standard * Intra-nasal ( insufflation), a method of administrating some medications and vaccines * Integrase, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predicate (grammar)
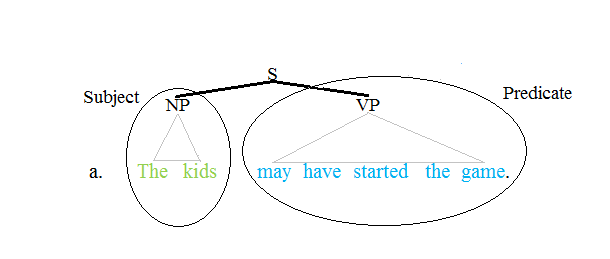
The term predicate is used in two ways in linguistics and its subfields. The first defines a predicate as everything in a standard declarative sentence except the subject (grammar), subject, and the other defines it as only the main content verb or associated predicative expression of a clause. Thus, by the first definition, the predicate of the sentence ''Frank likes cake'' is ''likes cake'', while by the second definition, it is only the content verb ''likes'', and ''Frank'' and ''cake'' are the argument (linguistics), arguments of this predicate. The conflict between these two definitions can lead to confusion. Syntax Traditional grammar The notion of a predicate in traditional grammar traces back to Aristotelian logic. A predicate is seen as a property that a subject has or is characterized by. A predicate is therefore an expression that can be ''true of'' something. Thus, the expression "is moving" is true of anything that is moving. This classical understanding of pred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerund
In linguistics, a gerund ( abbreviated ger) is any of various nonfinite verb forms in various languages; most often, but not exclusively, it is one that functions as a noun. The name is derived from Late Latin ''gerundium,'' meaning "which is to be carried out". In English, the gerund has the properties of both verb and noun, such as being modifiable by an adverb and being able to take a direct object. The term "''-ing'' form" is often used in English to refer to the gerund specifically. Traditional grammar makes a distinction within ''-ing'' forms between present participles and gerunds, a distinction that is not observed in such modern grammars as '' A Comprehensive Grammar of the English Language'' and '' The Cambridge Grammar of the English Language''. Traditional use The Latin gerund, in a restricted set of syntactic contexts, denotes the sense of the verb in isolation after certain prepositions, and in certain uses of the genitive, dative, and ablative cases. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Present Participle
In linguistics, a participle (; abbr. ) is a nonfinite verb form that has some of the characteristics and functions of both verbs and adjectives. More narrowly, ''participle'' has been defined as "a word derived from a verb and used as an adjective, as in a ''laughing face''". "Participle" is a traditional grammatical term from Greek and Latin that is widely used for corresponding verb forms in European languages and analogous forms in Sanskrit and Arabic grammar. In particular, Greek and Latin participles are inflected for gender, number and case, but also conjugated for tense and voice and can take prepositional and adverbial modifiers. Cross-linguistically, participles may have a range of functions apart from adjectival modification. In European and Indian languages, the past participle is used to form the passive voice. In English, participles are also associated with periphrastic verb forms ( continuous and perfect) and are widely used in adverbial clauses. In non-Ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperative Mood
The imperative mood is a grammatical mood that forms a command or request. The imperative mood is used to demand or require that an action be performed. It is usually found only in the present tense, second person. They are sometimes called ''directives'', as they include a feature that encodes directive force, and another feature that encodes modality of unrealized interpretation. An example of a verb used in the imperative mood is the English phrase "Go." Such imperatives imply a second-person subject (''you''), but some other languages also have first- and third-person imperatives, with the meaning of "let's (do something)" or "let them (do something)" (the forms may alternatively be called cohortative and jussive). Imperative mood can be denoted by the glossing abbreviation . It is one of the irrealis moods. Formation Imperative mood is often expressed using special conjugated verb forms. Like other finite verb forms, imperatives often inflect for person and nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Elliptical Sentences
IN, In or in may refer to: Dans * India (country code IN) * Indiana, United States (postal code IN) * Ingolstadt, Germany (license plate code IN) * In, Russia, a town in the Jewish Autonomous Oblast Businesses and organizations * Independent Network, a UK-based political association * Indiana Northeastern Railroad (Association of American Railroads reporting mark) * Indian Navy, a part of the India military * Infantry, the branch of a military force that fights on foot * IN Groupe, the producer of French official documents * MAT Macedonian Airlines (IATA designator IN) * Nam Air (IATA designator IN) * Office of Intelligence and Counterintelligence, sometimes abbreviated IN Science and technology * .in, the internet top-level domain of India * Inch (in), a unit of length * Indium, symbol In, a chemical element * Intelligent Network, a telecommunication network standard * Intra-nasal ( insufflation), a method of administrating some medications and vaccines * Integrase, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |