|
Dissection Into Orthoschemes
In geometry, it is an unsolved conjecture of Hugo Hadwiger that every simplex can be Dissection problem, dissected into Schläfli orthoscheme, orthoschemes, using a number of orthoschemes bounded by a function of the dimension of the simplex. If true, then more generally every convex polytope could be dissected into orthoschemes. Definitions and statement In this context, a simplex in d-dimensional Euclidean space is the convex hull of d+1 points that do not all lie in a common hyperplane. For example, a 2-dimensional simplex is just a triangle (the convex hull of three points in the plane) and a 3-dimensional simplex is a tetrahedron (the convex of four points in three-dimensional space). The points that form the simplex in this way are called its vertex (geometry), vertices. An orthoscheme, also called a path simplex, is a special kind of simplex. In it, the vertices can be connected by a path graph, path, such that every two edges in the path are at right angles to each other. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjecture
In mathematics, a conjecture is a conclusion or a proposition that is proffered on a tentative basis without proof. Some conjectures, such as the Riemann hypothesis or Fermat's conjecture (now a theorem, proven in 1995 by Andrew Wiles), have shaped much of mathematical history as new areas of mathematics are developed in order to prove them. Resolution of conjectures Proof Formal mathematics is based on ''provable'' truth. In mathematics, any number of cases supporting a universally quantified conjecture, no matter how large, is insufficient for establishing the conjecture's veracity, since a single counterexample could immediately bring down the conjecture. Mathematical journals sometimes publish the minor results of research teams having extended the search for a counterexample farther than previously done. For instance, the Collatz conjecture, which concerns whether or not certain sequences of integers terminate, has been tested for all integers up to 1.2 × 101 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Closed Set
In geometry, topology, and related branches of mathematics, a closed set is a Set (mathematics), set whose complement (set theory), complement is an open set. In a topological space, a closed set can be defined as a set which contains all its limit points. In a complete metric space, a closed set is a set which is Closure (mathematics), closed under the limit of a sequence, limit operation. This should not be confused with closed manifold. Sets that are both open and closed and are called clopen sets. Definition Given a topological space (X, \tau), the following statements are equivalent: # a set A \subseteq X is in X. # A^c = X \setminus A is an open subset of (X, \tau); that is, A^ \in \tau. # A is equal to its Closure (topology), closure in X. # A contains all of its limit points. # A contains all of its Boundary (topology), boundary points. An alternative characterization (mathematics), characterization of closed sets is available via sequences and Net (mathematics), net ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unsolved Problems In Geometry
Unsolved may refer to: * ''Unsolved'' (album), a 2000 album by the American band Karate * ''Unsolved'' (British TV programme), a 2004–2006 British crime documentary television programme that aired on STV in Scotland * ''Unsolved'' (South Korean TV series), a 2010 South Korean television series * ''Unsolved'' (U.S. TV series), a 2018 American television series *''Unsolved!'', a 2017 book about cryptography by Craig P. Bauer *'' Unsolved: The Boy Who Disappeared'', a 2016 online series by BBC Three *''The Unsolved'', a 1997 Japanese video game *''BuzzFeed Unsolved'', a show by BuzzFeed discussing unsolved crimes and haunted places See also *Solved (other) Solved may refer to: * Solved (TV series) * ''Solved'' (album), an album by MC Frontalot * Solved (EP), an EP by Svoy * solved game See also * Solution (other) * Resolution (other) * Unsolved (other) {{disambig ... *'' Unsolved Mysteries'', an American true crime television program t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjectures
In mathematics, a conjecture is a conclusion or a proposition that is proffered on a tentative basis without proof. Some conjectures, such as the Riemann hypothesis or Fermat's conjecture (now a theorem, proven in 1995 by Andrew Wiles), have shaped much of mathematical history as new areas of mathematics are developed in order to prove them. Resolution of conjectures Proof Formal mathematics is based on ''provable'' truth. In mathematics, any number of cases supporting a universally quantified conjecture, no matter how large, is insufficient for establishing the conjecture's veracity, since a single counterexample could immediately bring down the conjecture. Mathematical journals sometimes publish the minor results of research teams having extended the search for a counterexample farther than previously done. For instance, the Collatz conjecture, which concerns whether or not certain sequences of integers terminate, has been tested for all integers up to 1.2 × 1012 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elemente Der Mathematik
''Elemente der Mathematik'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering mathematics. It is published by the European Mathematical Society Publishing House on behalf of the Swiss Mathematical Society. It was established in 1946 by Louis Locher-Ernst, and transferred to the Swiss Mathematical Society in 1976. Rather than publishing research papers, it focuses on survey papers aimed at a broad audience. History The journal ''Elemente der Mathematik'' was founded in 1946 by Louis Locher-Ernst under the patronage of the Swiss Mathematical Society (SMG) to disseminate pedagogical and expository articles in mathematics and physics. Locher-Ernst outlined the scope and objectives—emphasising support for secondary and tertiary instruction—in a letter to the SMG president in August 1945 and at the autumn members' meeting in Fribourg later that year. Early editorial responsibilities were assumed by Locher-Ernst alongside Erwin Voellmy, Ernst Trost and Paul Buchner, while an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometriae Dedicata
''Geometriae Dedicata'' is a mathematical journal, founded in 1972, concentrating on geometry and its relationship to topology, group theory and the theory of dynamical systems. It was created on the initiative of Hans Freudenthal in Utrecht, the Netherlands.. It is published by Springer Netherlands. The Editor-in-Chief An editor-in-chief (EIC), also known as lead editor or chief editor, is a publication's editorial leader who has final responsibility for its operations and policies. The editor-in-chief heads all departments of the organization and is held accoun ... is Richard Alan Wentworth. References External links Springer site Geometry journals Springer Science+Business Media academic journals Algebra journals Dynamical systems journals Topology journals {{math-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperbolic Geometry
In mathematics, hyperbolic geometry (also called Lobachevskian geometry or János Bolyai, Bolyai–Nikolai Lobachevsky, Lobachevskian geometry) is a non-Euclidean geometry. The parallel postulate of Euclidean geometry is replaced with: :For any given line ''R'' and point ''P'' not on ''R'', in the plane containing both line ''R'' and point ''P'' there are at least two distinct lines through ''P'' that do not intersect ''R''. (Compare the above with Playfair's axiom, the modern version of Euclid's parallel postulate.) The hyperbolic plane is a plane (mathematics), plane where every point is a saddle point. Hyperbolic plane geometry is also the geometry of pseudosphere, pseudospherical surfaces, surfaces with a constant negative Gaussian curvature. Saddle surfaces have negative Gaussian curvature in at least some regions, where they local property, locally resemble the hyperbolic plane. The hyperboloid model of hyperbolic geometry provides a representation of event (relativity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spherical Geometry
300px, A sphere with a spherical triangle on it. Spherical geometry or spherics () is the geometry of the two-dimensional surface of a sphere or the -dimensional surface of higher dimensional spheres. Long studied for its practical applications to astronomy, navigation, and geodesy, spherical geometry and the metrical tools of spherical trigonometry are in many respects analogous to Euclidean plane geometry and trigonometry, but also have some important differences. The sphere can be studied either ''extrinsically'' as a surface embedded in 3-dimensional Euclidean space (part of the study of solid geometry), or ''intrinsically'' using methods that only involve the surface itself without reference to any surrounding space. Principles In plane (Euclidean) geometry, the basic concepts are points and (straight) lines. In spherical geometry, the basic concepts are points and great circles. However, two great circles on a plane intersect in two antipodal points, unlike coplan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altitude (triangle)
In geometry, an altitude of a triangle is a line segment through a given Vertex (geometry), vertex (called ''apex (geometry), apex'') and perpendicular to a line (geometry), line containing the side or edge (geometry), edge opposite the apex. This (finite) edge and (infinite) line extension are called, respectively, the ''base (geometry), base'' and ''extended side, extended base'' of the altitude. The point (geometry), point at the intersection of the extended base and the altitude is called the ''foot'' of the altitude. The length of the altitude, often simply called "the altitude" or "height", symbol , is the distance between the foot and the apex. The process of drawing the altitude from a vertex to the foot is known as ''dropping the altitude'' at that vertex. It is a special case of orthogonal projection. Altitudes can be used in the computation of the area of a triangle: one-half of the product of an altitude's length and its base's length (symbol ) equals the triangle's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altezza
The is a compact executive car (D-segment in Europe) sold by Lexus, a luxury division of Toyota, since 1998. The IS was originally sold under the nameplate in Japan from 1998 until 2005 (the word wiktionary:altezza, ''Altezza'' is Italian for 'height' or 'highness'). The IS was introduced as an entry-level sport model positioned below the Lexus ES, ES in the Lexus lineup. It was the smallest car in the Lexus lineup until the introduction of the Lexus CT, CT in 2011. The first-generation Altezza (codename XE10) was launched in Japan in October 1998, while the Lexus IS 200 (GXE10) made its debut in Europe in 1999 and in North America as the IS 300 (JCE10) in 2000. The first-generation models were powered by a Straight-six engine, straight-six engine and available in sedan and wagon variants. The second-generation IS (codename Lexus IS (XE20), XE20) was launched globally in 2005 with V6-powered IS 250 (GSE20) and IS 350 (GSE21) and Diesel engine, Diesel-powered IS 200d/2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperrectangle
In geometry, a hyperrectangle (also called a box, hyperbox, k-cell or orthotopeCoxeter, 1973), is the generalization of a rectangle (a plane figure) and the rectangular cuboid (a solid figure) to higher dimensions. A necessary and sufficient condition is that it is Congruence (geometry), congruent to the Cartesian product of finite interval (mathematics), intervals. This means that a k-dimensional rectangular solid has each of its edges equal to one of the closed intervals used in the definition. Every k-cell is compact (mathematics), compact. If all of the edges are equal length, it is a ''hypercube''. A hyperrectangle is a special case of a parallelohedron#Related shapes, parallelotope. Formal definition For every integer i from 1 to k, let a_i and b_i be real numbers such that a_i < b_i. The set of all points in whose coordinates satisfy the inequalities is a -cell. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
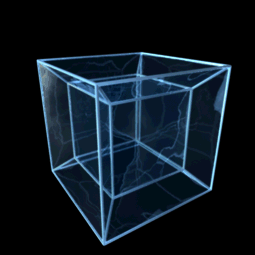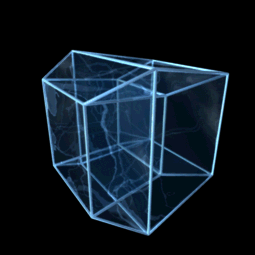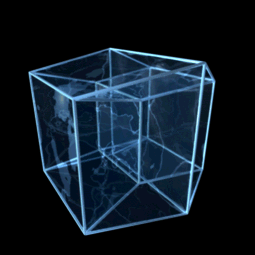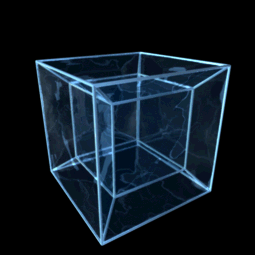
Hypercube
In geometry, a hypercube is an ''n''-dimensional analogue of a square ( ) and a cube ( ); the special case for is known as a ''tesseract''. It is a closed, compact, convex figure whose 1- skeleton consists of groups of opposite parallel line segments aligned in each of the space's dimensions, perpendicular to each other and of the same length. A unit hypercube's longest diagonal in ''n'' dimensions is equal to \sqrt. An ''n''-dimensional hypercube is more commonly referred to as an ''n''-cube or sometimes as an ''n''-dimensional cube. The term measure polytope (originally from Elte, 1912) is also used, notably in the work of H. S. M. Coxeter who also labels the hypercubes the γn polytopes. The hypercube is the special case of a hyperrectangle (also called an ''n-orthotope''). A ''unit hypercube'' is a hypercube whose side has length one unit. Often, the hypercube whose corners (or ''vertices'') are the 2''n'' points in R''n'' with each coordinate equal to 0 or 1 i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |