|
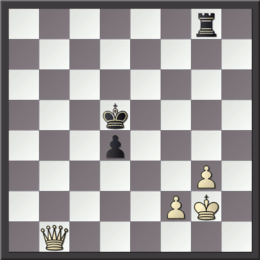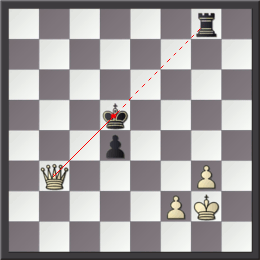
Discovered Attack
In chess, a discovered attack is a direct attack revealed when one piece moves out of the way of another. Discovered attacks can be extremely powerful, as the piece moved can make a threat independently of the piece it reveals. Like many chess tactics, they often succeed because the opponent would be unable to meet two threats at once unless one of the attacked pieces can simultaneously move away from its own attack and capture the other attacking piece. While typically the consequence of a discovered attack is the gain of , they do not have to do this to be effective; the tactic can be used merely to gain a tempo. at MarkLowery.net If the discovered attack is a check, it is ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skewer (chess)
In chess, a skewer is an attack upon two pieces in a line and is similar but opposite to a pin; the difference is that in a skewer, the more valuable piece is the one under direct attack and the less valuable piece is behind it. The opponent is compelled to move the more valuable piece to avoid its capture, thereby exposing the less valuable piece which can then be captured (see chess piece relative value). Only line pieces (i.e. bishops, rooks, and queens) can skewer; kings, knights, and pawns cannot. Details Compared to the pin, a passive action with only an implied threat, the skewer is a direct attack upon the more valuable piece, making it generally a much more powerful and effective tactic. The victim of a skewer often cannot avoid losing ; the only question is which material will be lost. The skewer occurs less often than the pin in actual play. When it does occur, however, it is often decisive. In this diagram, with White to move, the white king and queen are skew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chess
Chess is a board game for two players. It is an abstract strategy game that involves Perfect information, no hidden information and no elements of game of chance, chance. It is played on a square chessboard, board consisting of 64 squares arranged in an 8×8 grid. The players, referred to as White and Black in chess, "White" and "Black", each control sixteen Chess piece, pieces: one king (chess), king, one queen (chess), queen, two rook (chess), rooks, two bishop (chess), bishops, two knight (chess), knights, and eight pawn (chess), pawns, with each type of piece having a different pattern of movement. An enemy piece may be captured (removed from the board) by moving one's own piece onto the square it occupies. The object of the game is to "checkmate" (threaten with inescapable capture) the enemy king. There are also several ways a game can end in a draw (chess), draw. The recorded history of chess goes back to at least the emergence of chaturanga—also thought to be an ancesto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chess Tactics
In chess, a tactic is a sequence of moves that each makes one or more immediate threats – a check, a threat, a checkmating sequence threat, or the threat of another tactic or otherwise forcing moves – that culminates in the opponent's being unable to respond to all of the threats without making some kind of concession. Most often, the immediate benefit takes the form of a material advantage or ; however, some tactics are used for defensive purposes and can salvage material that would otherwise be lost, or to induce stalemate in an otherwise lost position. Tactics are usually contrasted with strategy, whereby the individual moves by themselves do not make indefensible threats, and the cumulative advantage of them takes longer to capitalise. The dichotomy can be summarised as tactics concerning short-term play and strategy concerning long-term play. Examples of strategic advantages are in, compromised pawn structure in, and sustained pressure on, the opponent's position. Of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tempo (chess)
In chess and other chess-like games, a tempo (from ) is a "turn" or single move (a half-move or ply made either by White or Black). When a player achieves a desired result in one fewer move, the player is said to "gain a tempo"; conversely, when a player takes one more move than necessary, the player is said to "lose a tempo". Similarly, when a player forces their opponent to make moves not according to their initial plan, one is said to "gain tempo" because the opponent is wasting moves. A move that gains a tempo is often called "a move with tempo". A simple example of losing a tempo may be moving a rook from the h1-square to h5 and from there to h8 in the first diagram; simply moving from h1 to h8 would have achieved the same result with a tempo to spare. However, such maneuvers do not always lose a tempo—the rook on h5 may make some threat which needs to be responded to. In this case, since both players have "lost" a tempo, the net result in terms of time is nil, but the cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Check (chess)
In chess and similar games, check is a condition that occurs when a player's king is under threat of on the opponent's next turn. A king so threatened is said to be ''in check''. A player must get out of check if possible by moving the king to an unattacked square, interposing a piece between the threatening piece and the king, or capturing the threatening piece. If the player cannot remove the check by any of these options, or if using any of these options would result in the player being in check by another piece, the game ends in checkmate and the player loses. Players cannot make any move that puts their own king in check. Overview A check is the result of a move that places the opposing king under an immediate threat of capture by one (or, in rare cases, two) of the player's pieces. Making a move that checks is sometimes called "giving check". Even if a piece is pinned against the player's own king, it may still give check. For example, in the diagrammed position ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
En Passant
In chess, ''en passant'' (, "in passing") describes the capture by a Pawn (chess), pawn of an enemy pawn on the same and an adjacent that has just made an initial two-square advance. This is a special case in the rules of chess. The capturing pawn moves to the square that the enemy pawn passed over, as if the enemy pawn had advanced only one square. The rule ensures that a pawn cannot use its two-square move to safely skip past an enemy pawn. Capturing ''en passant'' is permitted only on the turn immediately after the two-square advance; it cannot be done on a later turn. The capturing move is sometimes Chess notation, notated by appending the abbreviation e.p. Rules The conditions for a pawn to capture an enemy pawn ''en passant'' are as follows: * the enemy pawn Rules of chess#Basic moves, advanced two squares on the previous turn; * the capturing pawn attacks the square that the enemy pawn passed over. If these conditions are met, the capturing pawn can move diagonal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Check
In chess and other related games, a double check is a check delivered by two pieces simultaneously. In chess notation, it is almost always represented the same way as a single check ("+"), but is sometimes symbolized by "++". (The symbol "++", however, is also sometimes used to denote checkmate.) This article uses "++" for double check and "#" for checkmate. Chess The most common form of double check involves one piece moving to deliver check and revealing a discovered check at the same time from a piece it had been blocking. The only possible reply to a double check is a king move, as it is impossible to block or capture both checking pieces at once. In exceptional circumstances, it is possible for the moved piece in a double check to not give check. The only way for this to happen in orthodox chess is by way of an ''en passant'' capture. In the position shown from Gundersen–Faul, 1928, Black has just played 14...g7–g5. White replies 15.hxg6 #. The result is a doub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Checkmate
Checkmate (often shortened to mate) is any game position in chess and other chess-like games in which a player's king is in check (threatened with ) and there is no possible escape. Checkmating the opponent wins the game. In chess, the king is never actually captured. The player loses as soon as their king is checkmated. In formal games, it is usually considered good etiquette to resign an inevitably lost game before being checkmated. If a player is not in check but has no legal moves, then it is '' stalemate'', and the game immediately ends in a draw. A checkmating move is recorded in algebraic notation using the hash symbol "#", for example: 34.Qg3#. Examples A checkmate may occur in as few as two moves on one side with all of the pieces still on the board (as in fool's mate, in the opening phase of the game), in a middlegame position (as in the 1956 game called the Game of the Century between Donald Byrne and Bobby Fischer), or after many moves with as few as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Defence
The French Defence is a chess opening characterised by the moves: :1. e4 e6 This is most commonly followed by 2.d4 d5. Black usually plays ...c5 soon after, attacking White's and gaining on the . The French has a reputation for solidity and resilience, although some lines such as the Winawer Variation can lead to complications. Black's position is often somewhat in the early game; in particular, the pawn on e6 can impede the of the bishop on c8, known by many players as the French bishop. Basics Following the opening moves 1.e4 e6, the main line of the French Defence continues 2.d4 d5 (see below for alternatives). White sets up a , which Black immediately challenges by attacking the pawn on e4. The same position can be reached by transposition from a Queen's Pawn Game after 1.d4 e6 2.e4 d5 or the declining of a Blackmar–Diemer Gambit after 1.d4 d5 2.e4 e6. White's options include defending the e4-pawn with 3.Nc3 or 3.Nd2, advancing it with 3.e5, or exchangin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chess Tactics
In chess, a tactic is a sequence of moves that each makes one or more immediate threats – a check, a threat, a checkmating sequence threat, or the threat of another tactic or otherwise forcing moves – that culminates in the opponent's being unable to respond to all of the threats without making some kind of concession. Most often, the immediate benefit takes the form of a material advantage or ; however, some tactics are used for defensive purposes and can salvage material that would otherwise be lost, or to induce stalemate in an otherwise lost position. Tactics are usually contrasted with strategy, whereby the individual moves by themselves do not make indefensible threats, and the cumulative advantage of them takes longer to capitalise. The dichotomy can be summarised as tactics concerning short-term play and strategy concerning long-term play. Examples of strategic advantages are in, compromised pawn structure in, and sustained pressure on, the opponent's position. Of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |