|
Discorsi (other) '', an album by the Mina
{{disambiguation ...
''Discorsi'', an Italian word meaning "discourses", may refer to: *''Discourses on Livy'' (''Discorsi sopra la prima deca di Tito Livio''), a book by Machiavelli *''Discourses and Mathematical Demonstrations Relating to Two New Sciences,'' a book by Galileo *''I discorsi ''I discorsi'' is a studio album by Italian singer Mina, released in 1969 by PDU and distributed by EMI Italiana EMI Italiana was a record label, an Italian offshoot of British Electric and Musical Industries, based in Milan. It was founded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discourse
Discourse is a generalization of the notion of a conversation to any form of communication. Discourse is a major topic in social theory, with work spanning fields such as sociology, anthropology, continental philosophy, and discourse analysis. Following pioneering work by Michel Foucault, these fields view discourse as a system of thought, knowledge, or communication that constructs our experience of the world. Since control of discourse amounts to control of how the world is perceived, social theory often studies discourse as a window into power. Within theoretical linguistics, discourse is understood more narrowly as linguistic information exchange and was one of the major motivations for the framework of dynamic semantics, in which expressions' denotations are equated with their ability to update a discourse context. Social theory In the humanities and social sciences, discourse describes a formal way of thinking that can be expressed through language. Discourse is a so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discourses On Livy
The ''Discourses on Livy'' ( it, Discorsi sopra la prima deca di Tito Livio, ) is a work of political history and philosophy written in the early 16th century (c. 1517) by the Italian writer and political theorist Niccolò Machiavelli, best known as the author of ''The Prince''. The ''Discourses'' were published posthumously with papal privilege in 1531. The title identifies the work's subject as the first ten books of Livy's ''Ab Urbe Condita Libri, Ab urbe condita'', which relate the expansion of Roman Republic, Rome through the end of the Third Samnite War in 293 BC, although Machiavelli discusses what can be learned from many other eras including contemporary politics. Machiavelli saw history in general as a way to learn useful lessons from the past for the present, and also as a type of analysis which could be built upon, as long as each generation did not forget the works of the past. Machiavelli frequently describes Romans and other ancient peoples as superior models for his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two New Sciences
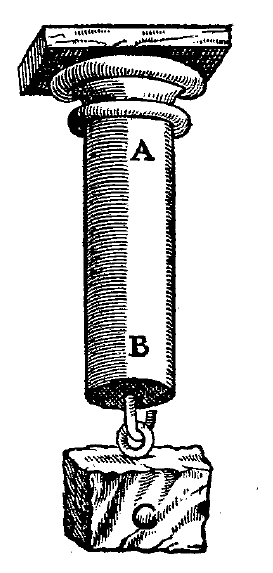
The ''Discourses and Mathematical Demonstrations Relating to Two New Sciences'' ( it, Discorsi e dimostrazioni matematiche intorno a due nuove scienze ) published in 1638 was Galileo Galilei's final book and a scientific testament covering much of his work in physics over the preceding thirty years. It was written partly in Italian and partly in Latin. After his ''Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems'', the Roman Inquisition had banned the publication of any of Galileo's works, including any he might write in the future. After the failure of his initial attempts to publish ''Two New Sciences'' in France, Germany, and Poland, it was published by Lodewijk Elzevir who was working in Leiden, South Holland, where the writ of the Inquisition was of less consequence (see House of Elzevir). Fra Fulgenzio Micanzio, the official theologian of the Republic of Venice, had initially offered to help Galileo publish in Venice the new work, but he pointed out that publishing the ''T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |