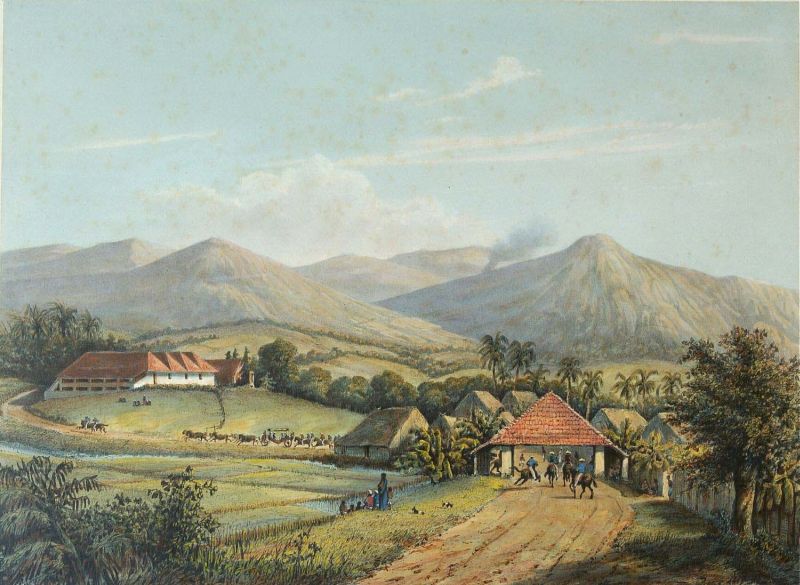|
Dirk Hartog
Dirk Hartog (; baptised 30 October 1580 – buried 11 October 1621) was a 17th-century Dutch sailor and explorer. Dirk Hartog's expedition was the second European group to land in Australia and the first to leave behind an artifact to record his visit, the Hartog Plate. His name is sometimes alternatively spelled Dirck Hartog or Dierick Hartochsz. Ernest Giles referred to him as Theodoric Hartog. The Western Australian island Dirk Hartog Island is named after Hartog. Life Born into a seafaring family, he received his first ship's command at the age of 30 and spent several years engaged in successful trading ventures in the Baltic and Mediterranean seas. In 1616, Hartog gained employment with the Dutch East India Company (, commonly abbreviated to VOC), and was appointed master of the (meaning "Concord" or "Unity"), in a fleet voyaging from the Netherlands to the Dutch East Indies. Hartog set sail in January 1616 in the company of several other VOC ships, but became separa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ac Dirkhartogplate
AC, A.C., A/C, or Ac often refers to: * Air conditioning, often abbreviated as A/C * Alternating current, a type of electrical current in which the current repeatedly changes direction AC, A.C. or Ac may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Gaming * ''Ace Combat'', a series of combat flight simulator games * ''Animal Crossing'', a series of community simulation games * ''Anonymous;Code'', a visual novel in the Science Adventure series * ''Another Code: Two Memories, Another Code'', a series of adventure games * ''Armored Core'', a series of mecha-based third person shooter games * ''Asheron's Call'', a fantasy massively multiplayer online role-playing game * ''Assassin's Creed'', a series of action-adventure games * ''Assetto Corsa'', a racing simulator game * ''Astral Chain'', an action-adventure hack and slash game * Armor Class, a combat-related parameter in the ''Dungeons & Dragons'' role playing game system * A.C., a character in ''Fortnite: Save the World'' Music * A.C. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Batavia, Dutch East Indies
Batavia was the capital of the Dutch East Indies. The area corresponds to present-day Jakarta, Indonesia. Batavia can refer to the city proper or its suburbs and hinterland, the , which included the much larger area of the Residency of Batavia in the present-day Indonesian provinces of Jakarta, Banten and West Java. The founding of Batavia by the Dutch in 1619, on the site of the ruins of History of Jakarta, Jayakarta, led to the establishment of a Dutch colony; Batavia became the center of the Dutch East India Company's trading network in Asia. Monopolies on local produce were augmented by non-indigenous cash crops. To safeguard their commercial interests, the company and the colonial administration absorbed surrounding territory. Batavia is on the north coast of Java, in a sheltered bay, on a land of marshland and hills crisscrossed with canals. The city had two centers: Kota Tua Jakarta, Oud Batavia (the oldest part of the city) and Sawah Besar, Weltevreden (the relatively n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banten (town)
Banten, also written as Bantam, is a port town near the western end of Java, Indonesia. It has a secure harbour at the mouth of Banten River, a navigable passage for light craft into the island's interior. The town is close to the Sunda Strait through which important ocean-going traffic passes between Java and Sumatra. Old Banten, the capital of the Banten Sultanate, was strategically important and a major centre for trade. History In the 5th century Banten was part of the Tarumanagara kingdom. The Lebak relic inscription, found in lowland villages on the edge of Ci Danghiyang, Munjul, Pandeglang, Banten, wad discovered in 1947 and contains two lines of poetry in Pallawa script and Sanskrit. The inscription mention the courage of king Purnawarman. After the collapse of the kingdom Tarumanagara following an attack by the Srivijaya empire, power in western Java fell to the Kingdom of Sunda. The Chinese source, '' Chu-fan-chi'', written c. 1200 by Chou Ju-kua, mentioned tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Language
Dutch ( ) is a West Germanic languages, West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, spoken by about 25 million people as a first language and 5 million as a second language and is the List of languages by total number of speakers, third most spoken Germanic language. In Europe, Dutch is the native language of most of the population of the Netherlands and Flanders (which includes 60% of the population of Belgium). "1% of the EU population claims to speak Dutch well enough in order to have a conversation." (page 153). Dutch was one of the official languages of South Africa until 1925, when it was replaced by Afrikaans, a separate but partially Mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible daughter language of Dutch. Afrikaans, depending on the definition used, may be considered a sister language, spoken, to some degree, by at least 16 million people, mainly in South Africa and Namibia, and evolving from Cape Dutch dialects. In South America, Dutch is the native l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hartog Plate
Hartog Plate or Dirk Hartog's Plate is either of two pewter plates, although primarily the first, which were left on Dirk Hartog Island on the western coast of Australia before European settlement there. The first plate, left in 1616 by Netherlands, Dutch explorer Dirk Hartog, is the oldest-known artefact of European maritime exploration of Australia, European exploration in Australia still in existence. A replacement, which includes the text of the original and some new text, was left in 1697; the original dish was returned to the Netherlands, where it is now on display in the Rijksmuseum. Further additions at the site, in 1801 and 1818, led to the location being named Cape Inscription. Dirk Hartog, 1616 Dirk Hartog was the first confirmed European to see Western Australia, reaching it in his ship the ''Eendracht (1615 ship), Eendracht''. On 25 October 1616, he landed at Cape Inscription on the very northernmost tip of Dirk Hartog Island, in Shark Bay. Before departing, Hartog le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pewter
Pewter () is a malleable metal alloy consisting of tin (85–99%), antimony (approximately 5–10%), copper (2%), bismuth, and sometimes silver. In the past, it was an alloy of tin and lead, but most modern pewter, in order to prevent lead poisoning, is not made with lead. Pewter has a low melting point, around , depending on the exact mixture of metals. The word ''pewter'' is possibly a variation of " spelter", a term for zinc alloys (originally a colloquial name for zinc). History Pewter was first used around the beginning of the Bronze Age in the Near East. The earliest known piece of pewter was found in an Egyptian tomb, , but it is unlikely that this was the first use of the material. Pewter was used for decorative metal items and tableware in ancient times by the Egyptians and later the Romans, and came into extensive use in Europe from the Middle Ages [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eendrachtsland
or (fully and ) are obsolete geographical names for an area centred on the Gascoyne region of Western Australia. Between 1616 and 1644, during the European Age of Exploration, was also a name for the entire Australian mainland. From 1644, it and the surrounding areas were known as '' New Holland'' (and, much later, as ''Western Australia''). In 1616, Dirk Hartog, captain of the Dutch East India Company ship , encountered the west coast of the Australian mainland, meeting it close to the 26th parallel south latitude (26° south), near what is now known as Dirk Hartog Island in Western Australia. After leaving the island, sailed in a northeastern direction along the coast of the mainland, Hartog charting as he went. He gave this land the name , in short, after his ship (translated as or ). Appearance on the charts The earliest known appearance of that name on the charts was eleven years later in 1627 on () by Hessel Gerritsz. However, the name was in use as early as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willem Janszoon
Willem Janszoon (; ) was a Dutch navigator and colonial governor. He served in the Dutch East Indies in the periods 1603–1611 and 1612–1616, including as governor of Fort Henricus on the island of Solor. During his voyage of 1605–1606, Janszoon and his crew became the first Europeans known to have seen and landed on the coast of Australia. His name is sometimes abbreviated to Willem Jansz, as was customary at his time, but "always pronounced in full and generally still is in the Netherlands where this bit of common knowledge is taught at school." However, the abbreviation ''Jansz'' is not the same as the now more predominant unabbreviated but identical ''Jansz'' that is a petrified form of ''Janszoon''. Early life Willem Janszoon (Willem Jansz) was born around 1570 as the son of Jan (, but nothing more is known of his early life or of his parents. Janszoon is first recorded as having entered into the service of the , one of the predecessors of the Dutch East India Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Janszoon Voyage Of 1605-6
Janszoon usually abbreviated to Jansz was a Dutch patronym ("son of Jan"). While Janse, Janssens, and especially Jansen and Janssen, are very common surnames derived from this patronym, the form Jansz is quite rare and Janszoon itself does not exist in the Netherlands. at the database of surnames in the Netherlands. Notable people with this name or its variants include: As a surname * Ernst Jansz (born 1948), Dutch musician and novelist, founding member of Doe Maar *[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shark Bay
Shark Bay () is a World Heritage Site in the Gascoyne region of Western Australia. The area is located approximately north of Perth, on the westernmost point of the Australian continent. UNESCO's listing of Shark Bay as a World Heritage Site reads: The bay features Australia's most abundant marine ecosystems. It is a popular fishing spot. History The record of Indigenous Australians, Australian Aboriginal occupation of Shark Bay extends to years Before Present, BP. At that time most of the area was dry land, and rising sea levels flooded Shark Bay between BP and BP. A considerable number of Aboriginal midden sites have been found, especially on Peron Peninsula and Dirk Hartog Island, which provide evidence of some of the foods gathered from the waters and nearby land areas. An expedition led by Dirk Hartog happened upon the area in 1616, becoming the second group of Europeans known to have visited Australia, after the crew of ''Duyfken'' under Willem Janszoon had visi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latitude
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pole, with 0° at the Equator. Parallel (latitude), Lines of constant latitude, or ''parallels'', run east-west as circles parallel to the equator. Latitude and longitude are used together as a coordinate pair to specify a location on the surface of the Earth. On its own, the term "latitude" normally refers to the ''geodetic latitude'' as defined below. Briefly, the geodetic latitude of a point is the angle formed between the vector perpendicular (or ''Normal (geometry), normal'') to the ellipsoidal surface from the point, and the equatorial plane, plane of the equator. Background Two levels of abstraction are employed in the definitions of latitude and longitude. In the first step the physical surface i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Java (island)
Java is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea (a part of Pacific Ocean) to the north. With a population of 156.9 million people (including Madura) in mid 2024, projected to rise to 158 million at mid 2025, Java is the world's List of islands by population, most populous island, home to approximately 55.7% of the Demographics of Indonesia, Indonesian population (only approximately 44.3% of Indonesian population live outside Java). Indonesia's capital city, Jakarta, is on Java's northwestern coast. Many of the best known events in Indonesian history took place on Java. It was the centre of powerful Hindu-Buddhist empires, the Islamic sultanates, and the core of the colonial Dutch East Indies. Java was also the center of the History of Indonesia, Indonesian struggle for independence during the 1930s and 1940s. Java dominates Indonesia politically, economically and culturally. Four of Indonesia's e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |