|
Direct Deep-sea Carbon Dioxide Injection
Direct deep-sea carbon dioxide injection was a (now abandoned) technology proposal with the aim to remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere by direct injection into the deep ocean and storing it there for some centuries. If carbon dioxide was to be injected to the ocean bottom, the pressures would be great enough for CO2 to be in its liquid phase. The idea behind ocean injection was to have stable, stationary pools of CO2 at the ocean floor. The ocean could potentially hold over a thousand billion tons of CO2. However, the interest in this avenue of carbon storage has much reduced since about 2001 because of concerns about the unknown impacts on marine life Marine life, sea life, or ocean life is the plants, animals and other organisms that live in the salt water of seas or oceans, or the brackish water of coastal estuaries. At a fundamental level, marine life affects the nature of the plane ..., high costs and concerns about its stability or permanence. A special IPCC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Life
Marine life, sea life, or ocean life is the plants, animals and other organisms that live in the salt water of seas or oceans, or the brackish water of coastal estuaries. At a fundamental level, marine life affects the nature of the planet. Marine organisms, mostly microorganisms, produce oxygen and sequester carbon. Marine life in part shape and protect shorelines, and some marine organisms even help create new land (e.g. coral building reefs). Most life forms evolved initially in marine habitats. By volume, oceans provide about 90% of the living space on the planet. The earliest vertebrates appeared in the form of fish, which live exclusively in water. Some of these evolved into amphibians, which spend portions of their lives in water and portions on land. One group of amphibians evolved into reptiles and mammals and a few subsets of each returned to the ocean as sea snakes, sea turtles, seals, manatees, and whales. Plant forms such as kelp and other algae grow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonate
A carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid (H2CO3), characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion with the formula . The word ''carbonate'' may also refer to a carbonate ester, an organic compound containing the carbonate group C(=O)(O–)2. The term is also used as a verb, to describe carbonation: the process of raising the concentrations of carbonate and bicarbonate ions in water to produce carbonated water and other carbonated beverageseither by the addition of carbon dioxide gas under pressure or by dissolving carbonate or bicarbonate salts into the water. In geology and mineralogy, the term "carbonate" can refer both to carbonate minerals and carbonate rock (which is made of chiefly carbonate minerals), and both are dominated by the carbonate ion, . Carbonate minerals are extremely varied and ubiquitous in chemically precipitated sedimentary rock. The most common are calcite or calcium carbonate, CaCO3, the chief constituent of limestone (as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puerto Rico Trench
The Puerto Rico Trench is located on the boundary between the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. The oceanic trench, the deepest in the Atlantic, is associated with a complex transition between the Lesser Antilles subduction zone to the south and the major transform fault zone or plate boundary, which extends west between Cuba and Hispaniola through the Cayman Trough to the coast of Central America. The trench is long and has a maximum depth of or 5.20 miles. This constitutes the single deepest point in the Atlantic Ocean. This point is commonly referred to as the Milwaukee Deep, with the Brownson Deep naming the seabed surrounding it. However, more recently, the latter term has also been used interchangeably with the former to refer to this point. The exact point was identified by the ''DSSV Pressure Drop'' using a state-of-the-art Kongsberg EM124 multibeam sonar in 2018, and then directly visited and its depth verified by the crewed submersible Deep-Submergence Vehicl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ryukyu Trench
The , also called Nansei-Shotō Trench, is a 1398 km (868 mi) long oceanic trench located along the southeastern edge of Japan's Ryukyu Islands in the Philippine Sea in the Pacific Ocean, between northeastern Taiwan and southern Japan. The trench has a maximum depth of 7460 m (24,476 ft). The trench is the result of oceanic crust of the Philippine Plate obliquely subducting beneath the continental crust of the Eurasian Plate at a rate of approximately 52 mm/yr. In conjunction with the adjacent Nankai Trough to the northeast, subduction of the Philippine plate has produced 34 volcanoes. The largest earthquake to have been recorded along the Ryukyu Trench, the 1968 Hyūga-nada earthquake, was magnitude 7.5 and occurred along the northernmost part of the trench on 1 April 1968. This earthquake also produced a tsunami. Ryukyu Trench and Ryukyu Arc structure near Taiwan An east-west planar seismic zone associated with the Ryukyu Trench occurs off the east c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunda Trench
The Sunda Trench, earlier known as and sometimes still indicated as the Java Trench, is an oceanic trench located in the Indian Ocean near Sumatra, formed where the Australian- Capricorn plates subduct under a part of the Eurasian Plate. It is long with a maximum depth of 7,290 metres (23,920 feet). Its maximum depth is the deepest point in the Indian Ocean. The trench stretches from the Lesser Sunda Islands past Java, around the southern coast of Sumatra on to the Andaman Islands, and forms the boundary between Indo-Australian Plate and Eurasian plate (more specifically, Sunda Plate). The trench is considered to be part of the Pacific Ring of Fire as well as one of a ring of oceanic trenches around the northern edges of the Australian Plate. In 2005, scientists found evidence that the 2004 earthquake activity in the area of the Java Trench could lead to further catastrophic shifting within a relatively short period of time, perhaps less than a decade. This threat has result ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supercritical Carbon Dioxide
Supercritical carbon dioxide (s) is a fluid state of carbon dioxide where it is held at or above its critical temperature and critical pressure. Carbon dioxide usually behaves as a gas in air at standard temperature and pressure (STP), or as a solid called dry ice when cooled and/or pressurised sufficiently. If the temperature and pressure are both increased from STP to be at or above the critical point for carbon dioxide, it can adopt properties midway between a gas and a liquid. More specifically, it behaves as a supercritical fluid above its critical temperature () and critical pressure (), expanding to fill its container like a gas but with a density like that of a liquid. Supercritical is becoming an important commercial and industrial solvent due to its role in chemical extraction in addition to its relatively low toxicity and environmental impact. The relatively low temperature of the process and the stability of also allows most compounds to be extracted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Carbon Dioxide
Liquid carbon dioxide is the liquid state of carbon dioxide (), which cannot occur under atmospheric pressure. It can only exist at a pressure above , under (temperature of critical point) and above (temperature of triple point). Low-temperature carbon dioxide is commercially used in its solid form, commonly known as "dry ice". Solid sublimes at at Earth atmospheric pressure — that is, it transitions directly from solid to gas without an intermediate liquid stage. The uses and applications of liquid carbon dioxide include decaffeinating coffee, extracting virgin olive oil from olive paste, in fire extinguishers, and as a coolant. Properties Liquid carbon dioxide is a type of liquid which is formed from highly compressed and cooled gaseous carbon dioxide. It does not form under atmospheric conditions. It only exists when the pressure is above 5.1 atm and the temperature is under (temperature of critical point) and above (temperature of triple point). The chemical symbol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrate
In chemistry, a hydrate is a substance that contains water or its constituent elements. The chemical state of the water varies widely between different classes of hydrates, some of which were so labeled before their chemical structure was understood. Chemical nature Inorganic chemistry Hydrates are inorganic salts "containing water molecules combined in a definite ratio as an integral part of the crystal" that are either bound to a metal center or that have crystallized with the metal complex. Such hydrates are also said to contain '' water of crystallization'' or ''water of hydration''. If the water is heavy water in which the constituent hydrogen is the isotope deuterium, then the term ''deuterate'' may be used in place of ''hydrate''. A colorful example is cobalt(II) chloride, which turns from blue to red upon hydration, and can therefore be used as a water indicator. The notation "''hydrated compound''⋅''n''", where ''n'' is the number of water molecules per for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide Clathrate
Carbon dioxide hydrate or carbon dioxide clathrate is a snow-like crystalline substance composed of water ice and carbon dioxide. It normally is a Type I gas clathrate. There has also been some experimental evidence for the development of a metastable Type II phase at a temperature near the ice melting point. The clathrate can exist below 283K (10 °C) at a range of pressures of carbon dioxide. CO2 hydrates are widely studied around the world due to their promising prospects of carbon dioxide capture from flue gas and fuel gas streams relevant to post-combustion and pre-combustion capture. It is also quite likely to be important on Mars due to the presence of carbon dioxide and ice at low temperatures. History The first evidence for the existence of CO2 hydrates dates back to the year 1882, when Zygmunt Florenty Wróblewski reported clathrate formation while studying carbonic acid. He noted that gas hydrate was a white material resembling snow and could be formed by r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dry Ice
Dry ice is the solid form of carbon dioxide. It is commonly used for temporary refrigeration as CO2 does not have a liquid state at normal atmospheric pressure and sublimates directly from the solid state to the gas state. It is used primarily as a cooling agent, but is also used in fog machines at theatres for dramatic effects. Its advantages include lower temperature than that of water ice and not leaving any residue (other than incidental frost from moisture in the atmosphere). It is useful for preserving frozen foods (such as ice cream) where mechanical cooling is unavailable. Dry ice sublimates at at Earth atmospheric pressure. This extreme cold makes the solid dangerous to handle without protection from frostbite injury. While generally not very toxic, the outgassing from it can cause hypercapnia (abnormally elevated carbon dioxide levels in the blood) due to buildup in confined locations. Properties Dry ice is the solid form of carbon dioxide (CO2), a molecul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
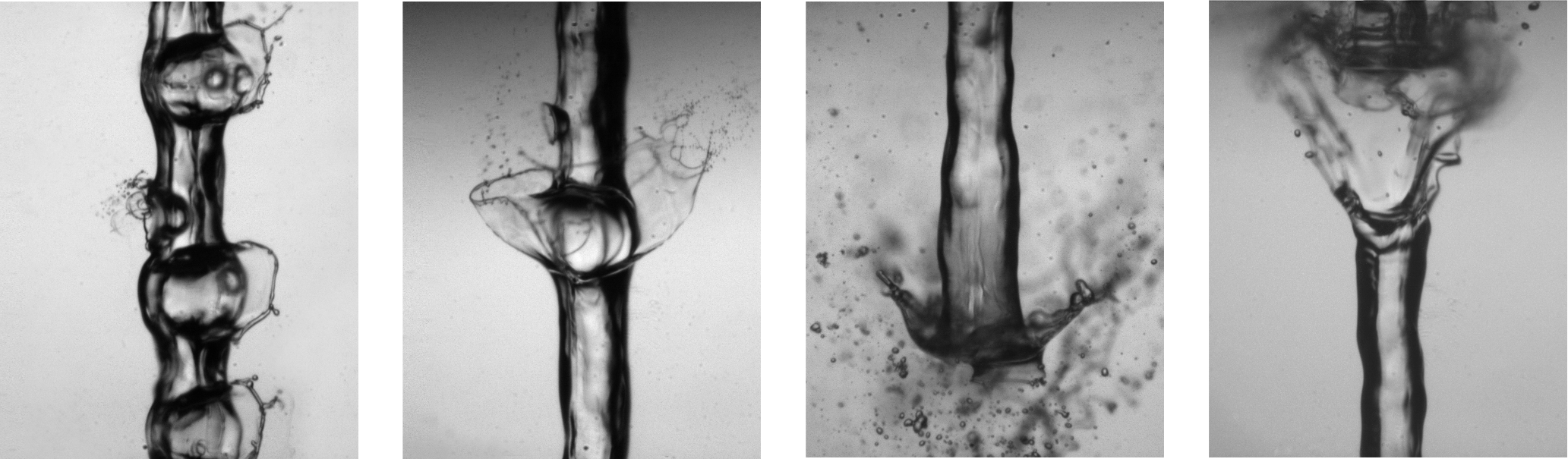
Bubble (physics)
A bubble is a globule of one substance in another, usually gas in a liquid. Due to the Marangoni effect, bubbles may remain intact when they reach the surface of the immersive substance. Common examples Bubbles are seen in many places in everyday life, for example: * As spontaneous nucleation of supersaturated carbon dioxide in soft drinks * As water vapor in boiling water * As air mixed into agitated water, such as below a waterfall * As sea foam * As a soap bubble * As given off in chemical reactions, e.g., baking soda + vinegar * As a gas trapped in glass during its manufacture * As the indicator in a spirit level Physics and chemistry Bubbles form and coalesce into globular shapes because those shapes are at a lower energy state. For the physics and chemistry behind it, see nucleation. Appearance Bubbles are visible because they have a different refractive index (RI) than the surrounding substance. For example, the RI of air is approximately 1.0003 and the RI of w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
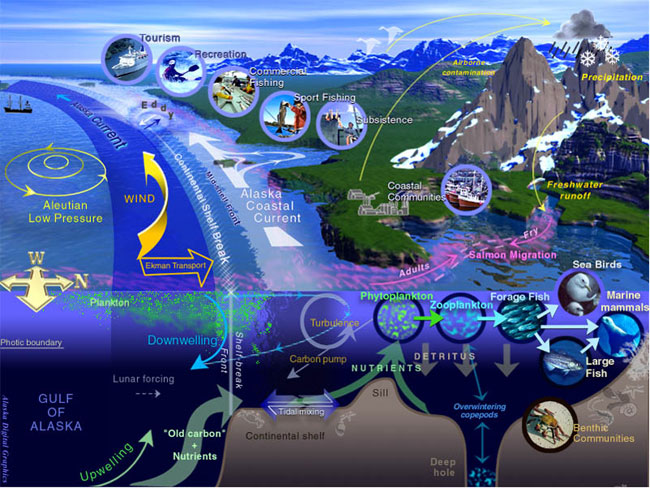
Ocean Current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of sea water generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, shoreline configurations, and interactions with other currents influence a current's direction and strength. Ocean currents are primarily horizontal water movements. An ocean current flows for great distances and together they create the global conveyor belt, which plays a dominant role in determining the climate of many of Earth’s regions. More specifically, ocean currents influence the temperature of the regions through which they travel. For example, warm currents traveling along more temperate coasts increase the temperature of the area by warming the sea breezes that blow over them. Perhaps the most striking example is the Gulf Stream, which makes northwest Europe much more temperate for its high latitude compared to other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_chloride.jpg)


