|
Direct Collapse Black Hole
Direct collapse black holes (DCBHs) are high-mass black hole seeds that form from the direct collapse of a large amount of material. They putatively formed within the redshift range ''z''=15–30, when the Universe was about 100–250 million years old. Unlike seeds formed from the first population of stars (also known as Population III stars), direct collapse black hole seeds are formed by a direct, General relativity, general relativistic instability. They are very massive, with a typical mass at formation of ~. This category of black hole seeds was originally proposed theoretically to alleviate the challenge in building supermassive black holes already at redshift z~7, as numerous observations to date have confirmed. __TOC__ Formation Direct collapse black holes (DCBHs) are massive black hole seeds theorized to have formed in the high-redshift Universe and with typical masses at formation of ~, but spanning between and . The environmental physical conditions to form a DCBH ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fabio Pacucci
Fabio Pacucci (born 1988) is an Italian-American astrophysicist and science communicator. He is currently a Staff Astrophysicist at the Center for Astrophysics , Harvard & Smithsonian, a collaboration between Harvard University and the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory. He is widely known for his research on black holes, quasars, high-redshift galaxies, and dark matter, with a particular emphasis on the formation and evolution of the first black holes in the Universe, also known as black hole seeds. Pacucci led the discovery of the first candidate direct collapse black holes and contributed to identifying the farthest gravitationally-lensed quasar and galaxy known prior to the launch of the James Webb Space Telescope. More recently, he has been a leading contributor to the study of " Little Red Dots", a population of compact, high-redshift sources potentially hosting overmassive black holes. Pacucci is also active in science communication. He has collaborated with TED-Ed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QSO J0313−1806
QSO J0313−1806 was the most distant, and hence also the oldest known quasar at ''z'' = 7.64, at the time of its discovery. In January 2021, it was identified as the most redshifted (highest ''z'') known quasar, with the oldest known supermassive black hole (SMBH) at solar masses. The 2021 announcement paper described it as "the most massive SMBH at ''z'' > 7". This quasar beat the prior recordsetting quasar, ULAS J1342+0928. In 2023, UHZ1 was discovered, setting a new record for most distant quasar, eclipsing that of QSO J0313−1806. One of the 2021 paper authors, Feige Wang, said that the existence of a supermassive black hole so early in the existence of the Universe posed problems for the current theories of formation since "black holes created by the very first massive stars could not have grown this large in only a few hundred million years". The redshift z = 7.642 corresponds to an age of about 600 million years. See also *Direct collapse black hole, a process by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UHZ1
UHZ1 is a background galaxy containing a quasar. At a redshift of approximately 10.1, UHZ1 is at a distance of 13.2 billion light-years, seen when our universe was about 3 percent of its current age. This redshift made it the most distant, and therefore earliest known quasar in the observable universe as of 2023. To detect this object, astronomers working at the Chandra X-ray Observatory used the Abell 2744's cluster mass as a gravitational lens A gravitational lens is matter, such as a galaxy cluster, cluster of galaxies or a point particle, that bends light from a distant source as it travels toward an observer. The amount of gravitational lensing is described by Albert Einstein's Ge ... in order to magnify distant objects directly behind it.200 Myr, or a massive seed. Data collected provides a clue to the seeding mechanism and supports it. UHZ1 as a potential first OBG candidate The Chandra X-ray source detected in UHZ1 is Compton-thick. It has a bolometric luminosity o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quasi-star
A quasi-star (also called black hole star) is a hypothetical star, hypothetical type of extremely large and luminosity, luminous star that may have existed early in the history of the Universe. They are thought to have existed for around 7–10 million years due to their immense mass. Unlike modern stars, which are powered by nuclear fusion in their cores, a quasi-star's energy would come from material falling into a black hole at its core. They were first proposed in the 1960s and have since provided valuable insights into the early universe, galaxy formation, and the behavior of black holes. Although they have not been observed, they are considered to be a possible progenitor of Supermassive black hole, supermassive black holes. Formation and properties A quasi-star would have resulted from the core of a large protostar collapsing into a black hole, where the outer layers of the protostar are massive enough to absorb the resulting burst of energy without being blown away o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Population III Star
Population is a set of humans or other organisms in a given region or area. Governments conduct a census to quantify the resident population size within a given jurisdiction. The term is also applied to non-human animals, microorganisms, and plants, and has specific uses within such fields as ecology and genetics. Etymology The word ''population'' is derived from the Late Latin ''populatio'' (a people, a multitude), which itself is derived from the Latin word ''populus'' (a people). Use of the term Social sciences In sociology and population geography, population refers to a group of human beings with some predefined feature in common, such as location, race, ethnicity, nationality, or religion. Ecology In ecology, a population is a group of organisms of the same species which inhabit the same geographical area and are capable of interbreeding. The area of a sexual population is the area where interbreeding is possible between any opposite-sex pair within the area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiation-dominated Era
The expansion of the universe is parametrized by a dimensionless scale factor a . Also known as the cosmic scale factor or sometimes the Robertson–Walker scale factor, this is a key parameter of the Friedmann equations. In the early stages of the Big Bang, most of the energy was in the form of radiation, and that radiation was the dominant influence on the expansion of the universe. Later, with cooling from the expansion the roles of matter and radiation changed and the universe entered a matter-dominated era. Recent results suggest that we have already entered an era dominated by dark energy, but examination of the roles of matter and radiation are most important for understanding the early universe. Using the dimensionless scale factor to characterize the expansion of the universe, the effective energy densities of radiation and matter scale differently. This leads to a radiation-dominated era in the very early universe but a transition to a matter-dominated era at a later tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflation (cosmology)
In physical cosmology, cosmic inflation, cosmological inflation, or just inflation, is a theory of exponential expansion of space in the very early universe. Following the inflationary period, the universe continued to expand, but at a slower rate. The re-acceleration of this slowing expansion due to dark energy began after the universe was already over 7.7 billion years old (5.4 billion years ago). Inflation theory was developed in the late 1970s and early 1980s, with notable contributions by several theoretical physicists, including Alexei Starobinsky at Landau Institute for Theoretical Physics, Alan Guth at Cornell University, and Andrei Linde at Lebedev Physical Institute. Starobinsky, Guth, and Linde won the 2014 Kavli Prize "for pioneering the theory of cosmic inflation". It was developed further in the early 1980s. It explains the origin of the large-scale structure of the cosmos. Quantum fluctuations in the microscopic inflationary region, magnified t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
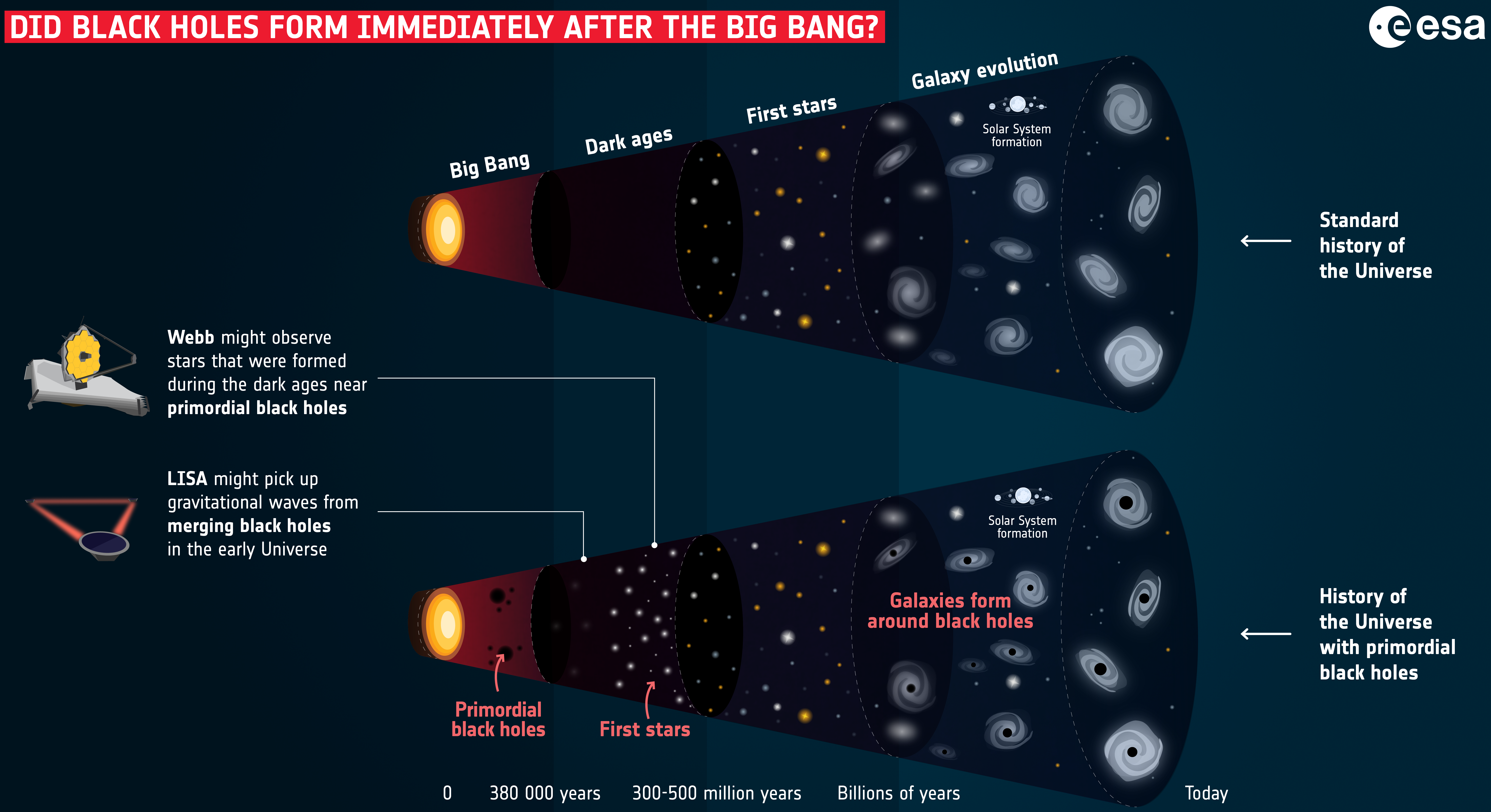
Primordial Black Hole
In cosmology, primordial black holes (PBHs) are hypothetical black holes that formed soon after the Big Bang. In the inflationary era and early radiation-dominated universe, extremely dense pockets of subatomic matter may have been tightly packed to the point of gravitational collapse, creating primordial black holes without the supernova compression typically needed to make black holes today. Because the creation of primordial black holes would pre-date the first stars, they are not limited to the narrow mass range of stellar black holes. In 1966, Yakov Zeldovich and Igor Novikov first proposed the existence of such black holes, while the first in-depth study was conducted by Stephen Hawking in 1971. However, their existence remains hypothetical. In September 2022, primordial black holes were proposed by some researchers to explain the unexpected very large early galaxies discovered by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). PBHs have long been considered possibly important i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Webb Space Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a space telescope designed to conduct infrared astronomy. As the largest telescope in space, it is equipped with high-resolution and high-sensitivity instruments, allowing it to view objects too old, List of the most distant astronomical objects, distant, or faint for the Hubble Space Telescope. This enables investigations across many fields of astronomy and cosmology, such as observation of the Population III star, first stars and the Galaxy formation and evolution, formation of the first galaxies, and detailed atmospheric characterization of potentially habitable exoplanets. Although the Webb's mirror diameter is 2.7 times larger than that of the Hubble Space Telescope, it produces images of comparable optical resolution, resolution because it observes in the longer-wavelength infrared spectrum. The longer the wavelength of the spectrum, the larger the information-gathering surface required (mirrors in the infrared spectrum or antenna a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrared
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with the waves that are just longer than those of red light (the longest waves in the visible spectrum), so IR is invisible to the human eye. IR is generally (according to ISO, CIE) understood to include wavelengths from around to . IR is commonly divided between longer-wavelength thermal IR, emitted from terrestrial sources, and shorter-wavelength IR or near-IR, part of the solar spectrum. Longer IR wavelengths (30–100 μm) are sometimes included as part of the terahertz radiation band. Almost all black-body radiation from objects near room temperature is in the IR band. As a form of EMR, IR carries energy and momentum, exerts radiation pressure, and has properties corresponding to both those of a wave and of a particle, the photon. It was long known that fires e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
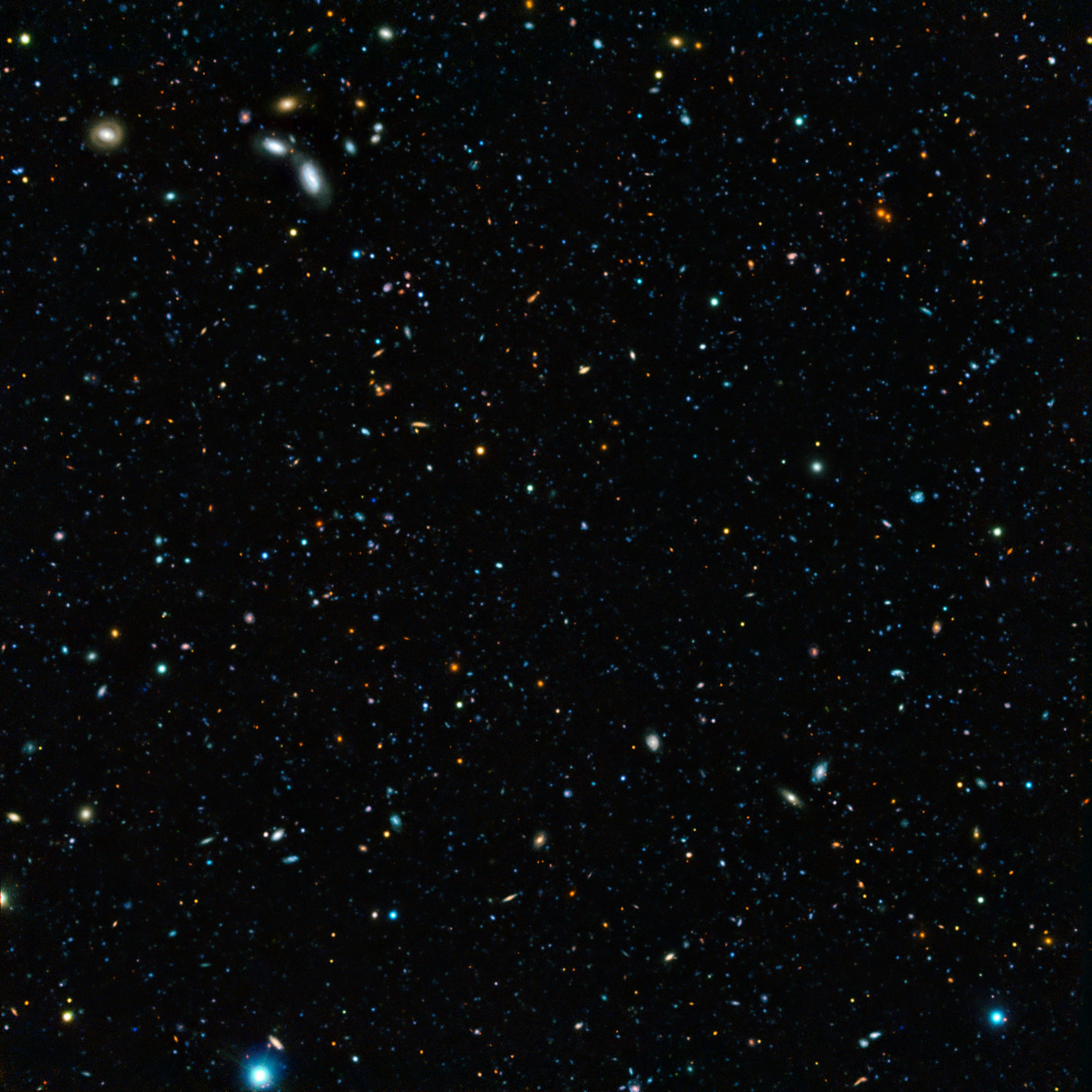
Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey
The Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey, or GOODS, is an astronomical survey An astronomical survey is a general celestial cartography, map or astrophotography, image of a region of the sky (or of the whole sky) that lacks a specific observational target. Alternatively, an astronomical survey may comprise a set of image ... combining deep observations from three of NASA's Great Observatories program, Great Observatories: the Hubble Space Telescope, the Spitzer Space Telescope, and the Chandra X-ray Observatory, along with data from other Space observatory, space-based telescopes, such as XMM Newton, and some of the world's most powerful ground-based telescopes. GOODS is intended to enable astronomers to study the galaxy formation and evolution, formation and evolution of galaxies in the distant, early universe. The Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey consists of optical and near-infrared imaging taken with the Advanced Camera for Surveys on the Hubble Space Telescope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |