|
Diphosphine
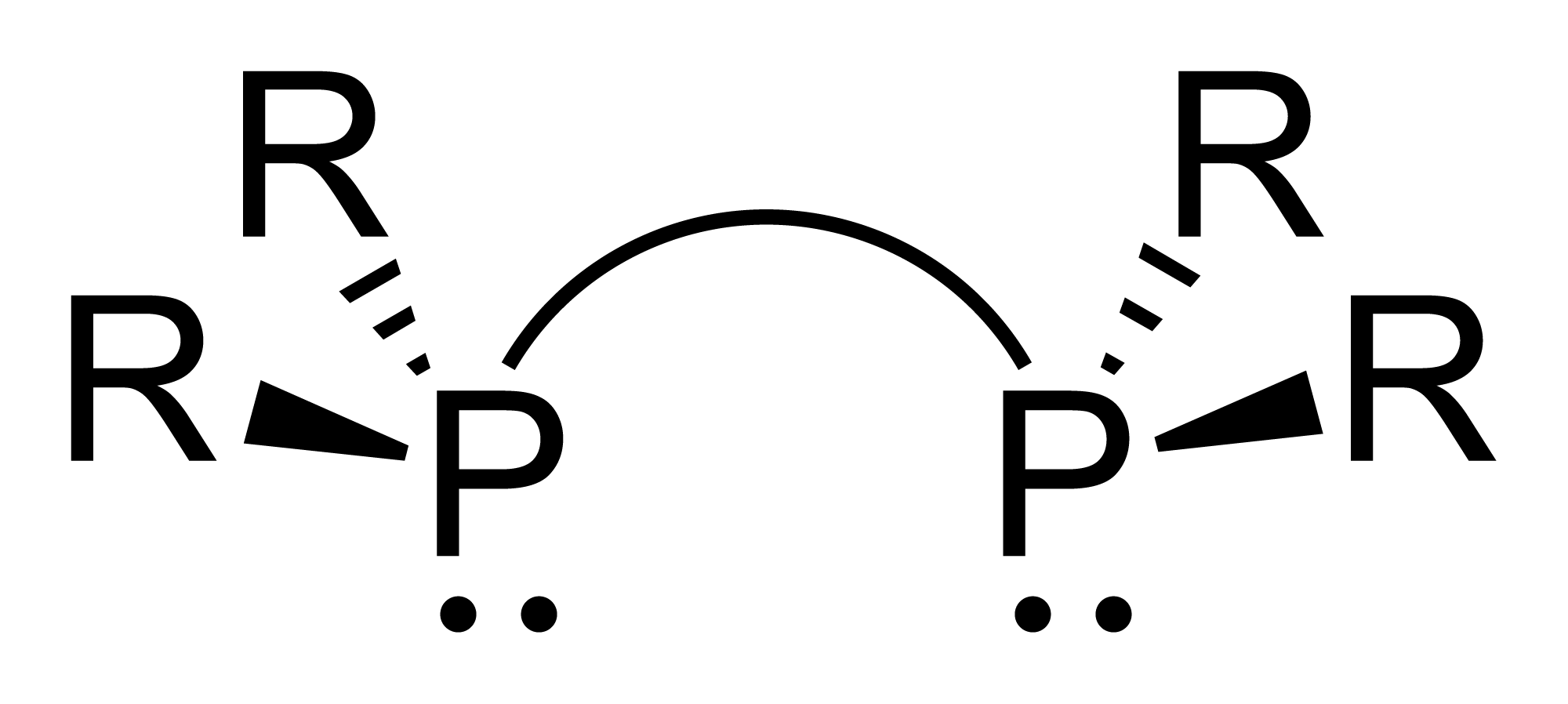
Diphosphane, or diphosphine, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . This colourless liquid is one of several binary phosphorus hydrides. It is the impurity that typically causes samples of phosphine to ignite in air. Properties, preparation, reactions Diphosphane adopts the gauche conformation (like hydrazine, less symmetrical than shown in the image) with a P−P distance of 2.219 angstroms. It is nonbasic, unstable at room temperature, and spontaneously flammable in air. It is only poorly soluble in water but dissolves in organic solvents. Its 1H NMR spectrum consists of 32 lines resulting from an A2XX'A'2 splitting system. Diphosphane is produced by the hydrolysis of calcium monophosphide, which can be described as the Ca2+ derivative of . According to an optimized procedure, hydrolysis of 400 g of CaP at −30 °C gives about 20 g of product, slightly contaminated with phosphine Phosphine (IUPAC name: phosphane) is a colorless, flammable, highly t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphosphines
Diphosphines, sometimes called bisphosphanes, are organophosphorus compounds most commonly used as bidentate phosphine ligand, phosphine ligands in inorganic chemistry, inorganic and organometallic chemistry. They are identified by the presence of two phosphino groups linked by a backbone, and are usually chelate, chelating. A wide variety of diphosphines have been synthesized with different linkers and R-groups. Alteration of the linker and R-groups alters the electronic and steric properties of the ligands which can result in different coordination geometries and catalytic behavior in Homogeneous catalysis, homogeneous catalysts. Synthesis image:IPr2PCl.png, 220px, Chlorodiisopropylphosphine is a popular building block for the preparation of diphosphines. From phosphide building blocks Many widely used diphosphine ligands have the general formula Ar2P(CH2)nPAr2. These compounds can be prepared from the reaction of X(CH2)nX (X=halogen) and MPPh2 (M = alkali metal): :Cl(CH2)nCl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphosphorus Tetrafluoride
Diphosphorus tetrafluoride is a gaseous compound of phosphorus and fluorine with formula . Two fluorine atoms are connected to each phosphorus atom, and there is a bond between the two phosphorus atoms. Phosphorus can be considered to have oxidation state +2, as indicated by the name phosphorus difluoride. Production Diphosphorus tetrafluoride was discovered in 1966 by Max Lustig, John K. Ruff and Charles B. Colburn at the Redstone Research Laboratories. The initial synthesis reacted phosphorus iododifluoride with mercury at room temperature: : Properties The P−P bond in diphosphorus tetrafluoride is much stronger than the corresponding N−N bond in dinitrogen tetrafluoride which easily breaks into nitrogen difluoride. The infrared spectrum has absorption at 842 cm−1, 830 cm−1, 820 cm−1, and weaker at 408 cm−1 and 356 cm−1. The molecule has C2h symmetry. Reactions Under ultraviolet light diphosphorus tetrafluoride reacts with alkynes conne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetraphenyldiphosphine
Tetraphenyldiphosphine is the organophosphorus compound with the formula Ph2sub>2, where Ph = phenyl (C6H5). It is a white, air-sensitive solid that dissolves in nonpolar solvents. It is a centrosymmetric molecule with a P-P bond of 2.2592 Å. Tetraphenyldiphosphine is produced by reductive coupling of chlorodiphenylphosphine... :2 Ph2PCl + 2 Na → Ph2P-PPh2 + 2 NaCl ...or dehydrogenation of diphenylphosphine catalyzed by bis(triphenylphospine)nickel(II) bromide: :2 Ph2PH → Ph2P-PPh2 + H2 The compound is used as a source of the Ph2P− group. :Ph2P-PPh2 + 2 Na → + 2 NaPPh2 Alternatively, the compound can homolyze along the weak P–P bond, in which case the resulting radicals add to alkenes and alkynes. Oxidation with oxygen or sulfur gives the corresponding diphosphine dioxide or disulfide.{{cite journal, doi=10.1021/ja00714a020, publisher=American Chemical Society The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a scientific society b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Monophosphide
Calcium monophosphide is the inorganic compound with the formula CaP. It is sometimes also known as "calcium phosphide", which also describes a different compound with composition Ca3P2. Calcium monophosphide is a black solid. Structure and properties The structures of CaP and sodium peroxide (Na2O2) are very similar. The solid is described as a salt: (Ca2+)2P24−, or Ca2P2. Since the bonding is ionic, the diphosphide centers carry negative charge and are easily protonated. Upon hydrolysis this material releases diphosphine (P2H4): :Ca2P2 + 4 H2O → 2 Ca(OH)2 + P2H4 The hydrolyses of CaP and calcium carbide Calcium carbide, also known as calcium acetylide, is a chemical compound with the chemical formula of . Its main use industrially is in the production of acetylene and calcium cyanamide. The pure material is colorless, while pieces of technica ... (CaC2) are similar, except that diphosphine spontaneously ignites in air. Thus, CaP must be protected from air. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphine
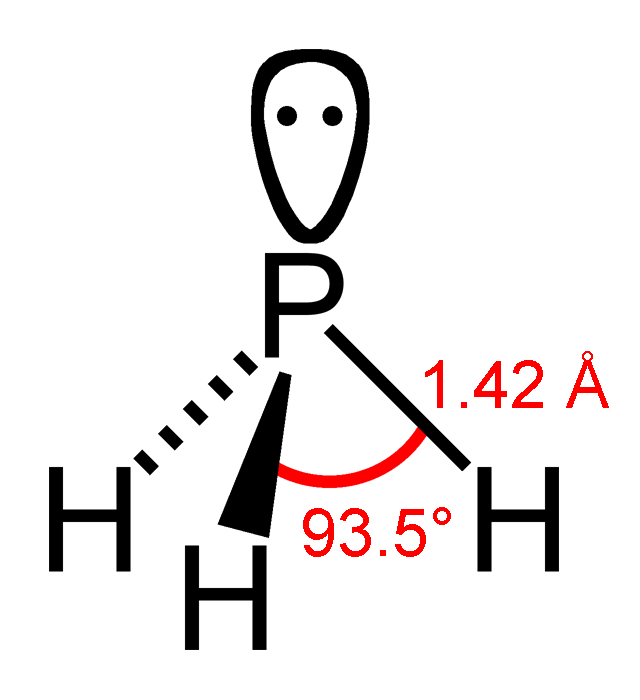
Phosphine (IUPAC name: phosphane) is a colorless, flammable, highly toxic compound with the chemical formula , classed as a pnictogen hydride. Pure phosphine is odorless, but technical grade samples have a highly unpleasant odor like rotting fish, due to the presence of substituted phosphine and diphosphane (). With traces of present, is spontaneously flammable in air ( pyrophoric), burning with a luminous flame. Phosphine is a highly toxic respiratory poison, and is immediately dangerous to life or health at 50 ppm. Phosphine has a trigonal pyramidal structure. Phosphines are compounds that include and the organophosphines, which are derived from by substituting one or more hydrogen atoms with organic groups. They have the general formula . Phosphanes are saturated phosphorus hydrides of the form , such as triphosphane. Phosphine () is the smallest of the phosphines and the smallest of the phosphanes. History Philippe Gengembre (1764–1838), a student of Lavoisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphosphenes
Diphosphene is a type of organophosphorus compound that has a phosphorus–phosphorus double bond, denoted by R-P=P-R'. These compounds are not common, but their properties have theoretical chemistry, theoretical importance. Normally, compounds with the empirical formula RP exist as rings. However, like other multiple bonds between heavy main-group elements, P=P double bonds can be stabilized by large steric effects, steric hindrance. In general, diphosphenes react like Alkene, alkenes. History In 1877, Köhler and Michaelis claimed what would have been the first isolated diphosphene (PhP=PPh), The structure of Köhler and Michaelis' product was later revised. and X-ray crystallographic analysis proved that this "diphosphene" only had P-P single bonds and was in fact primarily a four-membered ring of the form (PPh)4. The isolation of phosphorus ylide and phosphaalkenes suggested that compounds with P=P bonds could be made. Yoshifuji ''et al'''s isolated a sterically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triphosphane
Triphosphane (IUPAC systematic name) or triphosphine is an inorganic compound having the chemical formula . It can be generated from diphosphine but is highly unstable at room temperature: : Samples have been isolated by gas chromatography Gas chromatography (GC) is a common type of chromatography used in analytical chemistry for Separation process, separating and analyzing compounds that can be vaporized without Chemical decomposition, decomposition. Typical uses of GC include t .... The compound rapidly converts to and the cyclophosphine ''cyclo''-. References External linksIUPAC {{Hydrides by group Phosphines Phosphorus hydrides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphosphorus Tetraiodide
Diphosphorus tetraiodide is an orange crystalline solid with the formula >. It has been used as a reducing agent in organic chemistry. It is a rare example of a compound with phosphorus in the +2 oxidation state, and can be classified as a subhalide of phosphorus. It is the most stable of the diphosphorus tetrahalides. Synthesis and structure Diphosphorus tetraiodide is easily generated by the disproportionation of phosphorus triiodide in dry ether: : It can also be obtained by treating phosphorus trichloride and potassium iodide in anhydrous conditions. Another synthesis route involves combining phosphonium iodide with iodine in a solution of carbon disulfide. An advantage of this route is that the resulting product is virtually free of impurities. : The compound adopts a centrosymmetric structure with a P-P bond of 2.230 Å. Reactions Inorganic chemistry Diphosphorus tetraiodide reacts with bromine to form mixtures . With sulfur, it is oxidized to , retaining the P-P bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorodiphenylphosphine
Chlorodiphenylphosphine is an organophosphorus compound with the formula (C6H5)2PCl, abbreviated Ph2PCl. It is a colourless oily liquid with a pungent odor that is often described as being garlic-like and detectable even in the ppb range. It is useful reagent for introducing the Ph2P group into molecules, which includes many ligands.Quin, L. D. ''A Guide to Organophosphorus Chemistry''; Wiley IEEE: New York, 2000; pp 44-69. Like other halophosphines, Ph2PCl is reactive with many nucleophiles such as water and easily oxidized even by air. Synthesis and reactions Chlorodiphenylphosphine is produced on a commercial scale from benzene and phosphorus trichloride (PCl3). Benzene reacts with phosphorus trichloride at extreme temperatures around 600 °C to give dichlorophenylphosphine (PhPCl2) and HCl. Redistribution of PhPCl2 in the gas phase at high temperatures results in chlorodiphenylphosphine. :2PhPCl2 → Ph2PCl + PCl3 Alternatively such compounds are prepared by redistri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiophosphoryl Chloride
Thiophosphoryl chloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula .Spilling, C. D. "Thiophosphoryl Chloride" in Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis John Wiley & Sons, Weinheim, 2001 . Article Online Posting Date: April 15, 2001 It is a colorless pungent smelling liquid that fumes in air. It is synthesized from phosphorus chloride and used to thiophosphorylate organic compounds, such as to produce insecticides. Synthesis Thiophosphoryl chloride can be generated by several reactions starting from phosphorus trichloride. The most common and practical synthesis, hence used in industrial manufacturing, is directly reacting phosphorus trichloride with excess sulfur at 180 °C. : Using this method, yields can be very high after purification by distillation. Catalysts facilitate the reaction at lower temperatures, but are not usually necessary. Alternatively, it is obtained by combining phosphorus pentasulfide and phosphorus pentachloride.Martin, D. R.; Duvall, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pnictogen Hydride
Pnictogen hydrides or hydrogen pnictides are binary compounds of hydrogen with pnictogen ( or ; from "to choke" and -gen, "generator") atoms (elements of group 15: nitrogen, phosphorus, arsenic, antimony, bismuth, and moscovium) covalently bonded to hydrogen. Pnictogen trihydrides The simplest series has the chemical formula XH3 (less commonly H3X), with X representing any of the pnictogens. They take on the pyramidal structure (as opposed to the trigonal planar arrangement of the group 13 hydrides), and therefore are polar. These pnictogen trihydrides are generally increasingly unstable and poisonous with heavier elements. Some properties of the pnictogen trihydrides follow: These gases have no smell in pure form, instead gaining it when in contact with air. Ammonia has an infamous, intense odour resembling urine and/or fish, commonly the result of the decomposition of urea. Phosphine smells like fish or garlic, and stibine like rotten eggs, similar to hydrogen sulfide a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |