|
Dioxirane Oxidation
Oxidation with dioxiranes refers to the introduction of oxygen into organic substrates using dioxiranes. Dioxiranes are well known for epoxidations (synthesis of epoxides from alkenes). Dioxiranes oxidize other unsaturated functionality, heteroatoms, and alkane C-H bonds. Dioxiranes are metal-free oxidants. Epoxidations Dioxiranes are electrophilic oxidants that react more quickly with electron-rich than electron-poor double bonds; however, both classes of substrates can be epoxidized within a reasonable time frame. The mechanism of epoxidation with dioxiranes likely involves concerted oxygen transfer through a spiro compound, spiro transition state. As oxygen transfer occurs, the plane of the oxirane is perpendicular to and bisects the plane of the alkene pi system. The configuration of the alkene is maintained in the product, ruling out long-lived radical intermediates. In addition, the spiro transition state has been used to explain the selectivity in enantioselective epoxidatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dioxirane
In chemistry, dioxirane (systematically named dioxacyclopropane, also known as methylene peroxide or peroxymethane) is an organic compound with formula . The molecule consists of a ring with one methylene and two oxygen atoms. It is of interest as the smallest cyclic organic peroxide, but otherwise it is of little practical value. Synthesis Dioxirane is highly unstable and the majority of studies of it have been computational; it has been detected during the low temperature (–196 °C) reaction of ethylene and ozone, although even at these temperatures such a mixture can be explosive. Its formation is thought to be radical in nature, preceding via a Criegee intermediate. Microwave analysis has indicated C-H, C-O and O-O bond lengths of 1.090, 1.388 and 1.516 Å respectively. The very long and weak O-O bond (cf. hydrogen peroxide O-O = 1.47 Å) is the origin of its instability. Other dioxiranes Beyond the parent dioxirane, which is mainly of theoretical interest, more c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacobsen Epoxidation
The Jacobsen epoxidation, sometimes also referred to as Jacobsen-Katsuki epoxidation is a chemical reaction which allows enantioselective epoxidation of unfunctionalized alkyl- and aryl- substituted alkenes. It is complementary to the Sharpless epoxidation (used to form epoxides from the double bond in allylic alcohols). The Jacobsen epoxidation gains its stereoselectivity from a ''C2'' symmetric manganese(III) salen-like ligand, which is used in catalytic amounts. The manganese atom transfers an oxygen atom from chlorine bleach or similar oxidant. The reaction takes its name from its inventor, Eric Jacobsen, with Tsutomu Katsuki sometimes being included. Chiral-directing catalysts are useful to organic chemists trying to control the stereochemistry of biologically active compounds and develop enantiopure drugs. Several improved procedures have been developed. A general reaction scheme follows: : History In the early 1990s, Jacobsen and Katsuki independently released thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allene
In organic chemistry, allenes are organic compounds in which one carbon atom has double bonds with each of its two adjacent carbon atoms (, where R is hydrogen, H or some organyl group). Allenes are classified as diene#Classes, cumulated dienes. The parent compound of this class is propadiene (), which is itself also called ''allene''. A group of the structure is called allenyl, while a substituent attached to an allene is referred to as an allenic substituent (R is H or some alkyl group). In analogy to Allyl group, allylic and Propargyl group, propargylic, a substituent attached to a saturated carbon α (i.e., directly adjacent) to an allene is referred to as an allenylic substituent. While allenes have two consecutive ('cumulated') double bonds, compounds with three or more cumulated double bonds are called cumulenes. History For many years, allenes were viewed as curiosities but thought to be synthetically useless and difficult to prepare and to work with.The Chemistry of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Sieve
A molecular sieve is a material with pores of uniform size comparable to that of individual molecules, linking the interior of the solid to its exterior. These materials embody the molecular sieve effect, in which molecules larger than the pores are preferentially sieved, allowing for the selective adsorption of specific compounds based on their molecular size. Many kinds of materials exhibit some molecular sieves, but zeolites dominate the field. Zeolites are almost always aluminosilicates, or variants where some or all of the Si or Al centers are replaced by similarly charged elements. Sieving process The diameters of the pores that comprise molecular sieves are similar in size to small molecules. Large molecules cannot enter or be adsorbed, while smaller molecules can. As a mixture of molecules migrates through the stationary bed of porous, semi-solid substance referred to as a sieve (or matrix), the components of the highest molecular weight (which are unable to pass int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetone
Acetone (2-propanone or dimethyl ketone) is an organic compound with the chemical formula, formula . It is the simplest and smallest ketone (). It is a colorless, highly Volatile organic compound, volatile, and flammable liquid with a characteristic pungent odor. Acetone is miscibility, miscible with properties of water, water and serves as an important organic solvent in industry, home, and laboratory. About 6.7 million tonnes were produced worldwide in 2010, mainly for use as a solvent and for production of methyl methacrylate and bisphenol A, which are precursors to widely used plastics.Acetone World Petrochemicals report, January 2010Stylianos Sifniades, Alan B. Levy, "Acetone" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005. It is a common building block in organic chemistry. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
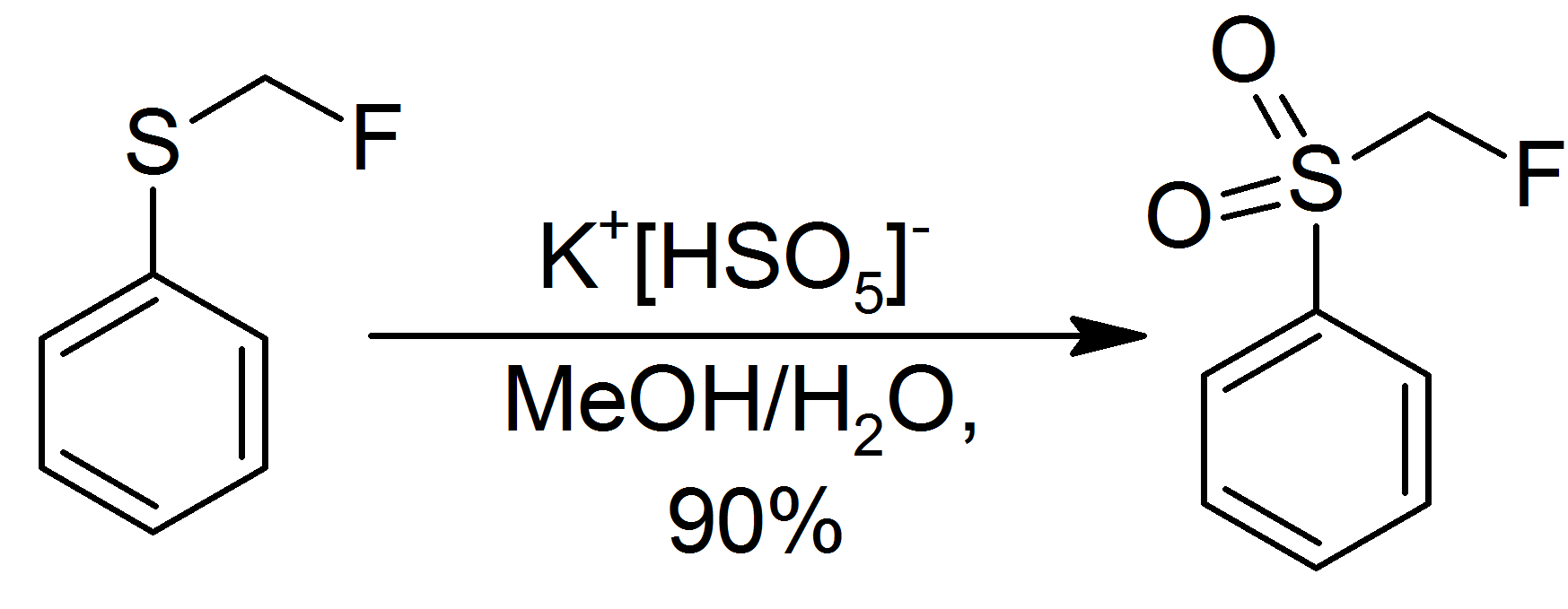
Oxone
Potassium peroxymonosulfate is widely used as an oxidizing agent, for example, in pools and spas (usually referred to as monopersulfate or "MPS"). It is the potassium salt of peroxymonosulfuric acid. Potassium peroxymonosulfate per se is rarely encountered. It is often confused with the triple salt , known as Oxone. The standard electrode potential for potassium peroxymonosulfate is +1.81 V with a half reaction generating the hydrogen sulfate (): : Oxone Potassium peroxymonosulfate per se is a relatively obscure salt, but its derivative called Oxone is of commercial value. Oxone refers to the triple salt . As such about one third by weight is potassium peroxymonosulfate. Oxone has a longer shelf life than does potassium peroxymonosulfate. A white, water-soluble solid, Oxone loses <1% of its oxidizing power per month. Oxone, which is commercially available, is produced from peroxysulfuric acid, which is generated in situ by combining |
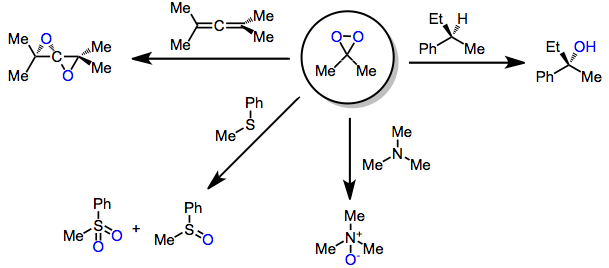
Dimethyldioxirane
Dimethyldioxirane (DMDO) is the organic compound with the formula . It is the dioxirane derived from acetone and can be viewed as the monomer of acetone peroxide. It is a powerful selective oxidizing agent that finds some use in organic synthesis. It is known only in the form of a dilute solution, usually in acetone, and hence the properties of the pure material are largely unknown. Synthesis DMDO is not commercially available because of chemical instability. DMDO can be prepared as dilute solutions (~0.1 M) by treatment of acetone with potassium peroxymonosulfate , usually in the form of Oxone (2KHSO5·KHSO4·K2SO4). : The preparation of DMDO is rather inefficient (typical yields < 3%) and typically only yields a relatively dilute solution in acetone (only up to approximately 0.1 M). This is tolerable as preparation uses inexpensive substances: acetone, sodium bicarbonate, and oxone. Cold solutions (−10 to −20 °C) of DMDO are stable for days. Decomposition is accelerat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |