|
Dinocephalosaurus
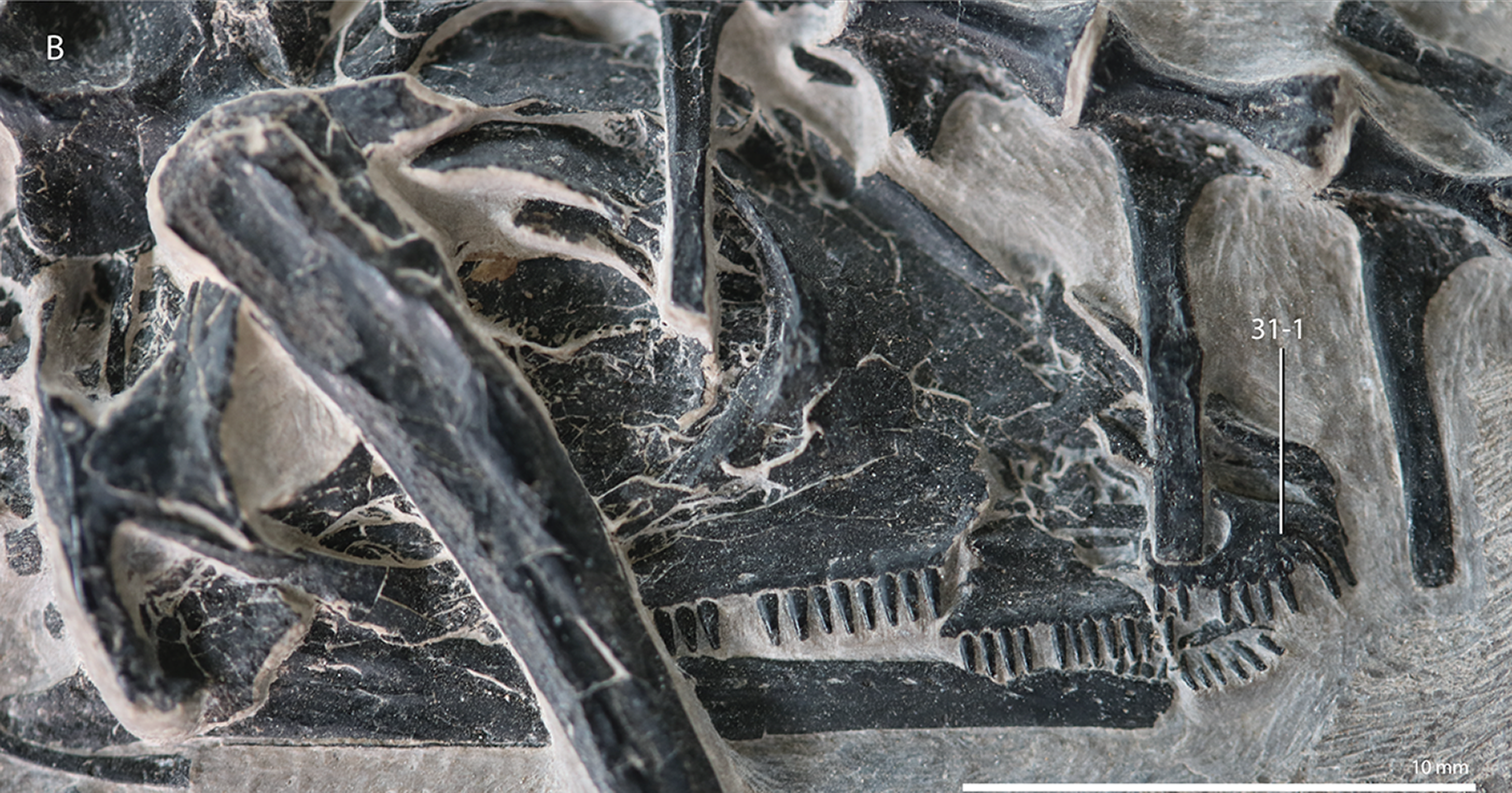
''Dinocephalosaurus'' (meaning "terrible-headed reptile") is a genus of long necked, aquatic protorosaur that inhabited the Triassic seas of China. The genus contains the type and only known species, ''D. orientalis'', which was named by Chun Li in 2003. Unlike other long-necked protorosaurs (which form a group known as the tanystropheids), ''Dinocephalosaurus'' convergently evolved a long neck not through elongation of individual neck vertebrae, but through the addition of neck vertebrae that each had a moderate length. As indicated by phylogenetic analyses, it belonged in a separate lineage that also included at least its closest relative '' Pectodens'', which was named the Dinocephalosauridae in 2021. Like tanystropheids, however, ''Dinocephalosaurus'' probably used its long neck to hunt, utilizing the fang-like teeth of its jaws to ensnare prey; proposals that it employed suction feeding have not been universally accepted. It was probably a marine animal by necessity, as s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinocephalosauridae
Trachelosauridae (also known as Dinocephalosauridae) is an extinct clade of archosauromorph reptiles that lived throughout the Triassic period. Like their close relatives the tanystropheids, they were "Protorosauria, protorosaur"-Evolutionary grade, grade archosauromorphs characterized by their long necks. Unlike tanystropheids, which lengthen their neck primarily by elongating the individual cervical vertebrae, cervical (neck) vertebrae, trachelosaurids achieved their long necks by the addition of more vertebrae. The most extreme example of this trend was ''Dinocephalosaurus'', which had at least 32 vertebrae in the neck alone, far more than the 13 neck vertebrae of ''Tanystropheus''. Trachelosaurids are known from Europe (Poland, Germany, Austria, Netherlands) and China. Some members of the family (i.e. ''Dinocephalosaurus'') were solely marine animals with paddle-like limbs, inhabiting the coastlines of the Tethys Ocean. ''Dinocephalosaurus'' was so specialized for aquatic life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
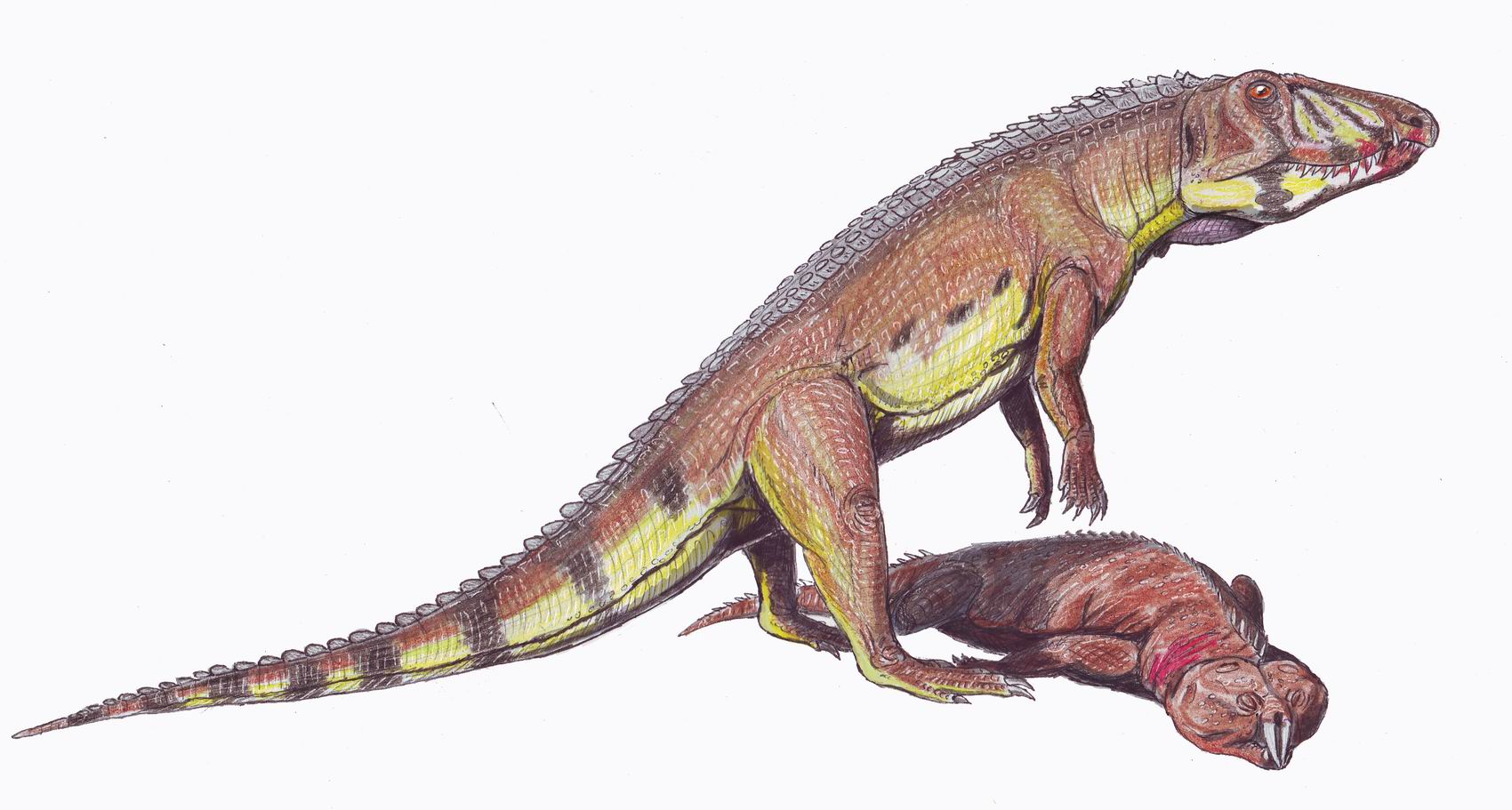
Pectodens
''Pectodens'' (meaning "comb tooth") is an extinction, extinct genus of archosauromorpha, archosauromorph reptile which lived during the Middle Triassic in China. The type and only species of the genus is ''P. zhenyuensis'', named by Chun Li and colleagues in 2017. It was a member of the Archosauromorpha, specifically part of the unnatural grouping Protorosauria. However, an unusual combination of traits similar (such as the long neck) and dissimilar (such as the absence of a hook on the fifth metatarsal bones, metatarsal bone) to other protorosaurs initially led to confusion over its evolutionary relationships. In 2021, it was placed in a newly-established group, Dinocephalosauridae, along with its closest relative ''Dinocephalosaurus''. A small, slender animal measuring long, ''Pectodens'' was named after the peculiar comb-like arrangement of long, conical teeth present in its mouth. Unlike ''Dinocephalosaurus'' and the other reptiles that it was preserved with, well-developed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protorosauria
Protorosauria is an extinct, likely paraphyletic group of basal archosauromorph reptiles from the latest Middle Permian ( Capitanian stage) to the end of the Late Triassic ( Rhaetian stage) of Asia, Europe and North America. It was named by the English anatomist and paleontologist Thomas Henry Huxley in 1871 as an order, originally to solely contain '' Protorosaurus''. Other names which were once considered equivalent to Protorosauria include Prolacertiformes and Prolacertilia. Protorosaurs are distinguished by their long necks formed by elongated cervical vertebrae, which have ribs that extend backward to the vertebrae behind them. Protorosaurs also have a gap between the quadrate bones and the jugal bones in the back of the skull near the jaw joint, making their skulls resemble those of lizards. While previously thought to be monophyletic, the group is now thought to consist of various groups of basal archosauromorph reptiles that lie outside Crocopoda, though some re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanystropheidae
Tanystropheidae is an extinct family (biology), family of archosauromorph reptiles that lived throughout the Triassic Period, often considered to be "protorosaurs". They are characterized by their long, stiff necks formed from elongated cervical vertebrae with very long cervical ribs. Members of the group include both terrestrial and aquatic forms. While some tanystropheids were small lizard-like animals, other tanystropheids such as ''Tanystropheus'' were large animals that had necks that were several meters long, longer than the rest of their bodies. Tanystropheids are known from Europe, Asia (Russia, China, and Saudi Arabia), North America and probably South America (Brazil). The presence of tanystropheids in Europe and China indicate that they lived along much of the coastline of the Tethys Ocean. However, species in western North America are found in terrestrial deposits, suggesting that as a group, tanystropheids were ecologically diverse. Relationships among tanystropheid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anisian
In the geologic timescale, the Anisian is the lower stage (stratigraphy), stage or earliest geologic age, age of the Middle Triassic series (stratigraphy), series or geologic epoch, epoch and lasted from million years ago until million years ago. The Anisian Age succeeds the Olenekian Age (part of the Lower Triassic Epoch) and precedes the Ladinian Age. Stratigraphic definitions The stage and its name were established by Austrian geologists Wilhelm Heinrich Waagen and Carl Diener in 1895. The name comes from ''Anisus'', the Latin name of the river Enns (river), Enns. The original type locality (geology), type locality is at Großreifling in the states of Austria, Austrian state of Styria. The base of the Anisian Stage (also the base of the Middle Triassic series) is sometimes laid at the first appearance of conodont species ''Chiosella, Chiosella timorensis'' in the stratigraphic record. Other stratigraphers prefer to use the base of magnetic chronozone MT1n. There is no accept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yunnan
Yunnan; is an inland Provinces of China, province in Southwestern China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 47.2 million (as of 2020). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the Chinese provinces of Guizhou, Sichuan, Autonomous regions of China, autonomous regions of Guangxi and Tibet Autonomous Region, Tibet, as well as Southeast Asian countries Myanmar (Burma), Vietnam, and Laos. Yunnan is China's fourth least developed province based on disposable income per capita in 2014. Yunnan is situated in a mountainous area, with high elevations in the Northwest and low elevations in the Southeast. Most of the population lives in the eastern part of the province. In the west, the altitude can vary from the mountain peaks to river valleys as much as . Yunnan is rich in natural resources and has the largest diversity of plant life in China. Of the approximately 30,000 species of Vascular plant, higher plants in China, Yunnan has perhaps 17, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dianopachysaurus
''Dianopachysaurus'' is an extinct genus of pachypleurosaur known from the lower Middle Triassic (Anisian age) of Yunnan Province, southwestern China. It was found in the Middle Triassic Lagerstätte of the Guanling Formation. It was first named by Jun Liu, Olivier Rieppel, Da-Yong Jiang, Jonathan C. Aitchison, Ryosuke Motani, Qi-Yue Zhang, Chang-Yong Zhou and Yuan-Yuan Sun in 2011 and the type species is ''Dianopachysaurus dingi,'' thanking a Professor Ding for his help. ''Dianopachysaurus'' is most closely related to '' Keichousaurus'', another Chinese pachypleurosaur. Both belong to the family Keichousauridae. Pachypleurosaurs are hypothesized to have originated in the eastern Tethys Ocean (South China) before spreading and diversifying in the western Tethys in what is now Europe. A large ghost lineage of eastern pachypleurosaurs has long been inferred based on the phylogeny of the group. ''Dianopachysaurus'' represents an early stage in the radiation of pachypleurosaurs and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinosaurosphargis
''Sinosaurosphargis'' is an extinct genus of basal marine saurosphargid reptile known from the Middle Triassic Guanling Formation of Yunnan and Guizhou Provinces, southwestern China. It contains a single species, ''Sinosaurosphargis yunguiensis''. Discovery ''Saurosphargis'' is known from several individuals, all of which were collected from Member II of the Guanling Formation, dating to the Pelsonian substage of the latest Anisian stage of the early Middle Triassic, about 243 million years ago. The holotype IVPP V 17040 and paratype IVPP V 16076 are housed at the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology in Beijing, and represent a nearly complete articulated skeleton and skull, and a partial disarticulated postcranial skeleton including dorsal vertebra, ribs, with osteoderms and gastral rib fragments, respectively. ZMNH M 8797, an incomplete postcranial skeleton showing a very well preserved right forelimb housed at the Zhejia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryo
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm cell. The resulting fusion of these two cells produces a single-celled zygote that undergoes many cell divisions that produce cells known as blastomeres. The blastomeres (4-cell stage) are arranged as a solid ball that when reaching a certain size, called a morula, (16-cell stage) takes in fluid to create a cavity called a blastocoel. The structure is then termed a blastula, or a blastocyst in mammals. The mammalian blastocyst hatches before implantating into the endometrial lining of the womb. Once implanted the embryo will continue its development through the next stages of gastrulation, neurulation, and organogenesis. Gastrulation is the formation of the three germ layers that will form all of the different parts of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archosauromorpha
Archosauromorpha ( Greek for "ruling lizard forms") is a clade of diapsid reptiles containing all reptiles more closely related to archosaurs (such as crocodilians and dinosaurs, including birds) than to lepidosaurs (such as tuataras, lizards, and snakes). Archosauromorphs first appeared during the late Middle Permian or Late Permian, though they became much more common and diverse during the Triassic period. Although Archosauromorpha was first named in 1946, its membership did not become well-established until the 1980s. Currently Archosauromorpha encompasses four main groups of reptiles: the stocky, herbivorous allokotosaurs and rhynchosaurs, the hugely diverse Archosauriformes, and a polyphyletic grouping of various long-necked reptiles including '' Protorosaurus'', tanystropheids, and '' Prolacerta''. Other groups including pantestudines (turtles and their extinct relatives) and the semiaquatic choristoderes have also been placed in Archosauromorpha by some authors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viviparity
In animals, viviparity is development of the embryo inside the body of the mother, with the maternal circulation providing for the metabolic needs of the embryo's development, until the mother gives birth to a fully or partially developed juvenile that is at least metabolically independent. This is opposed to oviparity, where the embryos develop independently outside the mother in eggs until they are developed enough to break out as hatchlings; and ovoviviparity, where the embryos are developed in eggs that remain carried inside the mother's body until the hatchlings emerge from the mother as juveniles, similar to a live birth. Etymology The term "viviparity" and its adjective form "viviparous" both derive from the Latin ''vivus'', meaning "living"; and ''pario'', meaning "give birth to". Reproductive mode Five modes of reproduction have been differentiated in animals based on relations between zygote and parents. The five include two nonviviparous modes: ovulipari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wumengosaurus
''Wumengosaurus'' is an extinct aquatic reptile from the Middle Triassic (late Anisian stage) Guanling Formation of Guizhou, southwestern China. It was originally described as a basal eosauropterygian and usually is recovered as such by phylogenetic analyses, although one phylogeny has placed it as the sister taxon to Ichthyosauromorpha while refraining from a formal re-positioning. It was a relatively small reptile, measuring in total body length. In 2021, Qin ''et al''. described an additional specimen from Guizhou ( Panzhou District) as a new species of ''Wumengosaurus'', ''W. rotundicarpus''. Classification In the 2023 description of '' Luopingosaurus'', Xu ''et al''. recovered ''Wumengosaurus'' as a derived pachypleurosaurid, as the sister taxon to the clade formed by ''Luopingosaurus'' and ''Honghesaurus''. The results of their phylogenetic analyses are shown in the cladogram A cladogram (from Greek language, Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |