|
Dimartinia
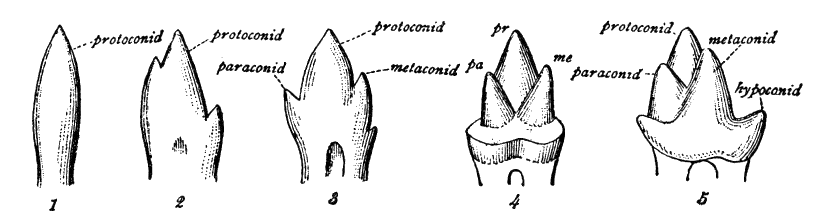
''Dimartinia'' (after Vicente Di Martino) is an extinct genus of carnivorous metatherian mammals from the Late Miocene Cerro Azul Formation of Argentina. The genus contains a single species, ''D. pristina'', known from a left mandible and teeth. ''Dimartinia'' is a primitive member of the Thylacosmiliformes, a group also containing the saber toothed thylacosmilids. Discovery and naming The ''Dimartinia'' holotype specimen, MMH-CH 87-7-111, was discovered in sediments of the Cerro Azul Formation ('Arroyo Chasicó' locality) in Buenos Aires Province, Argentina. The specimen consists of a left dentary and its associated teeth (partial canine, first–third premolars, and first–fourth molars). In 2025, Suarez et al. described ''Dimartinia pristina'' as a new genus and species of metatherian mammals based on these fossil remains. The generic name, ''Dimartinia'', honors Vicente Di Martino, the collector of the holotype and founder of the museum where the specimen is acces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thylacosmiliformes
Thylacosmiliformes is an extinct clade of predatory metatherian mammals in the order Sparassodonta, related to the marsupials. Members of this clade are known from the Miocene and Pliocene epochs of South America (Argentina, Colombia, and Uruguay). The most notable thylacosmiliforms, such as ''Thylacosmilus'', comprise the more exclusive family Thylacosmilidae and have prominent saber teeth. The clade was defined in 2025 to include thylacosmilids and their more " primitive" closest relatives such as ''Dimartinia''. Description Members of the Thylacosmiliformes are characterized by several anatomical features of the mandible and teeth. These include the presence of two or fewer lower incisors, a lower canine that is compressed laterally, a small or absent first premolar, and an expanded symphyseal region of the dentary's anterior horizontal ramus. Classification In their 2025 description of ''Dimartinia'', Suarez et al. performed a phylogenetic analysis to determine its po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerro Azul Formation
The Cerro Azul Formation (), also described as Epecuén Formation, is a formation (geology), geological formation of Late Miocene (Tortonian, or Huayquerian in the South American land mammal age, SALMA classification) age in the Colorado Basin, Argentina, Colorado Basin of the Buenos Aires Province, Buenos Aires and La Pampa Provinces in northeastern Argentina.Cerro Azul Formation in the Paleobiology DatabaseEpecuén Formation in the Paleobiology Database The fluvial and aeolian processes, aeolian siltstones, sandstones and tuffs of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2025 In Paleomammalogy
This article records new taxa of fossil mammals of every kind that are scheduled to be described during the year 2025, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to paleontology of mammals that are scheduled to occur in the year 2025. Afrotherians Proboscideans Proboscidean research * Dooley et al. (2025) reevaluate the affinities of mastodon fossil material from Oregon and Washington (United States), Alberta (Canada) and Hidalgo and Jalisco (Mexico), extending known geographical range of ''Mammut pacificus'', and providing probable evidence of presence of both ''M. pacificus'' and ''M. americanum'' in close geographical proximity. * Jukar, Millhouse & Carrano (2025) revise the fossil material attributed to '' Amebelodon floridanus'', assign a neotype specimen of this species and support its placement in the genus ''Amebelodon''. * Luna et al. (2025) study mandibular lesions in two specimens of ''Notiomastodon platensis'' from the Pleistocene strata from Argenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Miocene
The Late Miocene (also known as Upper Miocene) is a sub-epoch of the Miocene epoch (geology), Epoch made up of two faunal stage, stages. The Tortonian and Messinian stages comprise the Late Miocene sub-epoch, which lasted from 11.63 Ma (million years ago) to 5.333 Ma. The evolution of ''Homo'' The gibbons (family Hylobatidae) and orangutans (genus ''Pongo'') were the first groups to split from the line leading to the hominins, including humans, then gorillas (genus ''Gorilla''), and finally chimpanzees and bonobos (genus ''Pan (genus), Pan''). The splitting date between hominin and chimpanzee lineages is placed by some between 4 and 8 million years ago, that is, during the Late Miocene. References External links GeoWhen Database - Late Miocene Miocene, .03 Miocene geochronology, 03 Messinian, * Tortonian, * {{geochronology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species Description
A species description is a formal scientific description of a newly encountered species, typically articulated through a scientific publication. Its purpose is to provide a clear description of a new species of organism and explain how it differs from species that have been previously described or related species. For a species to be considered valid, a species description must follow established guidelines and naming conventions dictated by relevant nomenclature codes. These include the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) for animals, the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN) for plants, and the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) for viruses. A species description often includes photographs or other illustrations of type material and information regarding where this material is deposited. The publication in which the species is described gives the new species a formal scientific name. Some 1.9 million ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. Phylogeneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Name (zoology)
In zoological nomenclature, the specific name (also specific epithet, species epithet, or epitheton) is the second part (the second name) within the scientific name of a species (a binomen). The first part of the name of a species is the name of the genus or the generic name. The rules and regulations governing the giving of a new species name are explained in the article species description. For example, the scientific name for humans is ''Homo sapiens'', which is the species name, consisting of two names: ''Homo'' is the " generic name" (the name of the genus) and ''sapiens'' is the "specific name". Etymology Historically, ''specific name'' referred to the combination of what are now called the generic and specific names. Carl Linnaeus, who formalized binomial nomenclature, made explicit distinctions between specific, generic, and trivial names. The generic name was that of the genus, the first in the binomial, the trivial name was the second name in the binomial, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, Latin influence in English, including English, having contributed List of Latin words with English derivatives, many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianity in Anglo-Saxon England, Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin Root (linguistics), roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names, the sciences, List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes, medicine, and List of Latin legal terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thylacosmilid
Thylacosmilidae is an extinct family of metatherian predators, related to the modern marsupials, which lived in South America between the Miocene and Pliocene epochs. Like other South American mammalian predators that lived prior to the Great American Biotic Interchange, these animals belonged to the order Sparassodonta, which occupied the ecological niche of many eutherian mammals of the order Carnivora from other continents. The family's most notable feature are the elongated, laterally flattened fangs, which is a remarkable evolutionary convergence with other saber-toothed mammals like '' Barbourofelis'' and ''Smilodon''. Taxonomic history The family Thylacosmilidae was originally erected by Riggs in 1933, to accommodate '' Thylacosmilus'', found in the Pliocene Brochero Formation of Argentina. Later, the family was demoted to a subfamily, as Thylacosmilinae, within Borhyaenidae, a group of superficially canid-like sparassodonts, under the assumption that ''Thylacosmilus' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesion
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by injury or diseases. The term ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin meaning "injury". Lesions may occur in both plants and animals. Types There is no designated classification or naming convention for lesions. Because lesions can occur anywhere in the body and their definition is so broad, the varieties of lesions are virtually endless. Generally, lesions may be classified by their patterns, sizes, locations, or causes. They can also be named after the person who discovered them. For example, Ghon lesions, which are found in the lungs of those with tuberculosis, are named after the lesion's discoverer, Anton Ghon. The characteristic skin lesions of a varicella zoster virus infection are called '' chickenpox''. Lesions of the teeth are usually called dental caries, or "cavities". Location Lesions are often classified by their tissue types or locations. For example, "skin lesions" or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Locality (biology)
In biology, a type is a particular wikt:en:specimen, specimen (or in some cases a group of specimens) of an organism to which the scientific name of that organism is formally associated. In other words, a type is an example that serves to anchor or centralizes the defining features of that particular taxon. In older usage (pre-1900 in botany), a type was a taxon rather than a specimen. A taxon is a scientifically named grouping of organisms with other like organisms, a set (mathematics), set that includes some organisms and excludes others, based on a detailed published description (for example a species description) and on the provision of type material, which is usually available to scientists for examination in a major museum research collection, or similar institution. Type specimen According to a precise set of rules laid down in the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) and the ''International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants'' (ICN), the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molar (tooth)
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone tooth", from ''mola'', millstone and ''dens'', tooth. Molars show a great deal of diversity in size and shape across the mammal groups. The third molar of humans is sometimes vestigial. Human anatomy In humans, the molar teeth have either four or five cusps. Adult humans have 12 molars, in four groups of three at the back of the mouth. The third, rearmost molar in each group is called a wisdom tooth. It is the last tooth to appear, breaking through the front of the gum at about the age of 20, although this varies among individuals and populations, and in many cases the tooth is missing. The human mouth contains upper (maxillary) and lower (mandibular) molars. They are: maxillary first molar, maxillary second molar, maxillary third mol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |