|
Diimine
Diimines are organic compounds containing two imine (RCH=NR') groups. Common derivatives are 1,2-diimines and 1,3-diimines. These compounds are used as ligands, but they are also precursors to other organic compounds. Preparation Diimines are prepared by condensation reactions where a dialdehyde or diketone is treated with amine and water is eliminated. Many are derived from the condensation of 1,2-diketones and dialdehydes with amines, often anilines. The dialdehyde glyoxal is an especially common precursor. Similar methods are used to prepare Schiff bases and oximes. 1,2-Diimines The 1,2-diimines are also called α-diimines and 1,4-diazabutadienes. An example is glyoxal-bis(mesitylimine), a yellow solid that is synthesized by condensation of 2,4,6-trimethylaniline and glyoxal. 2,2'-Bipyridine is a 1,2-diimine. 1,2-Diketimines are “ non-innocent ligands”, akin to the dithiolenes. : 1,3-Diimines For example, acetylacetone (2,4-pentanedione) and a primary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2,4,6-trimethylaniline
2,4,6-Trimethylaniline is an organic compound with formula (CH3)3C6H2NH2. It is an aromatic amine that is of commercial interest as a precursor to dyes. It is prepared by selective nitration of mesitylene, avoiding oxidation of the methyl groups, followed by reduction of the resulting nitro group to the aniline. Coordination chemistry Trimethylaniline is a building block to a variety of bulky ligands. Condensation with glyoxal gives the 1,2-diimine ligands. An example is glyoxal-bis(mesitylimine), a yellow solid that is synthesized by condensation of 2,4,6-trimethylaniline and glyoxal. The diimine is a useful precursor to popular NHC ligands including IMes.Elon A. Ison, Ana Ison "Synthesis of Well-Defined Copper N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes and Their Use as Catalysts for a “Click Reaction”: A Multistep Experiment That Emphasizes the Role of Catalysis in Green Chemistry" J. Chem. Educ., 2012, volume 89, pp 1575–1577. N-heterocyclic carbenes, as found in 2nd generation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-innocent Ligand
In chemistry, a (redox) non-innocent ligand is a ligand in a metal complex where the oxidation state is not clear. Typically, complexes containing non-innocent ligands are redox active at mild potentials. The concept assumes that redox reactions in metal complexes are either metal or ligand localized, which is a simplification, albeit a useful one. C.K. Jørgensen first described ligands as "innocent" and "suspect": "Ligands are innocent when they allow oxidation states of the central atoms to be defined. The simplest case of a suspect ligand is NO..." Redox reactions of complexes of innocent vs. non-innocent ligands Conventionally, redox reactions of coordination complexes are assumed to be metal-centered. The reduction of MnO4− to MnO42− is described by the change in oxidation state of manganese from +7 to +6. The oxide ligands do not change in oxidation state, remaining −2. Oxide is an innocent ligand. Another example of conventional metal-centered redox couple i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-metallocene Catalyst
A post-metallocene catalyst is a kind of catalyst for the polymerization of olefins, i.e., the industrial production of some of the most common plastics. "Post-metallocene" refers to a class of homogeneous catalysts that are not metallocenes. This area has attracted much attention because the market for polyethylene, polypropylene, and related copolymers is large. There is a corresponding intense market for new processes as indicated by the fact that, in the US alone, 50,000 patents were issued between 1991-2007 on polyethylene and polypropylene. Many methods exist to polymerize alkenes, including the traditional routes using Philips catalyst and traditional heterogeneous Ziegler-Natta catalysts, which still are used to produce the bulk of polyethylene. Catalysts based on early transition metals File:VersifyCats.png, Generic structure of a post-metallocene catalyst based on Dow's pyridyl-amido design. File:Zirconium bisanionic.png, Early examples of postmetallocene catalysts in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NacNac
NacNac is a class of anionic bidentate ligands. 1,3-Diketimines are often referred to as "HNacNac", a modification of the abbreviation Hacetylacetone, acac used for 1,3-diketones. These species can exist as a mixture of tautomers. Preparation of ligands and complexes Acetylacetone and related 1,3-diketones Condensation reaction, condense with primary alkyl- or arylamines resulting in replacement of the carbonyl oxygen atoms with NR groups, where R = aryl, alkyl. To prepare 1,3-diketimines from Steric effects, bulky amines, e.g. 2,4,6-Trimethylaniline, 2,4,6-trimethylanilines, prolonged reaction times are required. 2,6-Diisopropylaniline is a common bulky building block. Deprotonation of HNacNac compounds affords anionic bidentate ligands that form a variety of coordination complexes. Some derivatives with large Side chain, R groups can be used to stabilize low valent p-block, main group and transition metal complexes. Unlike the situation for the acetylacetonates, the steric pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diiminopyridine Synthesis
Diiminopyridines (DIP, also known a pyridine diimines, PDIs) are a class of diimine ligands. They featuring a pyridine nucleus with imine sidearms appended to the 2,6–positions. The three nitrogen centres bind metals in a tridentate fashion, forming pincer complexes. Diiminopyridines are notable as non-innocent ligand that can assume more than one oxidation state. Complexes of DIPs participate in a range of chemical reactions, including ethylene polymerization, hydrosilylation, and hydrogenation. Synthesis and properties of DIP ligands Many DIPs have been prepared. They are synthesized by Schiff base condensation of commercially available 2,6-diacetylpyridine or 2,6-diformylpyridine with two equivalents of substituted anilines. Using substituted anilines, complexes one can obtain DIPs with diverse steric environments. Commonly used bulky anilines are 2,4,6-trimethylaniline and 2,6-Diisopropylaniline, 2,6-diisopropylaniline. Unsymmetric variations have been established by success ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glyoxal-bis(mesitylimine)
Glyoxal-bis(mesitylimine) is an organic compound with the formula H2C2(NC6H2Me3)2 (Me = methyl). It is a yellow solid that is soluble in organic solvents. It is classified as a diimine ligand. It is used in coordination chemistry and homogeneous catalysis. It is synthesized by condensation of 2,4,6-Trimethylaniline, 2,4,6-trimethylaniline and glyoxal. In addition to its direct use as a ligand, it is a precursor to imidazole precursors to the popular NHC ligand called IMes. Related compounds *Glyoxal-bis(triisopropylphenylimine), which is bulkier than glyoxal-bis(mesitylimine). {{cite journal, title=Late-Stage Deoxyfluorination of Phenols with PhenoFluorMix, first1=Junting, last1=Chen, first2=Tobias, last2=Ritter, journal=Org. Synth. , year=2019, volume=96, page=16, doi=10.15227/orgsyn.096.0016, doi-access=free References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diketone
In organic chemistry, a dicarbonyl is a molecule containing two carbonyl () groups. Although this term could refer to any organic compound containing two carbonyl groups, it is used more specifically to describe molecules in which both carbonyls are in close enough proximity that their reactivity is changed, such as 1,2-, 1,3-, and 1,4-dicarbonyls. Their properties often differ from those of monocarbonyls, and so they are usually considered functional groups of their own. These compounds can have symmetrical or unsymmetrical substituents on each carbonyl, and may also be functionally symmetrical (dialdehydes, diketones, diesters, ''etc.'') or unsymmetrical (keto-esters, keto-acids, ''etc.''). 1,2-Dicarbonyls 1,2-Dialdehyde The only 1,2-dialdehyde is glyoxal, . Like many alkyldialdehydes, glyoxal is encountered almost exclusively as its hydrate and oligomers thereof. These derivatives often behave equivalently to the aldehydes since hydration is reversible. Glyoxal condenses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
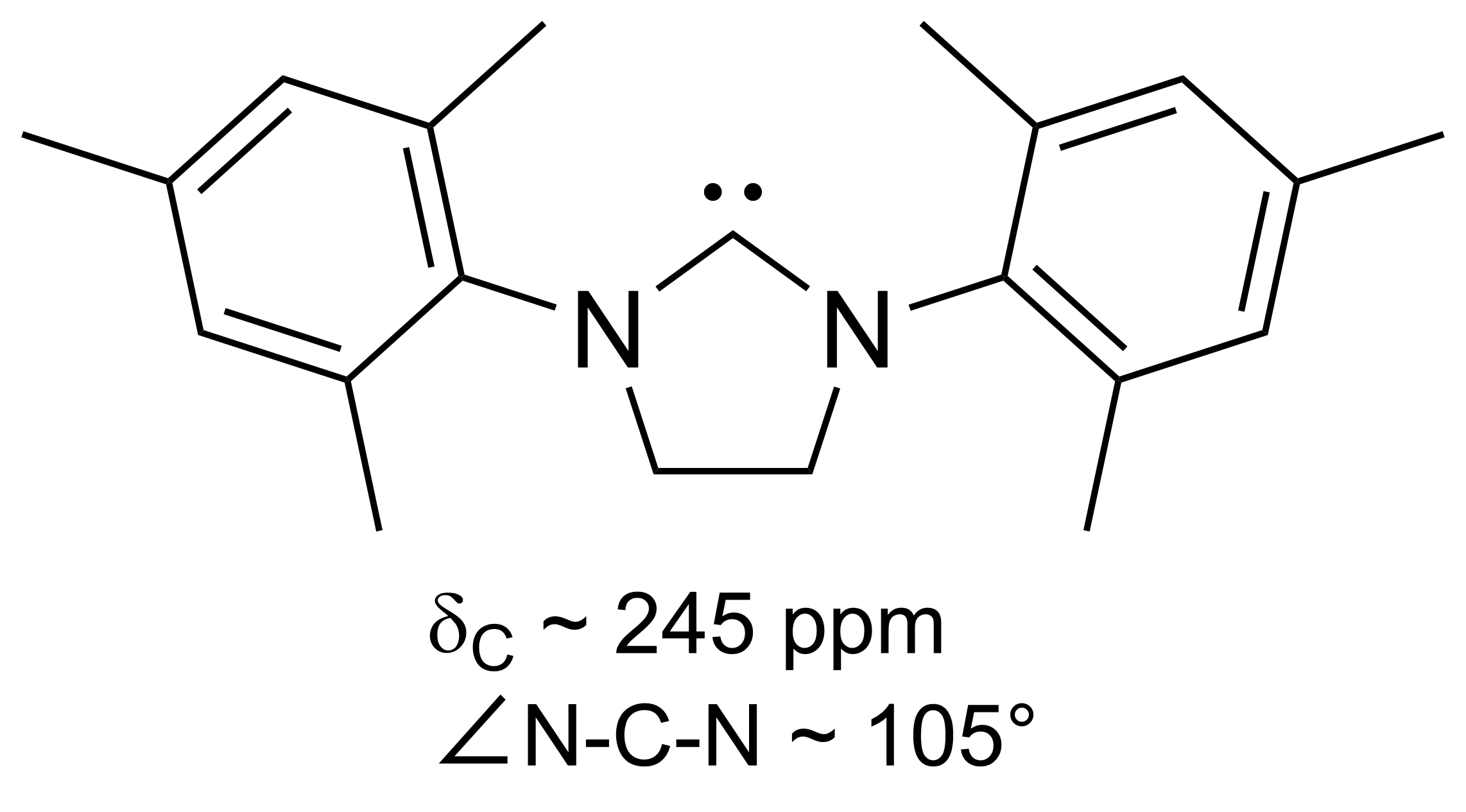
NHC Ligand
A persistent carbene (also known as stable carbene) is an organic molecule whose natural resonance structure has a carbon atom with incomplete octet (a carbene), but does not exhibit the tremendous instability typically associated with such moieties. The best-known examples and by far largest subgroup are the ''N''-heterocyclic carbenes (NHC) (sometimes called Arduengo carbenes), in which nitrogen atoms flank the formal carbene. Modern theoretical analysis suggests that the term "persistent carbene" is in fact a misnomer. Persistent carbenes do not in fact have a carbene electronic structure in their ground state, but instead an ylide stabilized by aromatic resonance or steric shielding. Excitation to a carbene structure then accounts for the carbene-like dimerization that some persistent carbenes undergo over the course of days. Persistent carbenes in general, and Arduengo carbenes in particular, are popular ligands in organometallic chemistry. History Early evidence In 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Reviews
''Chemical Reviews'' is peer-reviewed scientific journal published twice per month by the American Chemical Society. It publishes review articles on all aspects of chemistry. It was established in 1924 by William Albert Noyes (University of Illinois). The editor-in-chief is Sharon Hammes-Schiffer. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in Chemical Abstracts Service, CAB International, EBSCOhost, ProQuest, PubMed, Scopus, and the Science Citation Index. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2023 impact factor of 51.4. Journal ranking summary Based on the latest announced rankings, ''Chemical Reviews'' is positioned among the top journals in the field of chemistry across multiple citation databases. The following table summarizes its performance across Scopus and Web of Science. Journal ranking summary (2023)JRank: Chemical Reviewshttps://jrank.net/journals/chem-rev/metrics/ref> See also * Accounts of Chemical Research ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymerization
In polymer chemistry, polymerization (American English), or polymerisation (British English), is a process of reacting monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to form polymer chains or three-dimensional networks. There are many forms of polymerization and different systems exist to categorize them. In chemical compounds, polymerization can occur via a variety of reaction mechanisms that vary in complexity due to the functional groups present in the reactants and their inherent steric effects. In more straightforward polymerizations, alkenes form polymers through relatively simple radical reactions; in contrast, reactions involving substitution at a carbonyl group require more complex synthesis due to the way in which reactants polymerize. As alkenes can polymerize in somewhat straightforward radical reactions, they form useful compounds such as polyethylene and polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which are produced in high tonnages each year due to their usefulnes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetylacetone
Acetylacetone is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is classified as a 1,3-diketone. It exists in equilibrium with a tautomer . The mixture is a colorless liquid. These tautomers interconvert so rapidly under most conditions that they are treated as a single compound in most applications. Acetylacetone is a building block for the synthesis of many coordination complexes as well as heterocyclic compounds. Properties Tautomerism The Keto–enol tautomerism, keto and enol tautomers of acetylacetone coexist in solution. The enol form has C2v molecular symmetry, symmetry, meaning the hydrogen atom is shared equally between the two oxygen atoms. In the gas phase, the equilibrium constant, ''K''keto→enol, is 11.7, favoring the enol form. The two tautomeric forms can be distinguished by NMR spectroscopy, IR spectroscopy and other methods. The equilibrium constant tends to be high in nonpolar solvents; when ''K''keto→enol is equal or greater than 1, the enol form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Margin General Synth No English
Margin may refer to: Physical or graphical edges *Margin (typography), the white space that surrounds the content of a page *Continental margin, the zone of the ocean floor that separates the thin oceanic crust from thick continental crust *Leaf margin, the edge of a leaf *Resection margin, the tissue near a tumor that is removed to ensure that no cancer cells are left behind Economics and finance * Margin of profit, the fraction of revenue that is left after paying expenses * Margin (economics), a set of constraints conceptualised as a border *Margin (finance), a type of financial collateral used to cover credit risk *Contribution margin *Gross margin Figurative edges *Margin (machine learning), the distance between a decision boundary and a data point *Marginal frequency distribution, in statistics ( Frequency distribution § Joint frequency distributions) Other uses * ''Margins'' (film), a 2022 Italian film by Niccolò Falsetti * ''The Margin'' (album), a 1985 album by Peter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |