|
Differential Rotation
Differential rotation is seen when different parts of a rotating object move with different angular velocities (or rates of rotation) at different latitudes and/or depths of the body and/or in time. This indicates that the object is not rigid. In fluid objects, such as accretion disks, this leads to shearing. Galaxies and protostars usually show differential rotation; examples in the Solar System include the Sun, Jupiter and Saturn. Around the year 1610, Galileo Galilei observed sunspots and calculated the rotation of the Sun. In 1630, Christoph Scheiner reported that the Sun had different rotational periods at the poles and at the equator, in good agreement with modern values. Cause Stars and planets rotate in the first place because conservation of angular momentum turns random drifting of parts of the molecular cloud that they form from into rotating motion as they coalesce. Given this average rotation of the whole body, internal differential rotation is caused by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angular Velocity
In physics, angular velocity (symbol or \vec, the lowercase Greek letter omega), also known as the angular frequency vector,(UP1) is a pseudovector representation of how the angular position or orientation of an object changes with time, i.e. how quickly an object rotates (spins or revolves) around an axis of rotation and how fast the axis itself changes direction. The magnitude of the pseudovector, \omega=\, \boldsymbol\, , represents the '' angular speed'' (or ''angular frequency''), the angular rate at which the object rotates (spins or revolves). The pseudovector direction \hat\boldsymbol=\boldsymbol/\omega is normal to the instantaneous plane of rotation or angular displacement. There are two types of angular velocity: * Orbital angular velocity refers to how fast a point object revolves about a fixed origin, i.e. the time rate of change of its angular position relative to the origin. * Spin angular velocity refers to how fast a rigid body rotates around a f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservation Of Angular Momentum
Angular momentum (sometimes called moment of momentum or rotational momentum) is the rotational analog of Momentum, linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity because it is a Conservation law, conserved quantity – the total angular momentum of a closed system remains constant. Angular momentum has both a direction (geometry), direction and a magnitude, and both are conserved. Bicycle and motorcycle dynamics, Bicycles and motorcycles, flying discs, Rifling, rifled bullets, and gyroscopes owe their useful properties to conservation of angular momentum. Conservation of angular momentum is also why hurricanes form spirals and neutron stars have high rotational rates. In general, conservation limits the possible motion of a system, but it does not uniquely determine it. The three-dimensional angular momentum for a point particle is classically represented as a pseudovector , the cross product of the particle's position vector (relative to some origin) and its mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giovanni Domenico Cassini
Giovanni Domenico Cassini (8 June 1625 – 14 September 1712) was an Italian-French mathematician, astronomer, astrologer and engineer. Cassini was born in Perinaldo, near Imperia, at that time in the County of Nice, part of the Savoyard state. He discovered four satellites of Saturn (planet), Saturn and noted the division of its rings, later named the Cassini Division. Cassini was also the first of his family to begin work on the project of creating a topographic map of France. In addition, he also created the first scientific map of the Moon. The Cassini–Huygens, ''Cassini'' space probe, launched in 1997, was named after him and became the fourth to visit Saturn and the first to orbit it. Life Time in Italy Cassini was the son of Jacopo Cassini, a Tuscan, and Giulia Crovesi. In 1648 Cassini accepted a position at the observatory at :it:Panzano, Castelfranco Emilia, Panzano (Castelfranco Emilia), near Bologna, to work with Marquis Cornelio Malvasia, a rich amateur astron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tachocline
The tachocline is the transition region of stars of more than 0.3 solar masses, between the radiative interior and the differentially rotating outer convective zone. This causes the region to have a very large shear as the rotation rate changes very rapidly. The convective exterior rotates as a normal fluid with differential rotation with the poles rotating slowly and the equator rotating quickly. The radiative interior exhibits solid-body rotation, possibly due to a fossil field. The rotation rate through the interior is roughly equal to the rotation rate at mid-latitudes, i.e. in-between the rate at the slow poles and the fast equator. Recent results from helioseismology indicate that the tachocline is located at a radius of at most 0.70 times the solar radius (measured from the core, i.e., the surface is at 1 solar radius), with a thickness of 0.04 times the solar radius. This would mean the area has a very large shear profile that is one way that large scale magnetic fiel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heliographic Latitude
In solar observation and imaging, coordinate systems are used to identify and communicate locations on and around the Sun. The Sun is made of plasma, so there are no permanent demarcated points that can be referenced. Background The Sun is a rotating sphere of plasma at the center of the Solar System. It lacks a solid or liquid surface, so the interface separating its interior and its exterior is usually defined as the boundary where plasma becomes opaque to visible light, the photosphere. Since plasma is gaseous in nature, this surface has no permanent demarcated points that can be used for reference. Furthermore, its rate of rotation varies with latitude, rotating faster at the equator than at the poles. Cardinal directions In observations of the solar disk, cardinal directions are typically defined so that the Sun's northern and southern hemispheres point toward Earth's northern and southern celestial poles, respectively, and the Sun's eastern and western hemispheres point ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doppler-shifted
The Doppler effect (also Doppler shift) is the change in the frequency of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the source of the wave. The ''Doppler effect'' is named after the physicist Christian Doppler, who described the phenomenon in 1842. A common example of Doppler shift is the change of pitch (music), pitch heard when a vehicle sounding a horn approaches and recedes from an observer. Compared to the emitted frequency, the received frequency is higher during the approach, identical at the instant of passing by, and lower during the recession. When the source of the sound wave is moving towards the observer, each successive cycle of the wave is emitted from a position closer to the observer than the previous cycle. Hence, from the observer's perspective, the time between cycles is reduced, meaning the frequency is increased. Conversely, if the source of the sound wave is moving away from the observer, each cycle of the wave is emitted from a position ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
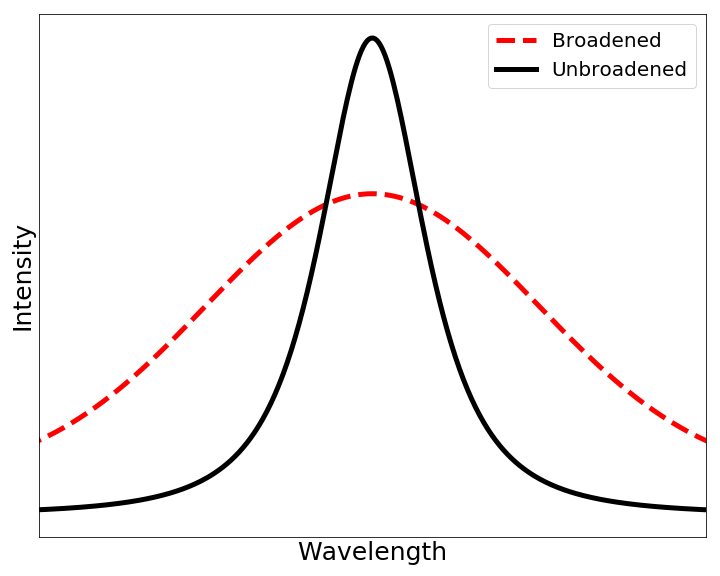
Doppler Broadening
In atomic physics, Doppler broadening is broadening of spectral lines due to the Doppler effect caused by a distribution of velocities of atoms or molecules. Different velocities of the emitting (or absorbing) particles result in different Doppler shifts, the cumulative effect of which is the emission (absorption) line broadening. This resulting line profile is known as a Doppler profile. A particular case is the thermal Doppler broadening due to the thermal motion of the particles. Then, the broadening depends only on the frequency of the spectral line, the mass of the emitting particles, and their temperature, and therefore can be used for inferring the temperature of an emitting (or absorbing) body being spectroscopically investigated. Derivation (non-relativistic case) When a particle moves (e.g., due to the thermal motion) towards the observer, the emitted radiation is shifted to a higher frequency. Likewise, when the emitter moves away, the frequency is lowered. In th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Cycle
The Solar cycle, also known as the solar magnetic activity cycle, sunspot cycle, or Schwabe cycle, is a periodic 11-year change in the Sun's activity measured in terms of Modern Maximum, variations in the number of observed sunspots on the Sun's surface. Over the period of a solar cycle, levels of solar radiation and ejection of solar material, the number and size of sunspots, solar flares, and coronal loops all exhibit a synchronized fluctuation from a Solar minimum, period of minimum activity to a Solar maximum, period of a maximum activity back to a period of minimum activity. The magnetic field of the Sun flips during each solar cycle, with the flip occurring when the solar cycle is near its maximum. After two solar cycles, the Sun's magnetic field returns to its original state, completing what is known as a Hale cycle. This cycle has been observed for centuries by changes in the Sun's appearance and by terrestrial phenomena such as aurora but was not clearly identified un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunspot
Sunspots are temporary spots on the Sun's surface that are darker than the surrounding area. They are one of the most recognizable Solar phenomena and despite the fact that they are mostly visible in the solar photosphere they usually affect the entire solar atmosphere. They are regions of reduced surface temperature caused by concentrations of magnetic flux that inhibit convection. Sunspots appear within active regions, usually in pairs of opposite magnetic polarity. Their number varies according to the approximately 11-year solar cycle. Individual sunspots or groups of sunspots may last anywhere from a few days to a few months, but eventually decay. Sunspots expand and contract as they move across the surface of the Sun, with diameters ranging from to . Larger sunspots can be visible from Earth without the aid of a telescope. They may travel at relative speeds, or proper motions, of a few hundred meters per second when they first emerge. Indicating intense magneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultra-cool Dwarf
An ultra-cool dwarf is a stellar or sub-stellar object that has an effective temperature lower than . This category of dwarf stars was introduced in 1997 by J. Davy Kirkpatrick, Todd J. Henry, and Michael J. Irwin. It originally included very low mass M-dwarf stars with spectral types of M7 but was later expanded to encompass stars ranging from the coldest known to brown dwarfs as cool as spectral type T6.5. Altogether, ultra-cool dwarfs represent about 15% of the astronomical objects in the stellar neighborhood of the Sun. One of the best known examples is TRAPPIST-1. Models of the formation of planets suggest that due to their low masses and the small size of their proto-planetary disks, these stars could host a relatively abundant population of terrestrial planets ranging from Mercury-sized to Earth-sized bodies, rather than a population of super-Earths and Jupiter-massed planets. The discovery of the TRAPPIST-1 planetary system, consisting of seven Earth-sized planets, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourier Transforms
In mathematics, the Fourier transform (FT) is an integral transform that takes a function (mathematics), function as input then outputs another function that describes the extent to which various Frequency, frequencies are present in the original function. The output of the transform is a complex number, complex-valued function of frequency. The term ''Fourier transform'' refers to both this complex-valued function and the Operation (mathematics), mathematical operation. When a distinction needs to be made, the output of the operation is sometimes called the frequency domain representation of the original function. The Fourier transform is analogous to decomposing the sound of a musical Chord (music), chord into the sound intensity, intensities of its constituent Pitch (music), pitches. Functions that are localized in the time domain have Fourier transforms that are spread out across the frequency domain and vice versa, a phenomenon known as the #Uncertainty principle, uncerta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helioseismology
Helioseismology is the study of the structure and dynamics of the Sun through its oscillations. These are principally caused by sound waves that are continuously driven and damped by convection near the Sun's surface. It is similar to geoseismology, or asteroseismology, which are respectively the studies of the Earth or stars through their oscillations. While the Sun's oscillations were first detected in the early 1960s, it was only in the mid-1970s that it was realized that the oscillations propagated throughout the Sun and could allow scientists to study the Sun's deep interior. The term was coined by Douglas Gough in the 90s. The modern field is separated into global helioseismology, which studies the Sun's resonant modes directly, and local helioseismology, which studies the propagation of the component waves near the Sun's surface. Helioseismology has contributed to a number of scientific breakthroughs. The most notable was to show that the anomaly in the predicted neutri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |