|
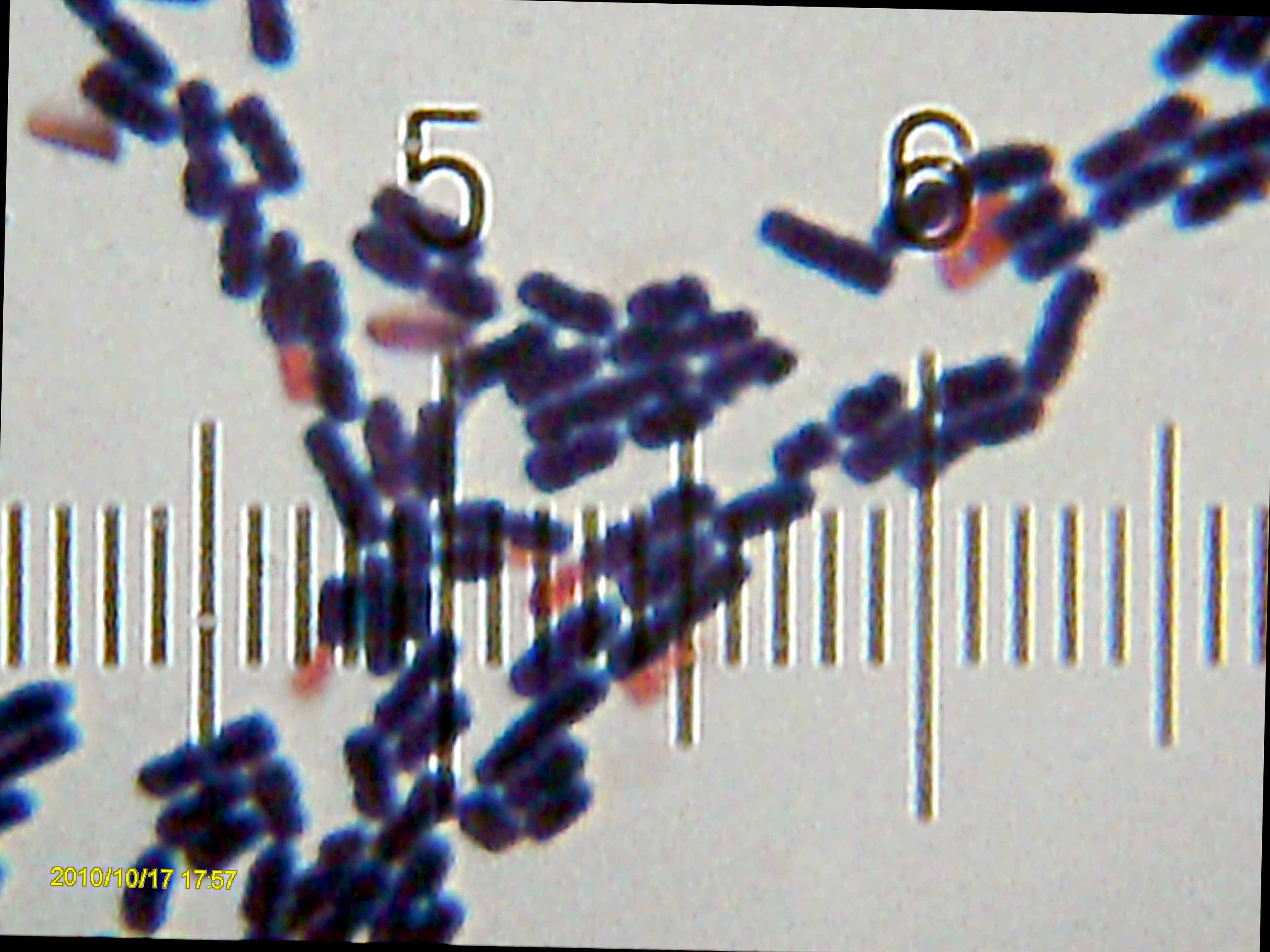
Dietzia Natronolimnaea
''Dietzia natronolimnaea'' is an alkaliphilic, aerobic, organotrophic An organotroph is an organism that obtains hydrogen or electrons from organic substrates. This term is used in microbiology to classify and describe organisms based on how they obtain electrons for their respiration processes. Some organotrophs su ... bacteria, with type strain 15LN1 (= CBS 107.95). References Further reading *Sneath, Peter HA, et al. Bergey's manual of systematic bacteriology. Volume 5. Williams & Wilkins, 2012. *Koerner, Roland J., Michael Goodfellow, and Amanda L. Jones. "The genus Dietzia: a new home for some known and emerging opportunist pathogens."FEMS Immunology & Medical Microbiology 55.3 (2009): 296–305. * * External links *LPSN [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaliphilic
Alkaliphiles are a class of extremophilic microbes capable of survival in alkaline ( pH roughly 8.5–11) environments, growing optimally around a pH of 10. These bacteria can be further categorized as obligate alkaliphiles (those that require high pH to survive), facultative alkaliphiles (those able to survive in high pH, but also grow under normal conditions) and haloalkaliphiles (those that require high salt content to survive).HORIKOSHI, KOKI. "Alkaliphiles: Some Applications of Their Products for Biotechnology." MICROBIOLOGY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY REVIEWS 63.4 (1999): 735-50. Print. Background information Microbial growth in alkaline conditions presents several complications to normal biochemical activity and reproduction, as high pH is detrimental to normal cellular processes. For example, alkalinity can lead to denaturation of DNA, instability of the plasma membrane and inactivation of cytosolic enzymes, as well as other unfavorable physiological changes.Higashibata, Akir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organotrophic
An organotroph is an organism that obtains hydrogen or electrons from organic substrates. This term is used in microbiology to classify and describe organisms based on how they obtain electrons for their respiration processes. Some organotrophs such as animals and many bacteria, are also heterotrophs. Organotrophs can be either anaerobic or aerobic. Antonym: Lithotroph, Adjective: Organotrophic. History The term was suggested in 1946 by Lwoff and collaborators.Lwoff, A., C.B. van Niel, P.J. Ryan, and E.L. Tatum (1946). Nomenclature of nutritional types of microorganisms. ''Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology'' (5th edn.), Vol. XI, The Biological Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, pp. 302–303 See also * Autotroph * Chemoorganotroph * Primary nutritional groups Primary nutritional groups are groups of organisms, divided in relation to the nutrition mode according to the sources of energy and carbon, needed for living, growth and reproduction. The sources of e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycobacteriales
The Mycobacteriales are an order of bacteria. Phylogeny The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) is an online database that maintains information on the naming and taxonomy Taxonomy is the practice and science of categorization or classification. A taxonomy (or taxonomical ... (LPSN). The phylogeny is based on whole-genome analysis. References Actinomycetia Bacteria orders {{actinobacteria-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |