|
Dicroidium Zuberi 2
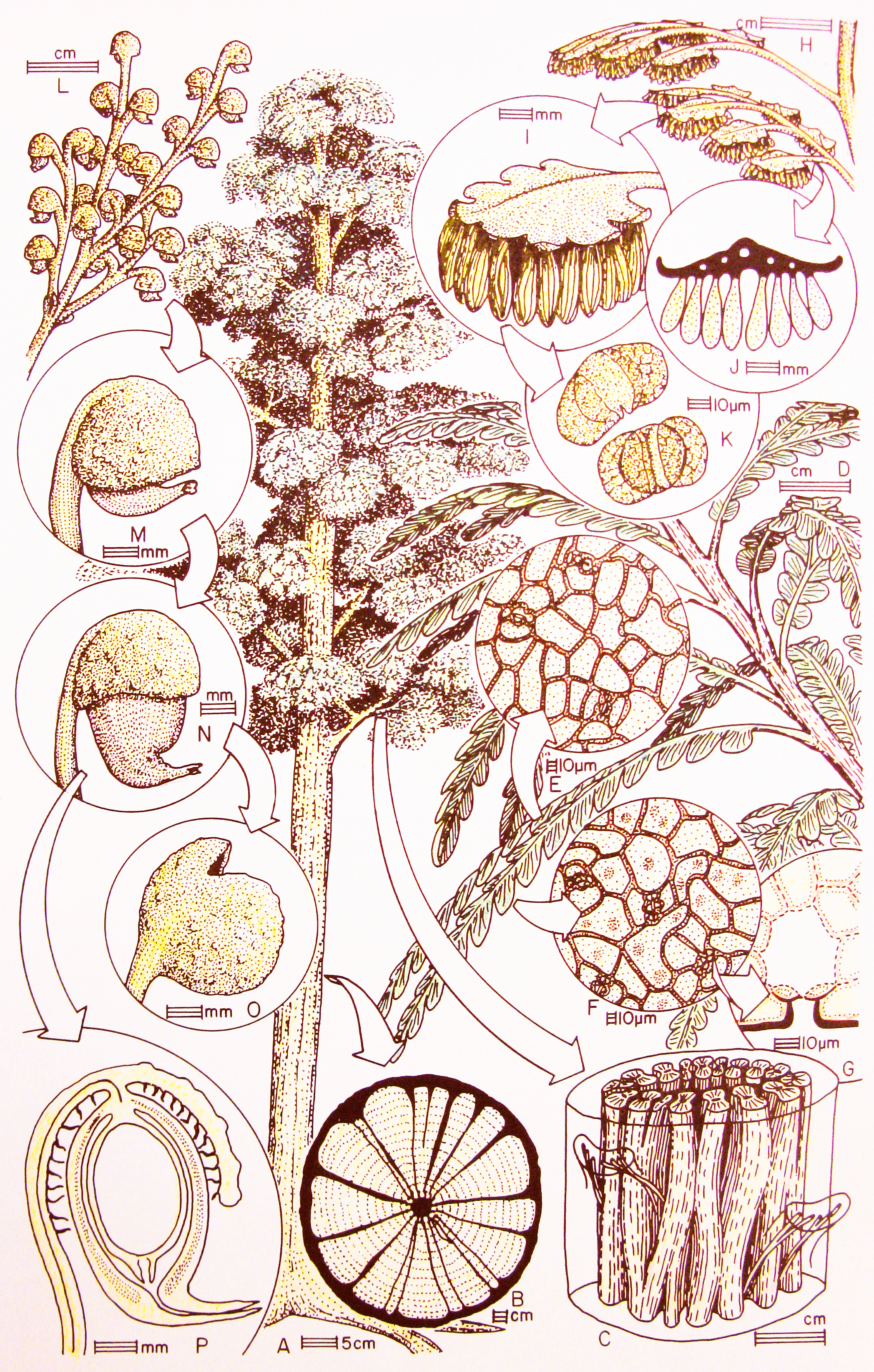
''Dicroidium'' is an extinct genus of fork-leaved seed ferns that were widely distributed over Gondwana during the Triassic (). Their fossils are known from South Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, Australia, New Zealand, South America, Madagascar, the Indian subcontinent and Antarctica. They were first discovered in Triassic sediments of Tasmania by Morris in 1845. Fossils from the Umm Irna Formation in Jordan and in Pakistan indicate that these plants already existed in Late Permian. Late surviving members of the genus are known from the Early Jurassic (Sinemurian) of East Antarctica. Within paleobotany, ''Dicroidium'' is a form genus used to refers to the leaves, associated with ovuluate organs classified as ''Umkomasia'' and pollen organs classified as ''Pteruchus,'' while ''Dicroidum'' is also used collectively to refer to the whole plant. Description The leaves are similar to those of modern ferns but like all seed ferns (Pteridospermatophyta) were thick and had substantia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dicroidium Odontopteroides
''Dicroidium odontopteroides'' was a common and widespread species of ''Dicroidium'' known from South Africa, Australia, New Zealand, South America and Antarctica. The species was first discovered in Triassic sediments of Tasmania and described by the palaeontologist John Morris in 1845. Description The leaves of ''Dicroidium odontopteroides'' differ from other species of ''Dicroidium ''Dicroidium'' is an extinct genus of fork-leaved seed ferns that were widely distributed over Gondwana during the Triassic (). Their fossils are known from South Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, Australia, New Zealand, South America, Madagascar, t ...'' in being unipinnate and having short rounded pinnae. Whole plant reconstructions ''Dicroidium odontopteroides'' may have been produced by the same plant as '' Umkomasia macleanii'' (ovulate structures) and '' Pteruchus africanus'' (pollen organs), based on cuticular similarities between these leaves and reproductive structures at the Umkomaas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Jurassic
The Early Jurassic Epoch (in chronostratigraphy corresponding to the Lower Jurassic Series) is the earliest of three epochs of the Jurassic Period. The Early Jurassic starts immediately after the Triassic-Jurassic extinction event, 201.3 Ma (million years ago), and ends at the start of the Middle Jurassic 174.1 Ma. Certain rocks of marine origin of this age in Europe are called "Lias" and that name was used for the period, as well, in 19th-century geology. In southern Germany rocks of this age are called Black Jurassic. Origin of the name Lias There are two possible origins for the name Lias: the first reason is it was taken by a geologist from an English quarryman's dialect pronunciation of the word "layers"; secondly, sloops from north Cornish ports such as Bude would sail across the Bristol Channel to the Vale of Glamorgan to load up with rock from coastal limestone quarries (lias limestone from South Wales was used throughout North Devon/North Cornwall as it conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triassic Plants
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic. The Triassic began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, which left the Earth's biosphere impoverished; it was well into the middle of the Triassic before life recovered its former diversity. Three categories of organisms can be distinguished in the Triassic record: survivors from the extinction event, new groups that flourished briefly, and other new groups that went on to dominate the Mesozoic Era. Reptiles, especially archosaurs, were the chief terrestrial vertebrates during this time. A specialized subgroup of archosau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pteruchus Barrealensis
''Pteruchus barrealensis'' is an unusually large species of ''Pteruchus'' with very elongate polleniferous heads from Early Triassic of Australia and Argentina. Description ''Pteruchus barrealensis'' is one of the geologically earliest species of ''Pteruchus'', and has very elongate polleniferous heads. Whole plant reconstruction ''Pteruchus barrealensis'' from the Early Triassic of Australia may have been produced by the same plant as '' Umkomasia feistmantelii'' (ovulate organs) and ''Dicroidium zuberi ''Dicroidium zuberi'' is a large bipinnate species of the seed fern ''Dicroidium ''Dicroidium'' is an extinct genus of fork-leaved seed ferns that were widely distributed over Gondwana during the Triassic (). Their fossils are known from Sout ...'' (leaves) References Triassic plants Pteridospermatophyta {{triassic-plant-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umkomasia Feistmantelii
''Umkomasia feistmantelii'' is an unusually large species of ''Umkomasia'' from the Early Triassic of New South Wales, Australia. Description ''Umkomasia feistmantelii'' is found both with cupules enclosing the large seeds and with cupules open and expandede into a star-shaped form. Whole Plant Reconstruction ''Umkomasia feistmantelii'' from the Early Triassic of Australia may have been produced by the same plant as ''Pteruchus barrealensis'' (pollen organs) and ''Dicroidium zuberi ''Dicroidium zuberi'' is a large bipinnate species of the seed fern ''Dicroidium ''Dicroidium'' is an extinct genus of fork-leaved seed ferns that were widely distributed over Gondwana during the Triassic (). Their fossils are known from Sout ...'' (leaves) See also * Evolution of plants References External links Paleodb.org: ''Umkomasia feistmanteli'' Permian plants Triassic plants Pteridospermatophyta Cisuralian life Early Triassic life Plants described in 1987 Ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pteruchus Africanus
''Pteruchus africanus'' is a pollen organ of a seed fern (Pteridospermatophyta). It was first described by Hamshaw Thomas from the Umkomaas locality of South Africa. Description The pollen organs ''Pteruchus africanus'' differ from other species of ''Pteruchus'' in small size, and equant blade supporting the pollen sacs. Whole plant reconstructions ''Pteruchus africanus'' may have been produced by the same plant as '' Umkomasia macleanii'' (ovulate organs) and ''Dicroidium odontopteroides ''Dicroidium odontopteroides'' was a common and widespread species of ''Dicroidium'' known from South Africa, Australia, New Zealand, South America and Antarctica. The species was first discovered in Triassic sediments of Tasmania and described ...'' (leaves), based on cuticular similarities between these leaves and reproductive structures at the Umkomaas locality of South Africa. References Triassic plants Pteridospermatophyta {{triassic-plant-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umkomasia Macleanii
''Umkomasia macleanii'' is an ovulate structure of a seed fern (Pteridospermatophyta and the nominate genus of Family Umkomasiaceae. It was first described by Hamshaw Thomas from the Umkomaas locality of South Africa. Description The ovulate structures of ''Umkomasia macleanii'' differ from other species of ''Umkomasia'' in small size, and limited geographic distribution. Whole plant reconstructions ''Umkomasia macleanii'' may have been produced by the same plant as ''Pteruchus africanus'' (pollen organs) and ''Dicroidium odontopteroides ''Dicroidium odontopteroides'' was a common and widespread species of ''Dicroidium'' known from South Africa, Australia, New Zealand, South America and Antarctica. The species was first discovered in Triassic sediments of Tasmania and described ...'' (leaves), based on cuticular similarities between these leaves and reproductive structures at the Umkomaas locality of South Africa. References Triassic plants Pteridospermatophyt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleobotany
Paleobotany, which is also spelled as palaeobotany, is the branch of botany dealing with the recovery and identification of plant remains from geological contexts, and their use for the biological reconstruction of past environments (paleogeography), and the evolutionary history of plants, with a bearing upon the evolution of life in general. A synonym is paleophytology. It is a component of paleontology and paleobiology. The prefix ''palaeo-'' means "ancient, old", and is derived from the Greek adjective , . Paleobotany includes the study of terrestrial plant fossils, as well as the study of prehistoric marine photoautotrophs, such as photosynthetic algae, seaweeds or kelp. A closely related field is palynology, which is the study of fossilized and extant spores and pollen. Paleobotany is important in the reconstruction of ancient ecological systems and climate, known as paleoecology and paleoclimatology respectively; and is fundamental to the study of green pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pteridospermatophyta
The term Pteridospermatophyta (or "seed ferns" or "Pteridospermatopsida") is a polyphyletic group of extinct seed-bearing plants (spermatophytes). The earliest fossil evidence for plants of this type is the genus ''Elkinsia'' of the late Devonian age. They flourished particularly during the Carboniferous and Permian periods. Pteridosperms declined during the Mesozoic Era and had mostly disappeared by the end of the Cretaceous Period, though some pteridosperm-like plants seem to have survived into Eocene times, based on fossil finds in Tasmania. With regard to the enduring utility of this division, many palaeobotanists still use the pteridosperm grouping in an informal sense to refer to the seed plants that are not angiosperms, coniferoids (conifers or cordaites), ginkgophytes or cycadophytes (cycads or bennettites). This is particularly useful for extinct seed plant groups whose systematic relationships remain speculative, as they can be classified as pteridosperms with no v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fern
A fern (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta ) is a member of a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. The polypodiophytes include all living pteridophytes except the lycopods, and differ from mosses and other bryophytes by being vascular, i.e., having specialized tissues that conduct water and nutrients and in having life cycles in which the branched sporophyte is the dominant phase. Ferns have complex leaves called megaphylls, that are more complex than the microphylls of clubmosses. Most ferns are leptosporangiate ferns. They produce coiled fiddleheads that uncoil and expand into fronds. The group includes about 10,560 known extant species. Ferns are defined here in the broad sense, being all of the Polypodiopsida, comprising both the leptosporangiate ( Polypodiidae) and eusporangiate ferns, the latter group including horsetails, whisk ferns, marattioid ferns, and ophioglossoid fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dicroidium Zuberi Leaf
''Dicroidium'' is an extinct genus of fork-leaved seed ferns that were widely distributed over Gondwana during the Triassic (). Their fossils are known from South Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, Australia, New Zealand, South America, Madagascar, the Indian subcontinent and Antarctica. They were first discovered in Triassic sediments of Tasmania by Morris in 1845. Fossils from the Umm Irna Formation in Jordan and in Pakistan indicate that these plants already existed in Late Permian. Late surviving members of the genus are known from the Early Jurassic (Sinemurian) of East Antarctica. Within paleobotany, ''Dicroidium'' is a form genus used to refers to the leaves, associated with ovuluate organs classified as '' Umkomasia'' and pollen organs classified as '' Pteruchus,'' while ''Dicroidum'' is also used collectively to refer to the whole plant. Description The leaves are similar to those of modern ferns but like all seed ferns (Pteridospermatophyta) were thick and had substan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pteruchus
''Pteruchus'' is a form genus for pollen organs of the seed fern (Pteridospermatophyta family Umkomasiaceae. It was first described by Hamshaw Thomas from the Umkomaas locality of South Africa. It is associated with the seed bearing organs '' Umkomasia'' and ''Dicroidium'' leaves. Description The pollen organ ''Pteruchus'' differs from other seed fern pollen organs in having numerous pendant pollen sacs from a blade-like head, in an arrangement similar to an epaulette. Whole plant reconstructions *'' Pteruchus africanus'' may have been produced by the same plant as '' Umkomasia macleanii'' (ovulate organs) and ''Dicroidium odontopteroides'' (leaves), based on cuticular similarities between these leaves and reproductive structures at the Umkomaas locality of South Africa. *'' Pteruchus barrealensis'' may have been produced by the same plant as '' Umkomasia feistmantelii'' (ovulate organs) and ''Dicroidium zuberi ''Dicroidium zuberi'' is a large bipinnate species of the se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
