|
Dichlorosalicylic Acid
Dichlorosalicylic acid may refer to: * 3,4-Dichlorosalicylic acid, RN = 14010-45-8 , m.p. not available * 3,5-Dichlorosalicylic acid, registry number, RN = 320-72-9 , m.p. 220-221 °C * 3,6-Dichlorosalicylic acid, RN = 3401-80-7, m.p. 187 °C * 4,5-Dichlorosalicylic acid, RN = 50274-58-3 , m.p. not available * 4,6-Dichlorosalicylic acid, RN = 99725-34-5 , m.p. not available * 5,6-Dichlorosalicylic acid, RN = 1806282-06-3 , m.p. not available 3,6-Dichlorosalicylic acid is the principal product of the biodegradation of the herbicide dicamba. See also * Chlorosalicylic acid References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biodegradation
Biodegradation is the breakdown of organic matter by microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi. It is generally assumed to be a natural process, which differentiates it from composting. Composting is a human-driven process in which biodegradation occurs under a specific set of circumstances. The process of biodegradation is threefold: first an object undergoes biodeterioration, which is the mechanical weakening of its structure; then follows biofragmentation, which is the breakdown of materials by microorganisms; and finally assimilation, which is the incorporation of the old material into new cells. In practice, almost all chemical compounds and materials are subject to biodegradation, the key element being time. Things like vegetables may degrade within days, while glass and some plastics take many millennia to decompose. A standard for biodegradability used by the European Union is that greater than 90% of the original material must be converted into , water and minerals b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
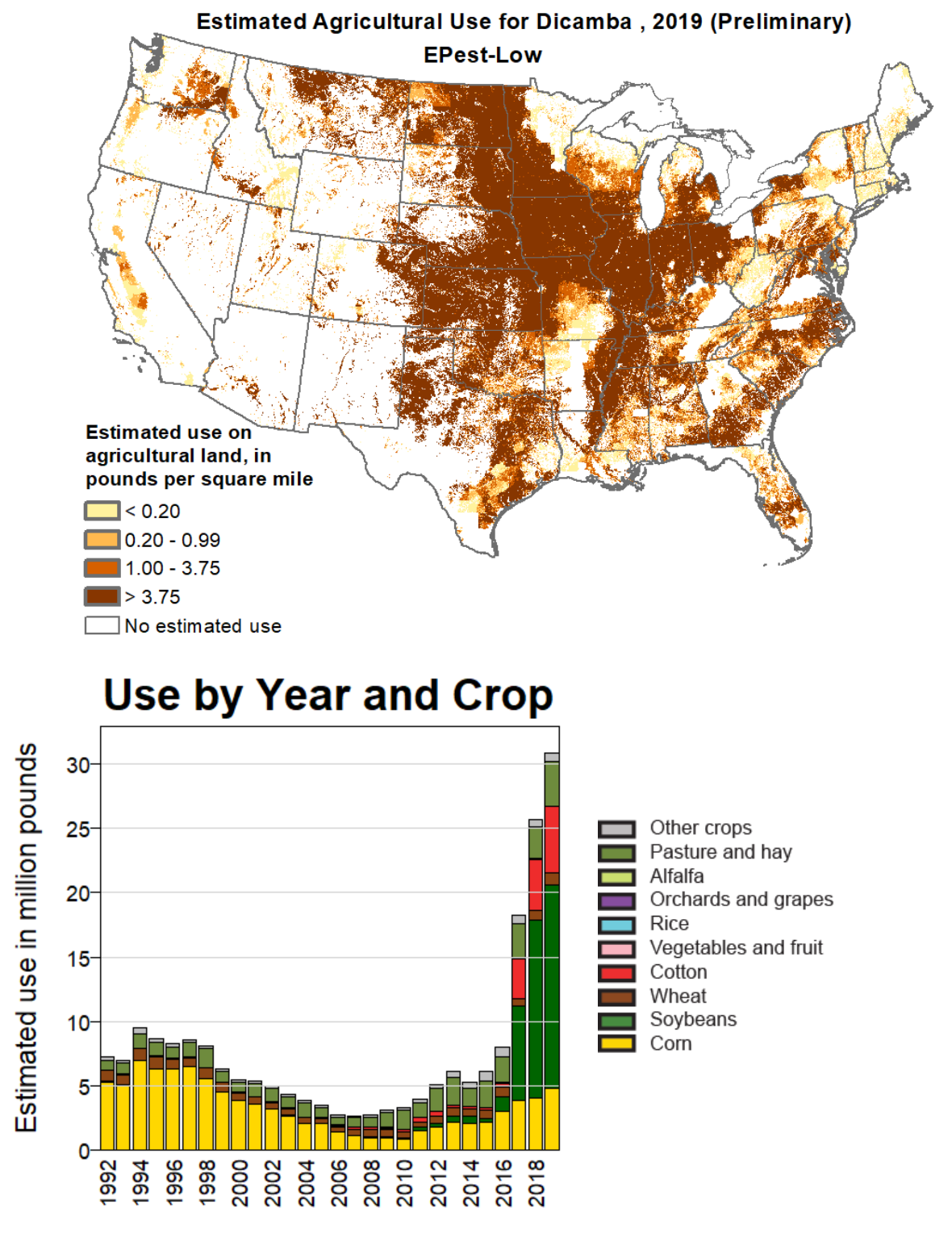
Dicamba
Dicamba (3,6-dichloro-2-methoxybenzoic acid) is a selective systemic herbicide first registered in 1967. Brand names for formulations of this herbicide include Dianat, Banvel, Diablo, Oracle and Vanquish. This chemical compound is a chlorinated derivative of ''o''-anisic acid. It has been described as a "widely used, low-cost, environmentally friendly herbicide that does not persist in soils and shows little or no toxicity to wildlife and humans." Despite its success in improving crop yields, dicamba has attracted controversy. According to the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), dicamba's primary ecological risk is for non-target terrestrial plants from exposure through spray drift, whereby dicamba inadvertently migrates to non-targeted neighboring areas, damaging those plants. In 2016, dicamba was approved for use in the United States over GMO dicamba-resistant crops created by Monsanto. Dicamba came under significant scrutiny due to its tendency to sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorosalicylic Acid
Chlorosalicylic acid may refer to: * 3-Chlorosalicylic acid, RN = 1829-32-9 , m.p. 180-182 °C * 4-Chlorosalicylic acid, RN = 5106-98-9, m.p. 211 °C * 5-Chlorosalicylic acid, RN = 321-14-2 , m.p. 171.5 °C * 6-Chlorosalicylic acid, RN = 56961-31-0 , m.p. 171.5-172.5 °C All have the formula group. See also * Dichlorosalicylic acid Dichlorosalicylic acid may refer to: * 3,4-Dichlorosalicylic acid, RN = 14010-45-8 , m.p. not available * 3,5-Dichlorosalicylic acid, registry number, RN = 320-72-9 , m.p. 220-221 °C * 3,6-Dichlorosalicylic acid, RN = 3401-80-7, m.p. 187 °C * 4, ... References {{Chemistry index Chlorobenzene derivatives Salicylic acids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorobenzene Derivatives
Chlorobenzene (abbreviated PhCl) is an aryl chloride and the simplest of the chlorobenzenes, consisting of a benzene ring substituted with one chlorine atom. Its chemical formula is C6H5Cl. This colorless, flammable liquid is a common solvent and a widely used intermediate in the manufacture of other chemicals. Uses The major use of chlorobenzene is as a precursor for further intermediates such as nitrophenols, nitroanisole, chloroaniline, and phenylenediamines, which are used in the production of herbicides, dyestuffs, chemicals for rubber, and pharmaceuticals. It is also used as a high-boiling solvent in industrial and laboratory applications, for materials such as oils, waxes, resins, and rubber. Chlorobenzene is nitrated on a large scale to give a mixture of 2-nitrochlorobenzene and 4-nitrochlorobenzene, which are separated and used as intermediates in production of other chemicals. These mononitrochlorobenzenes are converted to related 2-nitrophenol, 2-nitroanisole, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |