|
Diasystem
In the field of dialectology, a diasystem or polylectal grammar is a linguistic analysis set up to encode or represent a range of related varieties in a way that displays their structural differences. The term ''diasystem'' was coined by linguist and dialectologist Uriel Weinreich in a 1954 paper as part of an initiative in exploring how to extend advances in structuralist linguistic theory to dialectology to explain linguistic variation across dialects. Weinreich's paper inspired research in the late 1950s to test the proposal. However, the investigations soon showed it to be generally untenable, at least under structuralist theory. With the advent of generative theory in the 1960s, researchers tried applying a generative approach in developing diasystemic explanations; this also fell short. According to some leading sociolinguists, the diasystem idea for incorporating variation into linguistic theory has been superseded by William Labov's notion of the linguistic variabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaphoneme
A diaphoneme is an abstract phonology, phonological unit that identifies a correspondence between related sounds of two or more variety (linguistics), varieties of a language or language cluster. For example, some English varieties contrast the vowel of ''late'' () with that of ''wait'' or ''eight'' (). Other English varieties contrast the vowel of ''late'' or ''wait'' () with that of ''eight'' (). This non-overlapping pair of phonemes from two different varieties can be reconciled by positing three different diaphonemes: A first diaphoneme for words like ''late'' (), a second diaphoneme for words like ''wait'' (), and a third diaphoneme for words like ''eight'' (). Diaphonology studies the realization of diaphones across dialects, and is important if an orthography is to be adequate for more than one dialect of a language. In historical linguistics, it is concerned with the reflexes of an ancestral phoneme as a language splits into dialects, such as the modern realizations of O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dialectology
Dialectology (from Ancient Greek, Greek , ''dialektos'', "talk, dialect"; and , ''-logy, -logia'') is the scientific study of dialects: subsets of languages. Though in the 19th century a branch of historical linguistics, dialectology is often now considered a sub-field of, or subsumed by, sociolinguistics. It studies variations in language based primarily on geographic distribution and their associated features. Dialectology deals with such topics as divergence of two local dialects from a common ancestor and Historical_linguistics#Diachronic_and_synchronic_analysis, synchronic variation. Dialectologists are ultimately concerned with grammatical, lexical and phonological features that correspond to regional areas. Thus they usually deal not only with populations that have lived in certain areas for generations, but also with migrant groups that bring their languages to new areas (see language contact). Commonly studied concepts in dialectology include the problem of mutual intellig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generative Phonology
Generative grammar is a research tradition in linguistics that aims to explain the cognitive basis of language by formulating and testing explicit models of humans' subconscious grammatical knowledge. Generative linguists, or generativists (), tend to share certain working assumptions such as the competence–performance distinction and the notion that some domain-specific aspects of grammar are partly innate in humans. These assumptions are rejected in non-generative approaches such as usage-based models of language. Generative linguistics includes work in core areas such as syntax, semantics, phonology, psycholinguistics, and language acquisition, with additional extensions to topics including biolinguistics and music cognition. Generative grammar began in the late 1950s with the work of Noam Chomsky, having roots in earlier approaches such as structural linguistics. The earliest version of Chomsky's model was called Transformational grammar, with subsequent iterations kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creole Continuum
A post-creole continuum (or simply creole continuum) is a dialect continuum of varieties of a creole language between those most and least similar to the superstrate language (that is, a closely related language whose speakers assert or asserted dominance of some sort). Due to social, political, and economic factors, a creole language can decreolize towards one of the languages from which it is descended, aligning its morphology, phonology, and syntax to the local standard of the dominant language but to different degrees depending on a speaker's status. Stratification William Stewart, in 1965, proposed the terms acrolect, the highest or most prestigious variety on the continuum, and basilect, the lowest or least prestigious variety, as sociolinguistic labels for the upper and lower boundaries, respectively, of a post-creole speech continuum. In the early 1970s Derek Bickerton popularized these terms (as well as mesolect for intermediate points in the continuum) to refer to the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
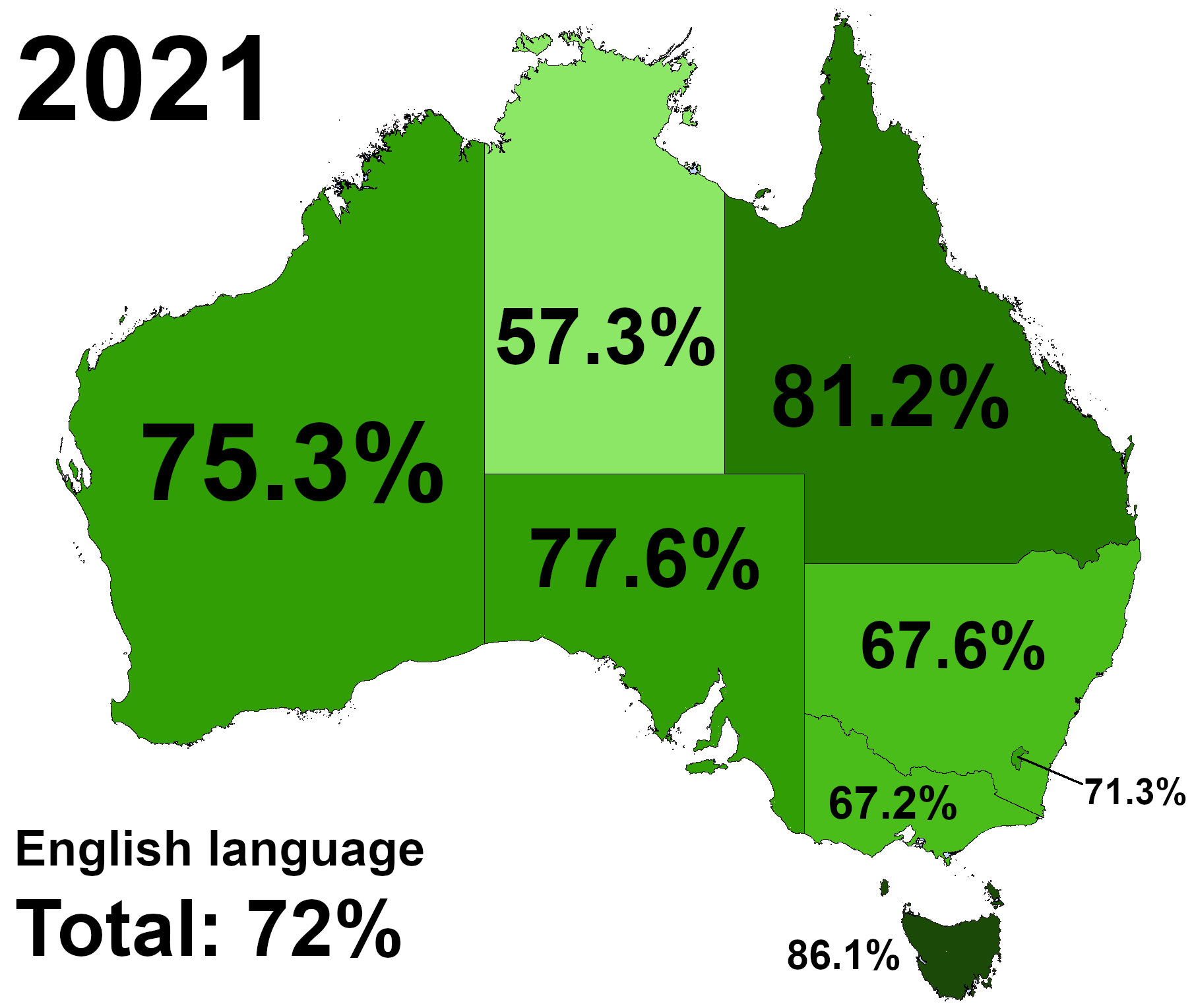
Australian English
Australian English (AusE, AusEng, AuE, AuEng, en-AU) is the set of variety (linguistics), varieties of the English language native to Australia. It is the country's common language and ''de facto'' national language. While Australia has no official language, English is the first language of Languages of Australia, the majority of the population, and has been entrenched as the ''de facto'' national language since the onset of History of Australia (1788–1850), British settlement, being the only language spoken in the home for 72% of Australians in 2021. It is also the main language used in compulsory education, as well as federal, state and territorial legislatures and courts. Australian English began to diverge from British English, British and Hiberno-English after the First Fleet established the Colony of New South Wales in 1788. Australian English arose from a Koiné language, dialectal melting pot created by the intermingling of early settlers who were from a variety of d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macquarie Dictionary
The ''Macquarie Dictionary'' () is a dictionary of Australian English. It is considered by many to be the standard reference on Australian English. It also pays considerable attention to New Zealand English. Originally it was a publishing project of Jacaranda Press, a Brisbane educational publisher, for which an editorial committee was formed, largely from the Linguistics department of Macquarie University in Sydney, Australia. It is now published by Macquarie Dictionary Publishers, an imprint of Macmillan Publishers, Pan Macmillan Australia Pty Ltd. In October 2007 it moved its editorial office from Macquarie University to the University of Sydney, and later to the Pan Macmillan offices in the Sydney central business district. In addition to its two-volume flagship dictionary, shorter editions including the ''Macquarie Concise Dictionary'', ''Macquarie Compact Dictionary'', ''Macquarie Budget Dictionary'' and ''Macquarie Little Dictionary'' are published. History The first sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English As A Foreign Or Second Language
English as a second or foreign language refers to the use of English by individuals whose native language is different, commonly among students learning to speak and write English. Variably known as English as a foreign language (EFL), English as a second language (ESL), English for speakers of other languages (ESOL), English as an additional language (EAL), or English as a new language (ENL), these terms denote the study of English in environments where it is not the dominant language. Programs such as ESL are designed as academic courses to instruct non-native speakers in English proficiency, encompassing both learning in English-speaking nations and abroad. Teaching methodologies include teaching English as a foreign language (TEFL) in non-English-speaking countries, teaching English as a second language (TESL) in English-speaking nations, and teaching English to speakers of other languages (TESOL) worldwide. These terms, while distinct in scope, are often used intercha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crow
A crow is a bird of the genus ''Corvus'', or more broadly, a synonym for all of ''Corvus''. The word "crow" is used as part of the common name of many species. The related term "raven" is not linked scientifically to any certain trait but is rather a general grouping for larger-sized species of ''Corvus''. The collective name for a group of crows is a "murder". Species * ''Corvus albus'' – Pied crow (Central African coasts to southern Africa) * ''Corvus bennetti'' – Little crow (bird), Little crow (Australia) * ''Corvus brachyrhynchos'' – American crow (United States, southern Canada, northern Mexico) * ''Corvus capensis'' – Cape crow or Cape rook (Eastern and southern Africa) * ''Corvus cornix'' – Hooded crow (Northern and Eastern Europe and Northern Africa and Middle East) * ''Corvus corone'' – Carrion crow (Europe and eastern Asia) *''Corvus culminatus'' – Indian jungle crow (South Asia) * ''Corvus edithae'' – Somali crow or dwarf raven (Eastern Africa) * '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norwich
Norwich () is a cathedral city and district of the county of Norfolk, England, of which it is the county town. It lies by the River Wensum, about north-east of London, north of Ipswich and east of Peterborough. The population of the Norwich City Council local authority area was estimated to be 144,000 in 2021, which was an increase from 143,135 in 2019. The wider Norwich List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, built-up area had a population of 213,166 at the 2011 census. As the seat of the Episcopal see, See of Norwich, the city has one of the country's largest medieval cathedrals. For much of the second millennium, from medieval to just before Industrial Revolution, industrial times, Norwich was one of the most prosperous and largest towns of England; at one point, it was List of towns and cities in England by historical population, second only to London. Today, it is the largest settlement in East Anglia. Heritage and status Norwich claims to be the most complete medie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Trudgill
Peter Trudgill, ( ; born 7 November 1943) is an English sociolinguist, academic and author. Biography Trudgill was born in Norwich, England, and grew up in the area of Thorpe St Andrew. He attended the City of Norwich School from 1955. Trudgill studied modern languages at King's College, Cambridge and obtained a PhD from the University of Edinburgh in 1971. Before becoming professor of sociolinguistics at the University of Essex he taught in the Department of Linguistic Science at the University of Reading from 1970 to 1986. He was professor of English language and linguistics at the University of Lausanne, Switzerland, from 1993 to 1998, and then at the University of Fribourg, also in Switzerland, from which he retired in September 2005, and where he is now professor emeritus of English Linguistics. He is an honorary Professor of Sociolinguistics at the University of East Anglia, in Norwich, England. On 2 June 1995 he received an honorary doctorate from the Faculty of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Standard Arabic
Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Modern Written Arabic (MWA) is the variety of Standard language, standardized, Literary language, literary Arabic that developed in the Arab world in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, and in some usages also the variety of spoken Arabic that approximates this written standard. MSA is the language used in literature, academia, print media, print and mass media, law and legislation, though it is generally not spoken as a first language, similar to Contemporary Latin. It is a Pluricentric language, pluricentric standard language taught throughout the Arab world in formal education, differing significantly from many vernacular varieties of Arabic that are commonly spoken as mother tongues in the area; these are only partially mutually intelligible with both MSA and with each other depending on their proximity in the Dialect continuum#Arabic, Arabic dialect continuum. Many linguists consider MSA to be distinct from Classical Arabic (CA; ) – t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varieties Of Arabic
Varieties of Arabic (or dialects or vernaculars) are the linguistic systems that Arabic speakers speak natively. Arabic is a Semitic languages, Semitic language within the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic family that originated in the Arabian Peninsula. There are considerable variations from region to region, with degrees of mutual intelligibility that are often related to geographical distance and some that are mutually unintelligible. Many aspects of the variability attested to in these modern variants can be found in the ancient Arabic dialects in the peninsula. Likewise, many of the features that characterize (or distinguish) the various modern variants can be attributed to the original settler dialects as well as local native languages and dialects. Some organizations, such as SIL International, consider these approximately 30 different varieties to be separate languages, while others, such as the Library of Congress, consider them all to be dialects of Arabic. In terms of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |