|
Diamond-like Carbon
Diamond-like carbon (DLC) is a class of amorphous carbon material that displays some of the typical properties of diamond. DLC is usually applied as coatings to other materials that could benefit from such properties. DLC exists in seven different forms. All seven contain significant amounts of sp3 hybridized carbon atoms. The reason that there are different types is that even diamond can be found in two crystalline polytypes. The more common one uses a cubic lattice, while the less common one, lonsdaleite, has a hexagonal lattice. By mixing these polytypes at the nanoscale, DLC coatings can be made that at the same time are amorphous, flexible, and yet purely sp3 bonded "diamond". The hardest, strongest, and slickest is tetrahedral amorphous carbon (ta-C). Ta-C can be considered to be the "pure" form of DLC, since it consists almost entirely of sp3 bonded carbon atoms. Fillers such as hydrogen, graphitic sp2 carbon, and metals are used in the other 6 forms to reduce produc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexagonal Crystal System
In crystallography, the hexagonal crystal family is one of the six crystal family, crystal families, which includes two crystal systems (hexagonal and trigonal) and two lattice systems (hexagonal and rhombohedral). While commonly confused, the trigonal crystal system and the rhombohedral lattice system are not equivalent (see section hexagonal crystal family#Crystal systems, crystal systems below). In particular, there are crystals that have trigonal symmetry but belong to the hexagonal lattice (such as α-quartz). The hexagonal crystal family consists of the 12 point groups such that at least one of their space groups has the hexagonal lattice as underlying lattice, and is the union of the hexagonal crystal system and the trigonal crystal system. There are 52 space groups associated with it, which are exactly those whose Bravais lattice is either hexagonal or rhombohedral. __TOC__ Lattice systems The hexagonal crystal family consists of two lattice systems: hexagonal and rhom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma Processing
Plasma processing is a plasma-based material processing technology that aims at modifying the chemical and physical properties of a surface. Plasma processing techniques include: *Plasma activation * Plasma ashing * Plasma cleaning * Plasma electrolytic oxidation *Plasma etching * Plasma functionalization * Plasma polymerization *Corona treatment *Plasma modification Related topics are plasma chemistry, chemical vapor deposition, and physical vapor deposition Physical vapor deposition (PVD), sometimes called physical vapor transport (PVT), describes a variety of vacuum deposition methods which can be used to produce thin films and coatings on substrates including metals, ceramics, glass, and polym ... processes like sputter deposition, plasma iondoping, vacuum plasmaspraying, and reactive ion etching. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Plasma Processing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friction Coefficient
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. Types of friction include dry, fluid, lubricated, skin, and internal -- an incomplete list. The study of the processes involved is called tribology, and has a history of more than 2000 years. Friction can have dramatic consequences, as illustrated by the use of friction created by rubbing pieces of wood together to start a fire. Another important consequence of many types of friction can be wear, which may lead to performance degradation or damage to components. It is known that frictional energy losses account for about 20% of the total energy expenditure of the world. As briefly discussed later, there are many different contributors to the retarding force in friction, ranging from asperity deformation to the generation of charges and changes in local structure. When two bodies in contact move relative to each other, due to these various ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sponge
Sponges or sea sponges are primarily marine invertebrates of the animal phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), a basal clade and a sister taxon of the diploblasts. They are sessile filter feeders that are bound to the seabed, and are one of the most ancient members of macrobenthos, with many historical species being important reef-building organisms. Sponges are multicellular organisms consisting of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of cells, and usually have tube-like bodies full of pores and channels that allow water to circulate through them. They have unspecialized cells that can transform into other types and that often migrate between the main cell layers and the mesohyl in the process. They do not have complex nervous, digestive or circulatory systems. Instead, most rely on maintaining a constant water flow through their bodies to obtain food and oxygen and to remove wastes, usually via flagella movements of the so-called " collar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cobblestone
Cobblestone is a natural building material based on Cobble (geology), cobble-sized stones, and is used for Road surface, pavement roads, streets, and buildings. Sett (paving), Setts, also called ''Belgian blocks'', are often referred to as "cobbles", although a sett is distinct from a cobblestone by being quarried and shaped into a regular form, while cobblestones are naturally occurring rounded forms less uniform in size. It has been used across various cultures for millennia, particularly in Europe, and became especially prominent during the medieval and early modern periods. Today, cobblestone streets are often associated with historic preservation and are used in many cities to maintain the historical character of certain neighborhoods. History as road surface During the Middle Ages, medieval period, cobblestone streets became common in many European towns and cities. Cobblestones were readily available, as they were often naturally occurring stones found in riverbeds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is the manipulation of matter with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometers (nm). At this scale, commonly known as the nanoscale, surface area and quantum mechanical effects become important in describing properties of matter. This definition of nanotechnology includes all types of research and technologies that deal with these special properties. It is common to see the plural form "nanotechnologies" as well as "nanoscale technologies" to refer to research and applications whose common trait is scale. An earlier understanding of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal of precisely manipulating atoms and molecules for fabricating macroscale products, now referred to as molecular nanotechnology. Nanotechnology defined by scale includes fields of science such as surface science, organic chemistry, molecular biology, semiconductor physics, energy storage, engineering, microfabrication, and molecular engineering. The associated rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalysis
Catalysis () is the increase in rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed by the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst. The rate increase occurs because the catalyst allows the reaction to occur by an alternative mechanism which may be much faster than the noncatalyzed mechanism. However the noncatalyzed mechanism does remain possible, so that the total rate (catalyzed plus noncatalyzed) can only increase in the presence of the catalyst and never decrease. Catalysis may be classified as either homogeneous, whose components are dispersed in the same phase (usual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amorphous
In condensed matter physics and materials science, an amorphous solid (or non-crystalline solid) is a solid that lacks the long-range order that is a characteristic of a crystal. The terms "glass" and "glassy solid" are sometimes used synonymously with amorphous solid; however, these terms refer specifically to amorphous materials that undergo a glass transition. Examples of amorphous solids include glasses, metallic glasses, and certain types of plastics and polymers. Etymology The term "Amorphous" comes from the Greek language, Greek ''a'' ("without"), and ''morphé'' ("shape, form"). Structure Amorphous materials have an internal structure of molecular-scale structural blocks that can be similar to the basic structural units in the crystalline phase of the same compound. Unlike in crystalline materials, however, no long-range regularity exists: amorphous materials cannot be described by the repetition of a finite unit cell. Statistical measures, such as the atomic density ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ion Beam Deposition
Ion beam deposition (IBD) is a process of applying materials to a target through the application of an ion beam. Ion beam deposition setup with mass separator An ion beam deposition apparatus typically consists of an ion source, ion optics, and the deposition target. Optionally a mass analyzer can be incorporated. In the ion source source materials in the form of a gas, an evaporated solid, or a solution (liquid) are ionized. For atomic IBD, electron ionization, field ionization (Penning ion source) or cathodic arc sources are employed. Cathodic arc sources are used particularly for carbon ion deposition. Molecular ion beam deposition employs electrospray ionization or MALDI sources. The ions are then accelerated, focused or deflected using high voltages or magnetic fields. Optional deceleration at the substrate can be employed to define the deposition energy. This energy usually ranges from a few eV up to a few keV. At low energy molecular ion beams are deposited intact (ion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
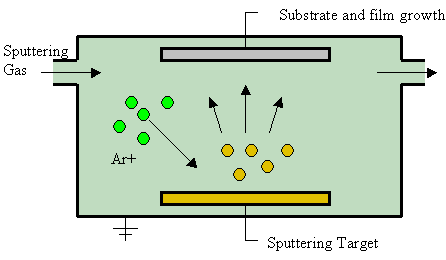
Sputter Deposition
Sputter deposition is a physical vapor deposition (PVD) method of thin film deposition by the phenomenon of sputtering. This involves ejecting material from a "target" that is a source onto a "substrate" such as a silicon wafer. Resputtering is re-emission of the deposited material during the deposition process by ion or atom bombardment. Sputtered atoms ejected from the target have a wide energy distribution, typically up to tens of eV (100,000 K). The sputtered ions (typically only a small fraction of the ejected particles are ionized — on the order of 1 percent) can ballistically fly from the target in straight lines and impact energetically on the substrates or vacuum chamber (causing resputtering). Alternatively, at higher gas pressures, the ions collide with the gas atoms that act as a moderator and move diffusively, reaching the substrates or vacuum chamber wall and condensing after undergoing a random walk. The entire range from high-energy ballistic impact to low-ene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |