|
Diadectomorphs
Diadectomorpha is a clade of large tetrapods that lived in Euramerica during the Carboniferous and Early Permian periods and in Asia during Late Permian (Wuchiapingian), They have typically been classified as advanced reptiliomorphs (transitional between "amphibians" ''sensu lato'' and amniotes) positioned close to, but outside of the clade Amniota, though some recent research has recovered them as the sister group to the traditional Synapsida within Amniota, based on inner ear anatomy and cladistic analyses. They include both large (up to 2 meters long) carnivorous and even larger (to 3 meters) herbivorous forms, some semi-aquatic and others fully terrestrial. The diadectomorphs seem to have originated during late Mississippian times, although they only became common after the Carboniferous rainforest collapse and flourished during the Late Pennsylvanian and Early Permian periods. Anatomy Diadectomorphs possessed both amphibian-like and amniote-like characteristics. Originally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limnoscelis21DB
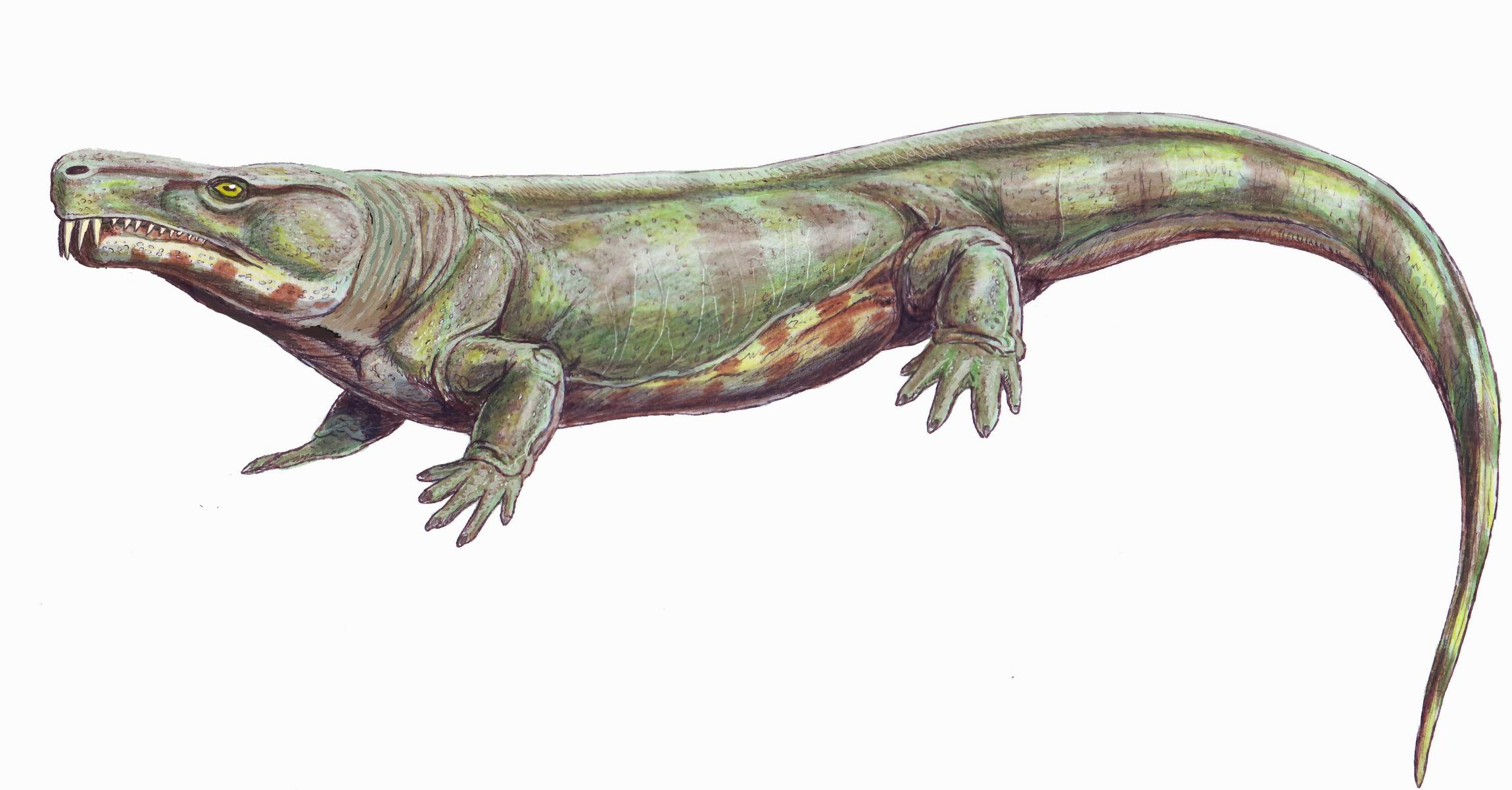
''Limnoscelis'' (/limˈnäsələ̇s/, meaning "marsh footed") was a genus of large diadectomorph tetrapods from the Late Carboniferous to early Permian of western North America. It includes two species: the type species ''Limnoscelis paludis'' from New Mexico, and ''Limnoscelis dynatis'' from Colorado, both of which are thought to have lived concurrently. No specimens of ''Limnoscelis'' are known from outside of North America. ''Limnoscelis'' was carnivorous, and likely semiaquatic, though it may have spent a significant portion of its life on land. ''Limnoscelis'' had a combination of derived amphibian and primitive reptilian features, and its placement relative to Amniota has significant implications regarding the origins of the first amniotes. Discovery and naming The type species ''Limnoscelis paludis'' was collected by the fossil hunter David Baldwin between 1877 and 1880 from the El Cobre Canyon beds of the Cutler Formation, New Mexico. Baldwin was collecting fossils in s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limnoscelis Paludis
''Limnoscelis'' (/limˈnäsələ̇s/, meaning "marsh footed") was a genus of large diadectomorph tetrapods from the Late Carboniferous to early Permian of western North America. It includes two species: the type species ''Limnoscelis paludis'' from New Mexico, and ''Limnoscelis dynatis'' from Colorado, both of which are thought to have lived concurrently. No specimens of ''Limnoscelis'' are known from outside of North America. ''Limnoscelis'' was carnivorous, and likely semiaquatic, though it may have spent a significant portion of its life on land. ''Limnoscelis'' had a combination of derived amphibian and primitive reptilian features, and its placement relative to Amniota has significant implications regarding the origins of the first amniotes. Discovery and naming The type species ''Limnoscelis paludis'' was collected by the fossil hunter David Baldwin between 1877 and 1880 from the El Cobre Canyon beds of the Cutler Formation, New Mexico. Baldwin was collecting fossils i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiliomorph
Reptiliomorpha (meaning reptile-shaped; in PhyloCode known as ''Pan-Amniota'') is a clade containing the amniotes and those tetrapods that share a more recent common ancestor with amniotes than with living amphibians (lissamphibians). It was defined by Michel Laurin (2001) and Vallin and Laurin (2004) as the largest clade that includes ''Homo sapiens'', but not '' Ascaphus truei'' (tailed frog). Laurin and Reisz (2020) defined Pan-Amniota as the largest total clade containing ''Homo sapiens'', but not '' Pipa pipa'', '' Caecilia tentaculata'', and '' Siren lacertina''. The informal variant of the name, "reptiliomorphs", is also occasionally used to refer to stem-amniotes, i.e. a grade of reptile-like tetrapods that are more closely related to amniotes than they are to lissamphibians, but are not amniotes themselves; the name is used in this meaning e.g. by Ruta, Coates and Quicke (2003). An alternative name, " Anthracosauria", is also commonly used for the group, but is confusin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amniote
Amniotes are tetrapod vertebrate animals belonging to the clade Amniota, a large group that comprises the vast majority of living terrestrial animal, terrestrial and semiaquatic vertebrates. Amniotes evolution, evolved from amphibious Stem tetrapoda, stem tetrapod ancestors during the Carboniferous geologic period, period. Amniota is defined as the smallest crown clade containing humans, the Greek tortoise, and the Nile crocodile. Amniotes are distinguished from the other living tetrapod clade — the anamniote, non-amniote lissamphibians (frogs/toads, salamanders/newts and caecilians) — by: the development of three fetal membranes, extraembryonic membranes (amnion for embryonic protection, chorion for gas exchange, and allantois for metabolic waste disposal or storage); thicker and keratinized skin; rib, costal respiration (breathing by expanding/constricting the rib cage); the presence of adrenal cortex, adrenocortical and chromaffin cell, chromaffin tissues as adrenal g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diadectes
''Diadectes'' (meaning ''crosswise-biter'') is an extinct genus of large reptiliomorphs or synapsids that lived during the early Permian period ( Artinskian- Kungurian stages of the Cisuralian epoch, between 290 and 272 million years ago). ''Diadectes'' was one of the first herbivorous tetrapods, and also one of the first fully terrestrial vertebrates to attain large size. Description ''Diadectes'' was a heavily built animal, up to long, with a thick-boned skull, heavy vertebrae and ribs, massive limb girdles, and short, robust limbs. The nature of the limbs and vertebrae clearly indicates a terrestrial animal. The rib cage was assumed to be barrel-shaped, but new fossils show the ribs were actually sticking out to the sides. High-resolution X-ray microcomputed tomography has revealed an endosseous labyrinth in the opisthotic, prootic, and supraoccipital of ''D. absitus'', along with a well-preserved vestibule, three semicircular canals, and a developed cochlear recess. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synapsida
Synapsida is a diverse group of tetrapod vertebrates that includes all mammals and their extinct relatives. It is one of the two major clades of the group Amniota, the other being the more diverse group Sauropsida (which includes all extant reptiles and therefore, birds). Unlike other amniotes, synapsids have a single temporal fenestra, an opening low in the skull roof behind each eye socket, leaving a bony arch beneath each; this accounts for the name "synapsid". The distinctive temporal fenestra developed about 318 million years ago during the Late Carboniferous period, when synapsids and sauropsids diverged, but was subsequently merged with the orbit in early mammals. The basal amniotes ( reptiliomorphs) from which synapsids evolved were historically simply called "reptiles". Therefore, stem group synapsids were then described as mammal-like reptiles in classical systematics, and non- therapsid synapsids were also referred to as pelycosaurs or pelycosaur- grade syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapod
A tetrapod (; from Ancient Greek :wiktionary:τετρα-#Ancient Greek, τετρα- ''(tetra-)'' 'four' and :wiktionary:πούς#Ancient Greek, πούς ''(poús)'' 'foot') is any four-Limb (anatomy), limbed vertebrate animal of the clade Tetrapoda (). Tetrapods include all Neontology#Extant taxa versus extinct taxa, extant and Extinction, extinct amphibians and amniotes, with the latter in turn Evolution, evolving into two major clades, the Sauropsida, sauropsids (reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (extinct pelycosaur, "pelycosaurs", therapsids and all extant mammals, including Homo sapiens, humans). Hox gene mutations have resulted in some tetrapods becoming Limbless vertebrate, limbless (snakes, legless lizards, and caecilians) or two-limbed (cetaceans, sirenians, Bipedidae, some lizards, kiwi (bird), kiwis, and the extinct moa and elephant birds). Nevertheless, they still qualify as tetrapods through their ancestry, and some retain a pair of ves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synapsid
Synapsida is a diverse group of tetrapod vertebrates that includes all mammals and their extinct relatives. It is one of the two major clades of the group Amniota, the other being the more diverse group Sauropsida (which includes all extant reptiles and therefore, birds). Unlike other amniotes, synapsids have a single temporal fenestra, an opening low in the skull roof behind each eye socket, leaving a zygomatic arch, bony arch beneath each; this accounts for the name "synapsid". The distinctive temporal fenestra developed about 318 million years ago during the Late Carboniferous period, when synapsids and sauropsids diverged, but was subsequently merged with the orbit in early mammals. The basal (phylogenetics), basal amniotes (reptiliomorphs) from which synapsids evolved were historically simply called "reptiles". Therefore, stem group synapsids were then described as mammal-like reptiles in classical systematics, and non-therapsid synapsids were also referred to as pelyco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Pennsylvanian
The Pennsylvanian ( , also known as Upper Carboniferous or Late Carboniferous) is, on the ICS geologic timescale, the younger of two subperiods of the Carboniferous Period (or the upper of two subsystems of the Carboniferous System). It lasted from roughly . As with most other geochronologic units, the rock beds that define the Pennsylvanian are well identified, but the exact date of the start and end are uncertain by a few hundred thousand years. The Pennsylvanian is named after the U.S. state of Pennsylvania, where the coal beds of this age are widespread. The division between Pennsylvanian and Mississippian comes from North American stratigraphy. In North America, where the early Carboniferous beds are primarily marine limestones, the Pennsylvanian was in the past treated as a full-fledged geologic period between the Mississippian and the Permian. In parts of Europe, the Mississippian and Pennsylvanian are one more-or-less continuous sequence of lowland continental deposi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cotylosauria
image:Labidosaurus hamatus.JPG, Fossil of ''Labidosaurus, Labidosaurus hamatus'' Captorhinida (older name: Cotylosauria) is a doubly paraphyletic grouping of early reptiles. Robert L. Carroll (1988) ranked it as an order in the subclass Anapsida, composed of the following suborders:R. L. Carroll (1988), ''Vertebrate Paleontology and Evolution'', W. H. Freeman and Company, New York * A paraphyletic Captorhinomorpha, containing the families Protorothyrididae, Captorhinidae, Bolosauridae, Acleistorhinidae and possibly also Batropetidae * Procolophonia, containing families Nyctiphruretidae, Procolophonidae and Sclerosauridae * Pareiasauroidea, with families Rhipaeosauridae and Pareiasauridae * Millerosauroidea, with a single family Millerettidae. While they all share primitive features and resemble the ancestors of all modern reptiles, some of these families are more closely related to (or belong to) the clade Parareptilia, while others are further along the line leading to diapsids. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphibian
Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniote, anamniotic, tetrapod, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class (biology), class Amphibia. In its broadest sense, it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all Tetrapod, tetrapods, but excluding the amniotes (tetrapods with an amniotic membrane, such as modern reptiles, birds and mammals). All extant taxon, extant (living) amphibians belong to the monophyletic subclass (biology), subclass Lissamphibia, with three living order (biology), orders: Anura (frogs and toads), Urodela (salamanders), and Gymnophiona (caecilians). Evolved to be mostly semiaquatic, amphibians have adapted to inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living in freshwater ecosystem, freshwater, wetland or terrestrial ecosystems (such as riparian woodland, fossorial and even arboreal habitats). Their biological life cycle, life cycle typically starts out as aquatic animal, aquatic larvae with gills known as tadpoles, but some species have devel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |