|
Diadectes Scale
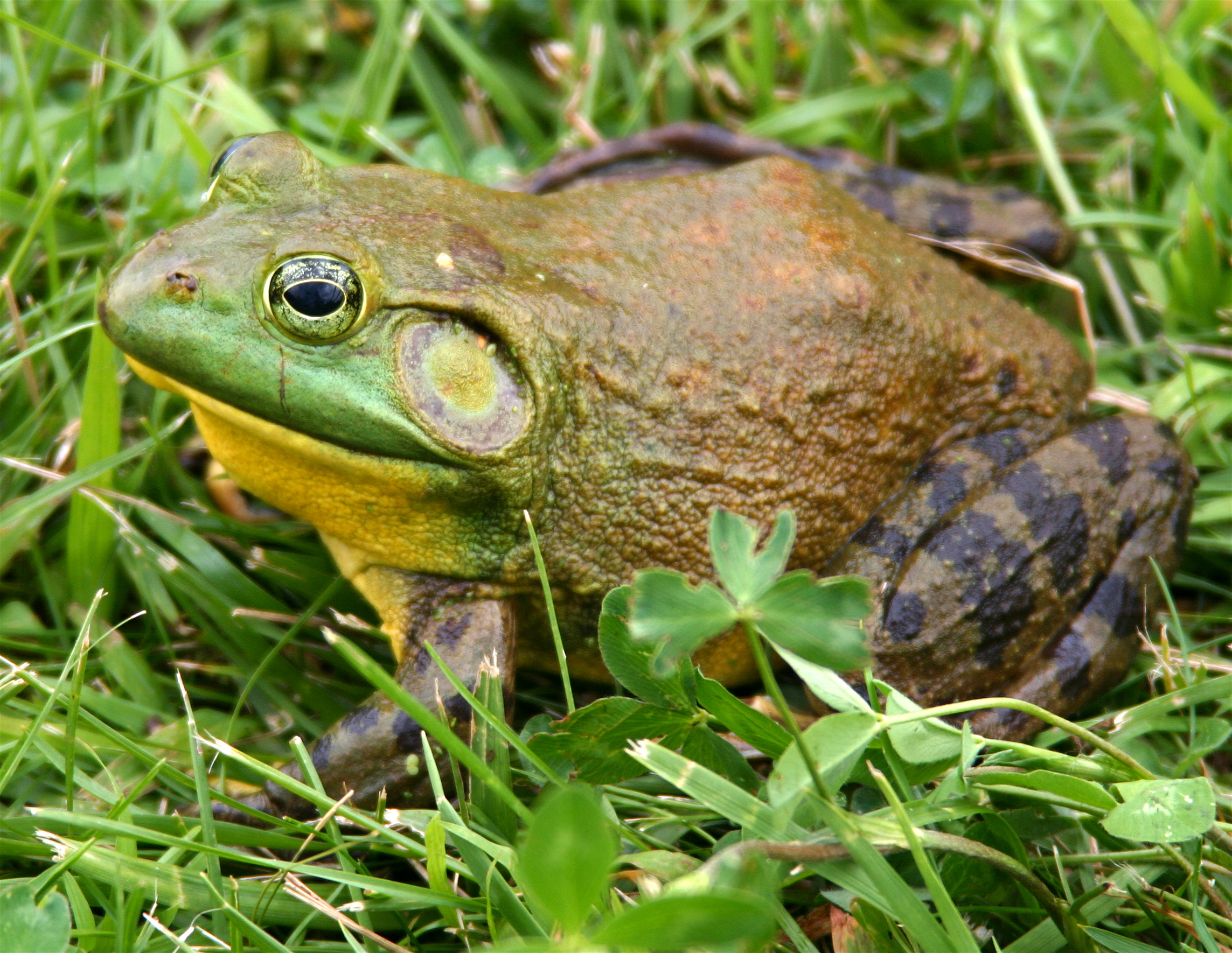
''Diadectes'' (meaning ''crosswise-biter'') is an extinct genus of large reptiliomorphs or synapsids that lived during the early Permian period (Artinskian-Kungurian stages of the Cisuralian epoch, between 290 and 272 million years ago). ''Diadectes'' was one of the first herbivore, herbivorous tetrapods, and also one of the first fully terrestrial vertebrates to attain large size. Description ''Diadectes'' was a heavily built animal, up to long, with a thick-boned skull, heavy vertebrae and ribs, massive limb girdles, and short, robust limbs. The nature of the limbs and vertebrae clearly indicates a terrestrial animal. The rib cage was assumed to be barrel-shaped, but new fossils show the ribs were actually sticking out to the sides. High-resolution X-ray microcomputed tomography has revealed an endosseous labyrinth in the opisthotic, prootic, and supraoccipital of ''D. absitus'', along with a well-preserved vestibule, three semicircular canals, and a developed cochlear rece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artinskian
In the geologic timescale, the Artinskian is an age (geology), age or stage (stratigraphy), stage of the Permian. It is a subdivision of the Cisuralian Epoch (geology), Epoch or series (stratigraphy), Series. The Artinskian likely lasted between and megaannum, million years ago (Ma) according to the most recent revision of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS) in 2022. It was preceded by the Sakmarian and followed by the Kungurian. Stratigraphy The Artinskian is named after the goniatite grits of Artinsk which was introduced by Roderick Murchison, Édouard de Verneuil and count Alexander von Keyserling in their ''The Geology of Russia in Europe and the Ural Mountains'' (1845). The grits of Artinsk, in turn, get its name from the Artinsky District with center in the Russian smalltown of Arti, Russia, Arti (formerly ''Artinsk zavod''), situated in the middle Ural Mountains, Urals, about 170 km southwest of Yekaterinburg. The stage was introduced into scientific li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebra
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal segment and the particular species. The basic configuration of a vertebra varies; the vertebral body (also ''centrum'') is of bone and bears the load of the vertebral column. The upper and lower surfaces of the vertebra body give attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch, in eleven parts, consisting of two pedicles (pedicle of vertebral arch), two laminae, and seven processes. The laminae give attachment to the ligamenta flava (ligaments of the spine). There are vertebral notches formed from the shape of the pedicles, which form the intervertebral foramina when the vertebrae articulate. These foramina are the entry and exit conduits for the spinal nerves. The body of the vertebr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
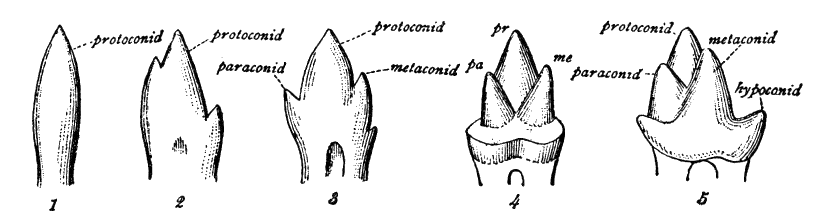
Molar (tooth)
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone tooth", from ''mola'', millstone and ''dens'', tooth. Molars show a great deal of diversity in size and shape across the mammal groups. The third molar of humans is sometimes vestigial. Human anatomy In humans, the molar teeth have either four or five cusps. Adult humans have 12 molars, in four groups of three at the back of the mouth. The third, rearmost molar in each group is called a wisdom tooth. It is the last tooth to appear, breaking through the front of the gum at about the age of 20, although this varies among individuals and populations, and in many cases the tooth is missing. The human mouth contains upper (maxillary) and lower (mandibular) molars. They are: maxillary first molar, maxillary second molar, maxillary third mol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occlusion (dentistry)
Occlusion, in a dental context, means simply the contact between teeth. More technically, it is the relationship between the maxillary (upper) and mandibular (lower) teeth when they approach each other, as occurs during chewing or at rest. Static occlusion refers to contact between teeth when the jaw is closed and stationary, while dynamic occlusion refers to occlusal contacts made when the jaw is moving. The masticatory system also involves the periodontium, the TMJ (and other skeletal components) and the neuromusculature, therefore the tooth contacts should not be looked at in isolation, but in relation to the overall masticatory system. Anatomy of Masticatory System One cannot fully understand occlusion without an in depth understanding of the anatomy including that of the teeth, TMJ, musculature surrounding this and the skeletal components. The Dentition and Surrounding Structures The human dentition consists of 32 permanent teeth and these are distributed between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incisor
Incisors (from Latin ''incidere'', "to cut") are the front teeth present in most mammals. They are located in the premaxilla above and on the mandible below. Humans have a total of eight (two on each side, top and bottom). Opossums have 18, whereas armadillos, anteaters and other animals in the order Edentata have none. Structure Adult humans normally have eight incisors, two of each type. The types of incisors are: * maxillary central incisor (upper jaw, closest to the center of the lips) * maxillary lateral incisor (upper jaw, beside the maxillary central incisor) * mandibular central incisor (lower jaw, closest to the center of the lips) * mandibular lateral incisor (lower jaw, beside the mandibular central incisor) Children with a full set of deciduous teeth (primary teeth) also have eight incisors, named the same way as in permanent teeth. Young children may have from zero to eight incisors depending on the stage of their tooth eruption and tooth development. Typic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tympanum (zoology)
The tympanum is an external hearing structure in animals such as mammals, birds, some reptiles, some amphibians and some insects. Using sound, vertebrates and many insects are capable of sensing their prey, identifying and locating their predators, warning other individuals, and locating potential mates and rivals by hearing the intentional or unintentional sounds they make. In general, any animal that reacts to sounds or communicates by means of sound, needs to have an auditory mechanism. This typically consists of a membrane capable of vibration known as the tympanum, an air-filled chamber and sensory organs to detect the auditory stimuli. Insects Amphibia Anura In frogs and toads, the tympanum is a large external oval shape membrane made up of nonglandular skin. It is located just behind the eye. It does not process sound waves; it simply transmits them to the inner parts of the amphibian's ear, which is protected from the entry of water and other foreign objects. A frog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiles
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocephalia. About 12,000 living species of reptiles are listed in the Reptile Database. The study of the traditional reptile orders, customarily in combination with the study of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. Reptiles have been subject to several conflicting Taxonomy, taxonomic definitions. In Linnaean taxonomy, reptiles are gathered together under the Class (biology), class Reptilia ( ), which corresponds to common usage. Modern Cladistics, cladistic taxonomy regards that group as Paraphyly, paraphyletic, since Genetics, genetic and Paleontology, paleontological evidence has determined that birds (class Aves), as members of Dinosauria, are more closely related to living crocodilians than to other reptiles, and are thus nested among re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labyrinthodontia
"Labyrinthodontia" (Greek, 'maze-toothed') is an informal grouping of extinct predatory amphibians which were major components of ecosystems in the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras (about 390 to 150 million years ago). Traditionally considered a subclass of the class Amphibia, modern classification systems recognize that labyrinthodonts are not a formal natural group (clade) exclusive of other tetrapods. Instead, they consistute an evolutionary grade (a paraphyletic group), ancestral to living tetrapods such as lissamphibians (modern amphibians) and amniotes (reptiles, mammals, and kin). "Labyrinthodont"-grade vertebrates evolved from lobe-finned fishes in the Devonian, though a formal boundary between fish and amphibian is difficult to define at this point in time. "Labyrinthodont" generally refers to extinct four-limbed tetrapods with a large body size and a crocodile-like lifestyle. The name describes the pattern of infolding of the dentin and enamel of the teeth, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otic Notch
Otic notches are invaginations in the posterior margin of the skull roof, one behind each orbit. Otic notches are one of the features lost in the evolution of amniotes from their tetrapod ancestors. The notches have been interpreted as part of an auditory structure and are often reconstructed as holding a tympanum similar to those seen in modern anurans. Analysis of the ''columella'' (the stapes in amphibians and reptiles) of labyrinthodonts however indicates that it did not function in transmitting low-energy vibrations, thus rendering these animals effectively deaf to airborne sound. The otic notch instead functioned as a spiracle, at least in the early forms.Laurin, M. (1996)Hearing in Stegocephalians from the Tree of Life Web Project The Tree of Life Web Project (ToL) is an Internet project providing information about the diversity and phylogeny of life on Earth. This collaborative peer reviewed project began in 1995, and is written by biologists from around the world. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diadectes Tenuitecus
''Diadectes'' (meaning ''crosswise-biter'') is an extinct genus of large reptiliomorphs or synapsids that lived during the early Permian period (Artinskian-Kungurian stages of the Cisuralian epoch, between 290 and 272 million years ago). ''Diadectes'' was one of the first herbivorous tetrapods, and also one of the first fully terrestrial vertebrates to attain large size. Description ''Diadectes'' was a heavily built animal, up to long, with a thick-boned skull, heavy vertebrae and ribs, massive limb girdles, and short, robust limbs. The nature of the limbs and vertebrae clearly indicates a terrestrial animal. The rib cage was assumed to be barrel-shaped, but new fossils show the ribs were actually sticking out to the sides. High-resolution X-ray microcomputed tomography has revealed an endosseous labyrinth in the opisthotic, prootic, and supraoccipital of ''D. absitus'', along with a well-preserved vestibule, three semicircular canals, and a developed cochlear recess. The sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amniote
Amniotes are tetrapod vertebrate animals belonging to the clade Amniota, a large group that comprises the vast majority of living terrestrial animal, terrestrial and semiaquatic vertebrates. Amniotes evolution, evolved from amphibious Stem tetrapoda, stem tetrapod ancestors during the Carboniferous geologic period, period. Amniota is defined as the smallest crown clade containing humans, the Greek tortoise, and the Nile crocodile. Amniotes are distinguished from the other living tetrapod clade — the anamniote, non-amniote lissamphibians (frogs/toads, salamanders/newts and caecilians) — by: the development of three fetal membranes, extraembryonic membranes (amnion for embryonic protection, chorion for gas exchange, and allantois for metabolic waste disposal or storage); thicker and keratinized skin; rib, costal respiration (breathing by expanding/constricting the rib cage); the presence of adrenal cortex, adrenocortical and chromaffin cell, chromaffin tissues as adrenal g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seymouriamorpha
Seymouriamorpha were a small but widespread group of limbed vertebrates (tetrapods). They have long been considered stem group, stem-amniotes (reptiliomorphs), and most paleontologists still accept this point of view, but some analyses suggest that seymouriamorphs are stem-tetrapods (not more closely related to Amniota than to Lissamphibia). Many seymouriamorphs were terrestrial or semi-aquatic. However, aquatic larvae bearing external gills and grooves from the lateral line system have been found, making them unquestionably non-amniotes. As they matured, they became more terrestrial and reptile-like. They ranged from 30 cm (1 ft) long lizard-sized creatures to the 1.5 m (5 ft) long ''Enosuchus''. If seymouriamorphs are reptiliomorphs, they were the distant relatives of amniotes. Seymouriamorphs are divided into three main groups: Kotlassiidae, Discosauriscidae, and Seymouriidae, which includes the best-known genus, ''Seymouria''. The last seymouriamorphs became Permian-Triassic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |