|
Dhakaiya
The Old Dhakaites ( bn, পুরান ঢাকাইয়া, Puran Dhakaiya) are an Indo-Aryan ethnocultural group viewed as the ''original'' inhabitants of Dhaka. They are sometimes referred to as simply Dhakaiya. Their history dates back to the Mughal period with the migration of Bengali cultivators and merchants to the city. The cultivators came to be known as Kutti and they speak Dhakaiya Kutti, a dialect of Bengali and the merchants came to be known as Khoshbas and speak Dhakaiya Urdu. There are sizeable populations in other parts of Bangladesh. The Dhakaiyas maintain a distinct identity in addition to their Bengali identity, due to cultural, linguistic, geographical and historical reasons. They have been described as a wealthy but very closed-off community; evidently being a minority in their own hometown. It is said that some people living in Greater Dhaka are even unaware of the existence of an Urdu-speaking non- Bihari minority community although their presence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dhakaiya Urdu
Dhakaiya Urdu sometimes referred to as Sobbasi Language, Khosbasi Language and the Language of Dhaka Nawab Family '' is a dialect of Urdu that is native to Old Dhaka and its immediate surrounding areas in Dhaka, Bangladesh. It is spoken by the city's Sobbas community, Khusbas community, Nawab Family, and other native communities. Sobbasi / Khosbasi is not Noun but Adjective. The usage of the language is gradually declining due to negative perceptions following it being forced upon the people of erstwhile East Bengal. Dhakaiya Urdu is one of the two dialects of Urdu spoken in Bangladesh; the other one being the Urdu spoken by the Biharis and Stranded Pakistanis in Bangladesh. Features The dialect differs from Standard Urdu as it takes a number of loanwords from Eastern Bengali, which the dialect's source of origin is geographically surrounded by. The intonations, aspirations and tone of the language is also shifted closer to Eastern Bengali than Standard Urdu. It is d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dhakaiya Kutti Language
Dhakaiya Kutti ( bn, ঢাকাইয়া কুট্টি, Dhakaiya Kutti, Dhakaiya of the rice-huskers), also known as Old Dhakaiya ( bn, পুরান ঢাকাইয়া, Purān Dhākāiyā) or simply Dhakaiya, is a Bengali dialect, spoken by the original Dhakaiyas of Old Dhaka in Bangladesh. This language is largely intelligible with Standard Bengali but has some differences in vocabulary. It is not used in formal settings anymore although historically the local Bais and Bara are said to have used it sometimes. Usage of the dialect is in decline as many families are opting to raise their children to speak in Standard Bengali due to it being the official medium in the country and the influence of Dhaka city as the capital, welcoming migrants from all over the country who are not familiar with their dialect. Features The dialect is an Eastern Bengali-based creole language with a large amount of Persian Language and some Hindustani vocabulary. It has only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Dhaka
Old Dhaka ( bn, পুরান ঢাকা, Puran Dhaka) is a term used to refer to the historic old city of Dhaka, the capital of Bangladesh. It was founded in 1608 as Jahangirabad or Jahangirnagar ( bn, জাহাঙ্গীরনগর, Jahangirnogor, City of Jahangir), the capital of Mughal Province of Bengal and named after the Mughal emperor Jahangir. It is located on the banks of the Buriganga River. It was one of the largest and most prosperous cities of South Asia and the center of the worldwide muslin trade. The then Nawab of Bengal Murshid Quli Khan shifted the capital from Dhaka to Murshidabad in the early-18th century. With the rise of Calcutta (now Kolkata) during the British rule, Dhaka began to decline and came to be known as the "City of Magnificent Ruins". The British however began to develop the modern city from the mid-19th century. Old Dhaka is famous for its variety of foods and amicable living of people of all religions in harmony. The main Mus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Paltan
New Paltan (Azimpur Natun Paltan in Dhaka City Corporation records) is near Dhaka's New Market in Azimpur. Several markets and a number of educational institutions (Dhaka University's Institute of Social Welfare and Research and arts faculty, Dhaka College, Government Laboratory High School, Dhaka City College and Eden Mohila College) are nearby. Border Guards Bangladesh headquarters is in neighbouring Pilkhana. Location New Paltan is situated within the bigger area known as Azimpur within the Police Station Lalbagh. The locality is butted and bounded by, on the North-Headquarters of BGB, previously known as EPR, during 1947–1971, East Pakistan Civil Armed Forces (EPCAF), during 1971 and then BDR after the independence and popularly known as Pilkhana, On the South Azimpur Road, On the East Azimpur graveyard and On the West Headquarters of BGB. This locality is half a kilometer in length, from North to South and quarter kilometer in breadth, from East to West. At the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urdu-speaking People
Native speakers of Urdu are spread across South Asia. The vast majority of them are Muslims of the Hindi–Urdu Belt of northern India, followed by the Deccani people of the Deccan plateau in south-central India (who speak Deccani Urdu) and the Muhajir people of Pakistan. The historical centres of Urdu speakers include Delhi and Lucknow, as well as the Deccan, and more recently, Karachi. Another defunct variety of the language was historically spoken in Lahore but centuries before the name "Urdu" first began to appear. However, little is known about this defunct Lahori variety as it has not been spoken for centuries. Although the majority of Urdu-speakers reside in Pakistan (including 30 million native speakers, and up to 94 million second-language speakers), where Urdu is the national and official language, most speakers who use Urdu as their native tongue live in India, where it is one of 22 official languages. The Urdu-speaking community is also present in other parts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengalis
Bengalis (singular Bengali bn, বাঙ্গালী/বাঙালি ), also rendered as Bangalee or the Bengali people, are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group originating from and culturally affiliated with the Bengal region of South Asia. The current population is divided between the independent country Bangladesh and the Indian states of West Bengal, Tripura and parts of Assam, Meghalaya and Manipur. Most of them speak Bengali, a language from the Indo-Aryan language family. Bengalis are the third-largest ethnic group in the world, after the Han Chinese and Arabs. Thus, they are the largest ethnic group within the Indo-Europeans and the largest ethnic group in South Asia. Apart from Bangladesh and the Indian states of West Bengal, Tripura, Manipur, and Assam's Barak Valley, Bengali-majority populations also reside in India's union territory of Andaman and Nicobar Islands, with significant populations in the Indian states of Arunachal Pradesh, Delhi, Odisha, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the List of countries and dependencies by population density, most densely populated countries in the world, and shares land borders with India to the west, north, and east, and Myanmar to the southeast; to the south it has a coastline along the Bay of Bengal. It is narrowly separated from Bhutan and Nepal by the Siliguri Corridor; and from China by the Indian state of Sikkim in the north. Dhaka, the capital and list of cities and towns in Bangladesh, largest city, is the nation's political, financial and cultural centre. Chittagong, the second-largest city, is the busiest port on the Bay of Bengal. The official language is Bengali language, Bengali, one of the easternmost branches of the Indo-Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajshahi University
The University of Rajshahi, also known as Rajshahi University or RU ( bn, রাজশাহী বিশ্ববিদ্যালয়), is a public co-educational research university in Bangladesh situated near the northern Bangladeshi city of Rajshahi in a campus at Motihar, East of the Rajshahi city center. It is the second largest, in terms of academic activities and campus area and also the second oldest, university in Bangladesh. The university's 60 departments are organized into ten faculties. It is considered one of the top research universities in Bangladesh. Researchers of this university have recently contributed a significant amount of effort and played a key role in bringing back medieval Bangladeshi Muslin fiber. It has a formidable alumnus base around Bangladesh and abroad. Because of its beautiful and well-planned verdurous campus, academic atmosphere and traditional inclination towards outdoor sports, it is popularly known as the Cambridge of the East. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
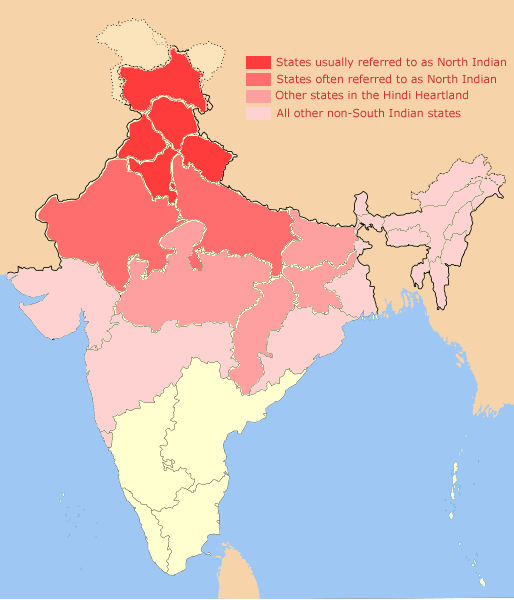
North India
North India is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Central Asia. The term North India has varying definitions. The Ministry of Home Affairs in its Northern Zonal Council Administrative division included the states of Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab and Rajasthan and Union Territories of Chandigarh, Delhi, Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh. The Ministry of Culture in its ''North Culture Zone'' includes the state of Uttarakhand but excludes Delhi whereas the Geological Survey of India includes Uttar Pradesh and Delhi but excludes Rajasthan and Chandigarh. Other states sometimes included are Bihar, Gujarat, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh and West Bengal. North India has been the historical centre of the Mughal Empire, the Delhi Sultanate and the British Indian Empire. It has a diverse c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the dynasty and the empire itself became indisputably Indian. The interests and futures of all concerned were in India, not in ancestral homelands in the Middle East or Central Asia. Furthermore, the Mughal empire emerged from the Indian historical experience. It was the end product of a millennium of Muslim conquest, colonization, and state-building in the Indian subcontinent." For some two hundred years, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus river basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to the highlands of present-day Assam and Bangladesh in the east, and the uplands of the Deccan Plateau in South India. Quote: "The realm so defined and governed was a vast territory of some , ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |