|
DevOps
DevOps is the integration and automation of the software development and information technology operations. DevOps encompasses necessary tasks of software development and can lead to shortening development time and improving the development life cycle. According to Neal Ford, DevOps, particularly through continuous delivery, employs the "Bring the pain forward" principle, tackling tough tasks early, fostering automation and swift issue detection. Software programmers and architects should use fitness functions to keep their software in check. Although debated, DevOps is characterized by key principles: shared ownership, workflow automation, and rapid feedback. From an academic perspective, Len Bass, Ingo Weber, and Liming Zhu—three computer science researchers from the CSIRO and the Software Engineering Institute—suggested defining DevOps as "a set of practices intended to reduce the time between committing a change to a system and the change being placed into normal produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DevOps Research And Assessment
''DevOps Research and Assessment'' (abbreviated to DORA) is a team that is part of Google Cloud that engages in opinion polling of software engineers to conduct research for the DevOps movement. The DORA team was founded by Nicole Forsgren, Jez Humble and Gene Kim. and conducted research for the DevOps company Puppet and later became an independent team (with Puppet continuing to produce reports by a new team). Whilst the founding members have departed, the DORA team continue to publish research in the form of annual ''State of DevOps Reports''. State of DevOps Reports The DORA team began publishing State of DevOps Reports in 2013. The latest DORA State of DevOps Report, published in 2024, surveyed "more than 39,000 professionals across many industries globally." It found AI is having a broad impact on software development, with largely positive results. "Flow," "productivity," and "job satisfaction" are cited among 8 benefits of AI adoption for software developers. The detri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicole Forsgren
Nicole Forsgren is an American technology executive, IT impact expert, and author. In 2020, she was named vice president of Research & Strategy at Microsoft's GitHub and, more recently, Partner at Microsoft Research. She coauthored '' Accelerate: The Science of Lean Software and DevOps,'' which won the Shingo Research and Professional Publication Award in 2019. Education Forsgren holds a Master of Accounting from the University of Arizona’s Eller College of Management and a PhD in Management Information Systems. Career In 2020, Forsgren was hired by Github as the VP of Research and Strategy. She served as Director of Organizational Performance and Analytics at Chef Software from 2014 to 2015. Towards the end of 2015, she left Chef and, along with Jez Humble and Gene Kim, founded DevOps Research and Assessment LLC (DORA) with Jez Humble and Gene Kim. DORA is known for the annual ''State of DevOps'' report, and their ''DevOps Scorecard''. Forsgren served as CEO. In 2018, D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuous Delivery
Continuous delivery (CD) is a software engineering approach in which teams produce software in short cycles, ensuring that the software can be reliably released at any time. It aims at building, testing, and releasing software with greater speed and frequency. The approach helps reduce the cost, time, and risk of delivering changes by allowing for more incremental updates to applications in production. A straightforward and repeatable deployment process is important for continuous delivery. Principles According to Neal Ford, continuous delivery adopts "Bring the pain forward," tackling tough tasks early, fostering automation and swift issue detection. Continuous delivery treats the commonplace notion of a ''deployment pipeline'' as a lean Poka-Yoke: a set of validations through which a piece of software must pass on its way to release. Code is compiled if necessary and then packaged by a build server every time a change is committed to a source control repository, then teste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Development
Software development is the process of designing and Implementation, implementing a software solution to Computer user satisfaction, satisfy a User (computing), user. The process is more encompassing than Computer programming, programming, writing source code, code, in that it includes conceiving the goal, evaluating feasibility, analyzing software requirements, requirements, software design, design, software testing, testing and software release life cycle, release. The process is part of software engineering which also includes management, organizational management, Software project management, project management, configuration management and other aspects. Software development involves many skills and job specializations including software programmer, programming, software test, testing, Technical writing, documentation, graphic design, user support, marketing, and fundraising. Software development involves many software tools, tools including: compiler, integrated develo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
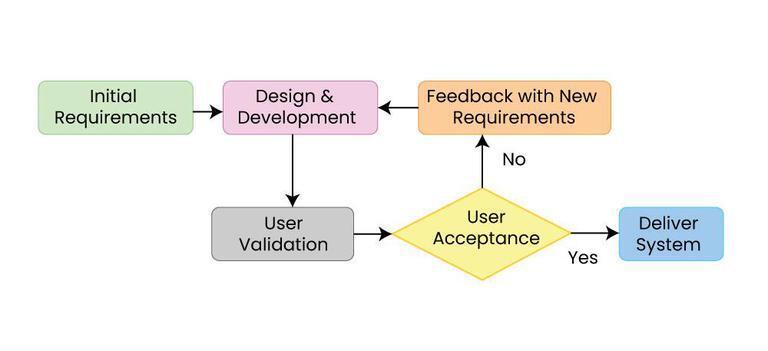
Software Development Process
In software engineering, a software development process or software development life cycle (SDLC) is a process of planning and managing software development. It typically involves dividing software development work into smaller, parallel, or sequential steps or sub-processes to improve design and/or product management. The methodology may include the pre-definition of specific deliverables and artifacts that are created and completed by a project team to develop or maintain an application. Most modern development processes can be vaguely described as agile. Other methodologies include waterfall, prototyping, iterative and incremental development, spiral development, rapid application development, and extreme programming. A life-cycle "model" is sometimes considered a more general term for a category of methodologies and a software development "process" is a particular instance as adopted by a specific organization. For example, many specific software development processe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Len Bass
Leonard Joel (Len) Bass (born c.1943) is an American software engineer, Emeritus professor and former researcher at the Software Engineering Institute (SEI), particularly known for his contributions on software architecture in practice. Biography Bass received his Ph.D. degree in Computer Science from Purdue University in 1970 under the supervision of Paul Ruel Young with the thesis, entitled "Hierarchies based on computational complexity and irregularities of class determining measured sets." Bass was appointed Professor of Computer Science at the University of Rhode Island in 1970. In 1986, he moved to the Software Engineering Institute at Carnegie Mellon University, where he started as head of the user-interface software group, and later focused on the analysis of software architectures. Since 2011, he has been Senior Principal Researcher at NICTA (National ICT Australia). Len Bass was awarded the ''Software Development Magazines Jolt Productivity Award twice in 1999 and 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puppet (software)
Puppet is a software configuration management tool developed used to manage stages of the IT infrastructure lifecycle. Puppet uses an open-core model; its free-software version was released under version 2 of the GNU General Public License (GPL) until version 2.7.0, and later releases use the Apache License, while Puppet Enterprise uses a Proprietary software, proprietary license. Puppet and Puppet Enterprise operate on multiple Unix-like systems (including Linux, Solaris (operating system), Solaris, Berkeley Software Distribution, BSD, Mac OS X, AIX, HP-UX) and has Microsoft Windows support. Puppet itself is written in Ruby (programming language), Ruby. Facter, Puppet’s cross-platform system profiling library, is written in C++. Puppet Server and Puppet DB are written in Clojure. It is developed by Puppet Inc., which is owned by Perforce, which is owned in turn by private equity firms. Design Puppet consists of a custom Declarative programming, declarative language to desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
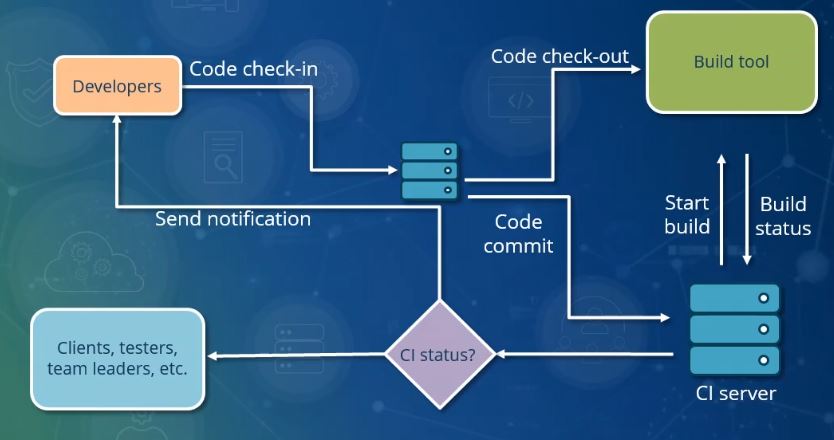
Continuous Integration
Continuous integration (CI) is the practice of integrating source code changes frequently and ensuring that the integrated codebase is in a workable state. Typically, developers Merge (version control), merge changes to an Branching (revision control), integration branch, and an automated system Software build, builds and software testing, tests the software system. Often, the automated process runs on each Commit (version control), commit or runs on a schedule such as once a day. Grady Booch first proposed the term CI in Booch method, 1991, although he did not advocate integrating multiple times a day, but later, CI came to include that aspect. History The earliest known work (1989) on continuous integration was the Infuse environment developed by G. E. Kaiser, D. E. Perry, and W. M. Schell. In 1994, Grady Booch used the phrase continuous integration in ''Object-Oriented Analysis and Design with Applications'' (2nd edition) to explain how, when developing using micro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ITIL
ITIL (previously and also known as Information Technology Infrastructure Library) is a framework with a set of practices (previously processes) for IT activities such as IT service management (ITSM) and IT asset management (ITAM) that focus on aligning IT services with the needs of the business. ITIL describes best practices, including processes, procedures, tasks, and checklists which are neither organization-specific nor technology-specific. It is designed to allow organizations to establish a baseline and can be used to demonstrate compliance and to measure improvements. There is no formal independent third-party compliance assessment available to demonstrate ITIL compliance in an organization. Certification in ITIL is only available to individuals and not organizations. Since 2021, the ITIL trademark has been owned by PeopleCert. History Responding to growing dependence on IT, the UK Government's Central Computer and Telecommunications Agency (CCTA) in the 1980s develo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Programmer
A programmer, computer programmer or coder is an author of computer source code someone with skill in computer programming. The professional titles ''software developer'' and ''software engineer'' are used for jobs that require a programmer. Identification Sometimes a programmer or job position is identified by the language used or target platform. For example, assembly programmer, web developer. Job title The job titles that include programming tasks have differing connotations across the computer industry and to different individuals. The following are notable descriptions. A ''software developer'' primarily implements software based on specifications and fixes bugs. Other duties may include reviewing code changes and testing. To achieve the required skills for the job, they might obtain a computer science or associate degree, attend a programming boot camp or be self-taught. A ''software engineer'' usually is responsible for the same tasks as a dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Toyota Way
The Toyota Way is a set of principles defining the organizational culture of Toyota Motor Corporation. The company formalized the Toyota Way in 2001, after decades of academic research into the Toyota Production System and its implications for lean manufacturing as a methodology that other organizations could adopt. The two pillars of the Toyota Way are respect for people and continuous improvement. Jeffrey K. Liker popularized the philosophy in his 2004 book, ''The Toyota Way: 14 Management Principles from the World's Greatest Manufacturer.'' Subsequent research has explored the extent to which the Toyota Way can be applied in other contexts. Background The principles were first collated into a single document in the company's pamphlet "The Toyota Way 2001", to help codify the company's organizational culture. The philosophy was subsequently analyzed in the 2004 book ''The Toyota Way'' by industrial engineering researcher Jeffrey Liker and has received attention in business ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |