|
Determination Of Equilibrium Constants
Equilibrium constants are determined in order to quantify chemical equilibria. When an equilibrium constant is expressed as a concentration quotient, :K=\frac it is implied that the activity quotient is constant. For this assumption to be valid, equilibrium constants must be determined in a medium of relatively high ionic strength. Where this is not possible, consideration should be given to possible activity variation. The equilibrium expression above is a function of the concentrations etc. of the chemical species in equilibrium. The equilibrium constant value can be determined if any one of these concentrations can be measured. The general procedure is that the concentration in question is measured for a series of solutions with known analytical concentrations of the reactants. Typically, a titration is performed with one or more reactants in the titration vessel and one or more reactants in the burette. Knowing the analytical concentrations of reactants initially i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equilibrium Constant
The equilibrium constant of a chemical reaction is the value of its reaction quotient at chemical equilibrium, a state approached by a dynamic chemical system after sufficient time has elapsed at which its composition has no measurable tendency towards further change. For a given set of reaction conditions, the equilibrium constant is independent of the initial analytical concentrations of the reactant and product species in the mixture. Thus, given the initial composition of a system, known equilibrium constant values can be used to determine the Chemical equilibrium#Composition of a mixture, composition of the system at equilibrium. However, reaction parameters like temperature, solvent, and ionic strength may all influence the value of the equilibrium constant. A knowledge of equilibrium constants is essential for the understanding of many chemical systems, as well as the biochemical processes such as oxygen transport by hemoglobin in blood and acid–base homeostasis in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
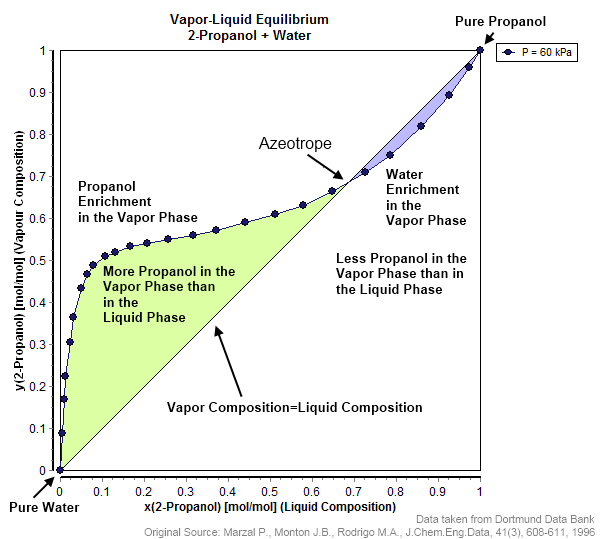
Azeotrope
An azeotrope () or a constant heating point mixture is a mixture of two or more liquids whose proportions cannot be changed by simple distillation.Moore, Walter J. ''Physical Chemistry'', 3rd e Prentice-Hall 1962, pp. 140–142 This happens because when an azeotrope is boiled, the vapour has the same proportions of constituents as the unboiled mixture. Knowing an azeotrope's behavior is important for distillation. Each azeotrope has a characteristic boiling point. The boiling point of an azeotrope is either less than the boiling point temperatures of any of its constituents (a positive azeotrope), or greater than the boiling point of any of its constituents (a negative azeotrope). For both positive and negative azeotropes, it is not possible to separate the components by fractional distillation and azeotropic distillation is usually used instead. For technical applications, the pressure-temperature-composition behavior of a mixture is the most important, but other important ther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerold Schwarzenbach
Gerold Karl Schwarzenbach (15 March 1904 — 20 May 1978) was a Swiss chemist. Schwarzenbach was born and grew up in Horgen, Switzerland. He studied chemistry at the ETH Zurich and graduated in 1928 with his dissertation ''Studien über die Salzbildung von Beizenfarbstoffen'' (Studies on the formation of pickling salt dyes). From 1930 to 1955 he was a lecturer and later professor of special inorganic and analytical chemistry at the University of Zurich. He retired in 1973. One of his main research topics was coordination chemistry. Gerold was substantially involved in the study of EDTA and the involvement of ligands. Honours and awards *1963 Marcel Benoist Prize.Marcel-Benoist-Preis – Die bisherigen Preisträger: Gerold Schwarzenbach'' *1966 Paul Karrer Gold Medal *1967 Torbern Bergman Medal.''http://www.dac-euchems.org/events/reportanalysdagarna03.pdf'' *1971 Honorary doctorate from the University of Berne The University of Bern (, , ) is a public research university in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isothermal Titration Calorimetry
In chemical thermodynamics, isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) is a physical technique used to determine the Conjugate variables (thermodynamics), thermodynamic parameters of interactions in Solution (chemistry), solution. ITC is the only technique capable comprehensively characterizing Thermodynamics, thermodynamic and even Kinetic energy, kinetic profile of the interaction by simultaneously determining binding constants (K_a), reaction stoichiometry (n), enthalpy (\Delta H), Gibbs free energy (\Delta G) and entropy (\Delta S) within a single experiment. It consists of two cells which are enclosed in an adiabatic jacket. The compounds to be studied are placed in the sample cell, while the other cell, the reference cell, is used as a Treatment and control groups, control and contains the Buffer solution, buffer in which the sample is dissolved. The technique quantifies the heat released or absorbed during the binding process by incrementally adding one reactant (via a syringe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enthalpy
Enthalpy () is the sum of a thermodynamic system's internal energy and the product of its pressure and volume. It is a state function in thermodynamics used in many measurements in chemical, biological, and physical systems at a constant external pressure, which is conveniently provided by the large ambient atmosphere. The pressure–volume term expresses the work (physics), work W that was done against constant external pressure P_\text to establish the system's physical dimensions from V_\text=0 to some final volume V_\text (as W=P_\text\Delta V), i.e. to make room for it by displacing its surroundings. The pressure-volume term is very small for solids and liquids at common conditions, and fairly small for gases. Therefore, enthalpy is a stand-in for energy in chemical systems; Bond energy, bond, Lattice energy, lattice, solvation, and other chemical "energies" are actually enthalpy differences. As a state function, enthalpy depends only on the final configuration of internal e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
Proton nuclear magnetic resonance (proton NMR, hydrogen-1 NMR, or 1H NMR) is the application of nuclear magnetic resonance in NMR spectroscopy with respect to hydrogen-1 Atomic nucleus, nuclei within the molecules of a substance, in order to determine the structure of its molecules. In samples where natural hydrogen (H) is used, practically all the hydrogen consists of the isotope 1H (hydrogen-1; i.e. having a proton for a nucleus). Simple NMR spectra are recorded in Solution (chemistry), solution, and solvent protons must not be allowed to interfere. deuterium, Deuterated (deuterium = 2H, often symbolized as D) solvents especially for use in NMR are preferred, e.g. heavy water, deuterated water, D2O, deuterated acetone, (CD3)2CO, deuterated methanol, CD3OD, deuterated dimethyl sulfoxide, (CD3)2SO, and deuterated chloroform, CDCl3. However, a solvent without hydrogen, such as carbon tetrachloride, CCl4 or carbon disulfide, CS2, may also be used. Historically, deuterated solvents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ion-selective Electrode
An ion-selective electrode (ISE), also known as a specific ion electrode (SIE), is a simple membrane-based potentiometric device which measures the activity of ions in solution. It is a transducer (or sensor) that converts the change in the concentration of a specific ion dissolved in a solution into an electrical potential. ISE is a type of sensor device that senses changes in signal based on the surrounding environment through time. This device will have an input signal, a property that we wish to quantify, and an output signal, a quantity we can register. In this case, ion selective electrode are electrochemical sensors that give potentiometric signals. The voltage is theoretically dependent on the logarithm of the ionic activity, according to the Nernst equation. Analysis with ISEs expands throughout a range of technological fields such as biology, chemistry, environmental science and other industrial workplaces like agriculture. Ion-selective electrodes are used in analytical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon-13 NMR
Carbon-13 (C13) nuclear magnetic resonance (most commonly known as carbon-13 NMR spectroscopy or 13C NMR spectroscopy or sometimes simply referred to as carbon NMR) is the application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy to carbon. It is analogous to proton NMR ( NMR) and allows the identification of carbon atoms in an organic molecule just as proton NMR identifies hydrogen atoms. 13C NMR detects only the isotope. The main carbon isotope, does not produce an NMR signal. Although ca. 1 mln. times less sensitive than 1H NMR spectroscopy, 13C NMR spectroscopy is widely used for characterizing organic and organometallic compounds, primarily because 1H-decoupled 13C-NMR spectra are more simple, have a greater sensitivity to differences in the chemical structure, and, thus, are better suited for identifying molecules in complex mixtures. At the same time, such spectra lack quantitative information about the atomic ratios of different types of carbon nuclei, because n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citric Acid
Citric acid is an organic compound with the formula . It is a Transparency and translucency, colorless Weak acid, weak organic acid. It occurs naturally in Citrus, citrus fruits. In biochemistry, it is an intermediate in the citric acid cycle, which occurs in the metabolism of all aerobic organisms. More than two million tons of citric acid Commodity chemicals, are manufactured every year. It is used widely as acidifier, flavoring, preservative, and chelating agent. A citrate is a derivative of citric acid; that is, the salt (chemistry), salts, esters, and the polyatomic ion, polyatomic anion found in solutions and salts of citric acid. An example of the former, a salt is trisodium citrate; an ester is triethyl citrate. When citrate anion, trianion is part of a salt, the formula of the citrate trianion is written as or . Natural occurrence and industrial production Citric acid occurs in a variety of fruits and vegetables, most notably Citrus, citrus fruits. Lemons and Lime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroxyl
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy groups. Both the negatively charged anion , called hydroxide, and the neutral radical , known as the hydroxyl radical, consist of an unbonded hydroxy group. According to IUPAC definitions, the term ''hydroxyl'' refers to the hydroxyl radical () only, while the functional group is called a ''hydroxy group''. Properties Water, alcohols, carboxylic acids, and many other hydroxy-containing compounds can be readily deprotonated due to a large difference between the electronegativity of oxygen (3.5) and that of hydrogen (2.1). Hydroxy-containing compounds engage in intermolecular hydrogen bonding increasing the electrostatic attraction between molecules and thus to higher boiling and melting points than found for compounds that lack thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beer–Lambert Law
The Beer–Bouguer–Lambert (BBL) extinction law is an empirical relationship describing the attenuation in intensity of a radiation beam passing through a macroscopically homogenous medium with which it interacts. Formally, it states that the intensity of radiation decays exponentially in the absorbance of the medium, and that said absorbance is proportional to the length of beam passing through the medium, the concentration of interacting matter along that path, and a constant representing said matter's propensity to interact. The extinction law's primary application is in chemical analysis, where it underlies the Beer–Lambert law, commonly called Beer's law. Beer's law states that a beam of visible light passing through a chemical solution of fixed geometry experiences absorption proportional to the solute concentration. Other applications appear in physical optics, where it quantifies astronomical extinction and the absorption of photons, neutrons, or rarefied gas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |