|
Desonide Phosphate
Desonide (INN) is a low-potency topical corticosteroid anti-inflammatory that has been available since the 1970s. It is primarily used to treat atopic dermatitis (eczema), seborrheic dermatitis, contact dermatitis and psoriasis Psoriasis is a long-lasting, noncontagious autoimmune disease characterized by patches of abnormal skin. These areas are red, pink, or purple, dry, itchy, and scaly. Psoriasis varies in severity from small localized patches to complete b ... in both adults and children. It has a fairly good safety profile and is available as a cream, ointment, lotion, and as a foam under the tradename Verdeso Foam. Other trade names for creams, lotions, and ointments include Tridesilon, DesOwen, Desonate. It is a group VI corticosteroid under US classification, the second least potent group. Medical uses Desonide is a prescription topical treatment for redness, swelling, itching, and discomfort of various skin conditions. Regardless of the vehicle used, desoni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potency (pharmacology)
In pharmacology, potency or biological potency is a measure of a drug's biological activity expressed in terms of the dose required to produce a pharmacological effect of given intensity. A highly potent drug (e.g., fentanyl, clonazepam, risperidone, benperidol, bumetanide) evokes a given response at low concentrations, while a drug of lower potency (e.g. morphine, alprazolam, ziprasidone, haloperidol, furosemide) evokes the same response only at higher concentrations. Higher potency does not necessarily mean greater effectiveness nor more side effects nor less side effects. Types of potency The International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology (IUPHAR) has stated that "potency is an imprecise term that should always be further defined", and lists of types of potency as follows: Miscellaneous Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) is one of the most potent psychoactive drug A psychoactive drug, psychopharmaceutical, mind-altering drug, consciousness-altering drug, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involved in a wide range of physiological processes, including stress response, immune response, and regulation of inflammation, carbohydrate metabolism, protein catabolism, blood electrolyte levels, and behavior. Some common naturally occurring steroid hormones are cortisol (), corticosterone (), cortisone () and aldosterone () (cortisone and aldosterone are isomers). The main corticosteroids produced by the adrenal cortex are cortisol and aldosterone. The etymology of the '' cortico-'' part of the name refers to the adrenal cortex, which makes these steroid hormones. Thus a corticosteroid is a "cortex steroid". Classes * Glucocorticoids such as cortisol affect carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism, and have anti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis (AD), also known as atopic eczema, is a long-term type of inflammation of the skin. Atopic dermatitis is also often called simply eczema but the same term is also used to refer to dermatitis, the larger group of skin conditions. Atopic dermatitis results in puritis, itchy, red, swollen, and cracked skin. Clear fluid may come from the affected areas, which can thicken over time. Atopic dermatitis affects about 20% of people at some point in their lives. It is more common in younger children. Females are affected slightly more often than males. Many people outgrow the condition. While the condition may occur at any age, it typically starts in childhood, with changing severity over the years. In children under one year of age, the face and limbs and much of the body may be affected. As children get older, the areas on the insides of the knees and folds of the elbows and around the neck are most commonly affected. In adults, the hands and feet are commonly affec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eczema
Dermatitis is a term used for different types of skin inflammation, typically characterized by itchiness, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened. The area of skin involved can vary from small to covering the entire body. Dermatitis is also called eczema but the same term is often used for the most common type of skin inflammation, atopic dermatitis. The exact cause of the condition is often unclear. Cases may involve a combination of allergy and poor venous return. The type of dermatitis is generally determined by the person's history and the location of the rash. For example, irritant dermatitis often occurs on the hands of those who frequently get them wet. Allergic contact dermatitis occurs upon exposure to an allergen, causing a hypersensitivity reaction in the skin. Prevention of atopic dermatitis is typically with essential fatty acids, and may be treated with moisturi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
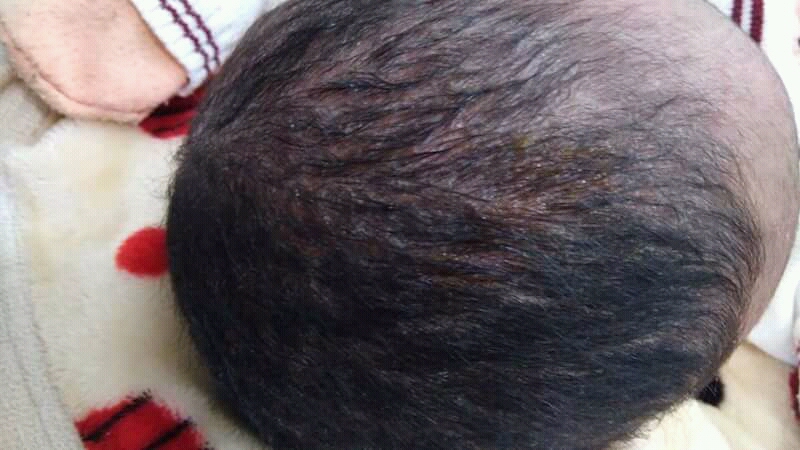
Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrhoeic dermatitis (also spelled seborrheic dermatitis in American English) is a long-term skin disorder. Symptoms include flaky, scaly, greasy, and occasionally itchy and inflamed skin. Areas of the skin rich in sebum, oil-producing glands are often affected including the scalp, face, and chest. It can result in social or self-esteem problems. In babies, when the scalp is primarily involved, it is called cradle cap. Mild seborrhoeic dermatitis of the scalp may be described in lay terms as dandruff due to the dry, flaky character of the skin. However, as dandruff may refer to any dryness or scaling of the scalp, not all dandruff is seborrhoeic dermatitis. Seborrhoeic dermatitis is sometimes inaccurately referred to as seborrhoea. The cause is unclear but believed to involve a number of genetic and environmental factors. Risk factors for seborrhoeic dermatitis include immunocompromised, poor immune function, Parkinson's disease, and alcoholic pancreatitis. The condition ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is a type of acute or chronic inflammation of the skin caused by exposure to chemical or physical agents. Symptoms of contact dermatitis can include itchy or dry skin, a red rash, bumps, blisters, or swelling. These rashes are not contagious or life-threatening, but can be very uncomfortable. Contact dermatitis results from either exposure to allergens ( allergic contact dermatitis), or irritants ( irritant contact dermatitis). Allergic contact dermatitis involves a delayed type of hypersensitivity and previous exposure to an allergen to produce a reaction. Irritant contact dermatitis is the most common type and represents 80% of all cases. It is caused by prolonged exposure to irritants, leading to direct injury of the epidermal cells of the skin, which activates an immune response, resulting in an inflammatory cutaneous reaction. Phototoxic dermatitis occurs when the allergen or irritant is activated by sunlight. Diagnosis of allergic contact dermati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a long-lasting, noncontagious autoimmune disease characterized by patches of abnormal skin. These areas are red, pink, or purple, dry, itchy, and scaly. Psoriasis varies in severity from small localized patches to complete body coverage. Injury to the skin can trigger psoriatic skin changes at that spot, which is known as the Koebner phenomenon. The five main types of psoriasis are plaque, guttate, inverse, pustular, and erythrodermic. Plaque psoriasis, also known as psoriasis vulgaris, makes up about 90% of cases. It typically presents as red patches with white scales on top. Areas of the body most commonly affected are the back of the forearms, shins, navel area, and scalp. Guttate psoriasis has drop-shaped lesions. Pustular psoriasis presents as small, noninfectious, pus-filled blisters. Inverse psoriasis forms red patches in skin folds. Erythrodermic psoriasis occurs when the rash becomes very widespread and can develop from any of the other types. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetonides
In organic chemistry, an acetonide is the functional group composed of the cyclic ketal of a diol with acetone. The more systematic name for this structure is an isopropylidene ketal. Acetonide is a common protecting group for 1,2- and 1,3-diols. The protecting group can be removed by hydrolysis of the ketal using dilute aqueous acid. Example The acetonides of small di- and triols, as well as many sugars and sugar alcohols, are common. The hexaol mannitol reacts with 2,2-dimethoxypropane to give the bis-acetonide, which oxidizes to give the acetonide of glyceraldehyde: :(CHOHCHOHCH2OH)2 + 2 (MeO)2CMe2 → (CHOHCHCH2O2CMe2)2 + 4 MeOH :(CHOHCHOCH2OCMe2)2 + → 2 OCHCHCH2O2CMe2 + H2O An example of its use as a protecting group in a complex organic synthesis is the Nicolaou Taxol total synthesis. It is a common protecting group for sugars and sugar alcohols, a simple example being solketal. The acetonides of corticosteroid are used in dermatology, because their increased lipo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corticosteroid Cyclic Ketals
This is a list of corticosteroid cyclic ketals, including cyclic ketals (cyclic acetals) of steroidal glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids. They are almost all C16α,17α cyclic ketals of corticosteroids. One of the most widely used corticosteroid cyclic ketals is triamcinolone acetonide, which is the C16α,17α acetonide (cyclic ketone with acetone) of triamcinolone. This list mostly does not include esters of corticosteroid cyclic ketals, which are listed here instead. Acetonides Acetonides (cyclic ketals with acetone): * Cicortonide * Ciprocinonide (fluocinolone acetonide cyclopropylcarboxylate) * Descinolone acetonide (desoxytriamcinolone acetonide) * Desonide (desfluorotriamcinolone acetonide) * Drocinonide * Fluclorolone acetonide (flucloronide) * Fludroxycortide (flurandrenolide, flurandrenolone) * Flumoxonide * Flunisolide * Fluocinolone acetonide * Fluocinonide (fluocinolone acetonide 21-acetate) * Flupamesone (triamcinolone acetonide metembonate) * F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involved in a wide range of physiological processes, including stress response, immune response, and regulation of inflammation, carbohydrate metabolism, protein catabolism, blood electrolyte levels, and behavior. Some common naturally occurring steroid hormones are cortisol (), corticosterone (), cortisone () and aldosterone () (cortisone and aldosterone are isomers). The main corticosteroids produced by the adrenal cortex are cortisol and aldosterone. The etymology of the '' cortico-'' part of the name refers to the adrenal cortex, which makes these steroid hormones. Thus a corticosteroid is a "cortex steroid". Classes * Glucocorticoids such as cortisol affect carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism, and have anti-inflam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |