|
Descending Palatine Vessels
The descending palatine artery is a branch of the third part of the maxillary artery supplying the hard and soft palate. Course It descends through the greater palatine canal with the greater and lesser palatine branches of the pterygopalatine ganglion, and, emerging from the greater palatine foramen, runs forward in a groove on the medial side of the alveolar border of the hard palate to the incisive canal; the terminal branch of the artery passes upward through this canal to anastomosis, anastomose with the sphenopalatine artery. Branches Branches are distributed to the gums, the palatine glands, and the mucous membrane of the roof of the mouth; while in the Greater palatine canal, pterygopalatine canal it gives off twigs which descend in the lesser palatine canals to supply the soft palate and palatine tonsil, anastomosing with the ascending palatine artery. According to Terminologia Anatomica, the descending palatine artery branches into the greater palatine artery and lesser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxillary Artery
The maxillary artery supplies deep structures of the face. It branches from the external carotid artery just deep to the neck of the mandible. Structure The maxillary artery, the larger of the two terminal branches of the external carotid artery, arises behind the neck of the mandible, and is at first imbedded in the substance of the parotid gland; it passes forward between the ramus of the mandible and the sphenomandibular ligament, and then runs, either superficial or deep to the lateral pterygoid muscle, to the pterygopalatine fossa. It supplies the deep structures of the face, and may be divided into mandibular, pterygoid, and pterygopalatine portions. First portion The ''first'' or ''mandibular '' or ''bony'' portion passes horizontally forward, between the neck of the mandible and the sphenomandibular ligament, where it lies parallel to and a little below the auriculotemporal nerve; it crosses the inferior alveolar nerve, and runs along the lower border of the lateral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
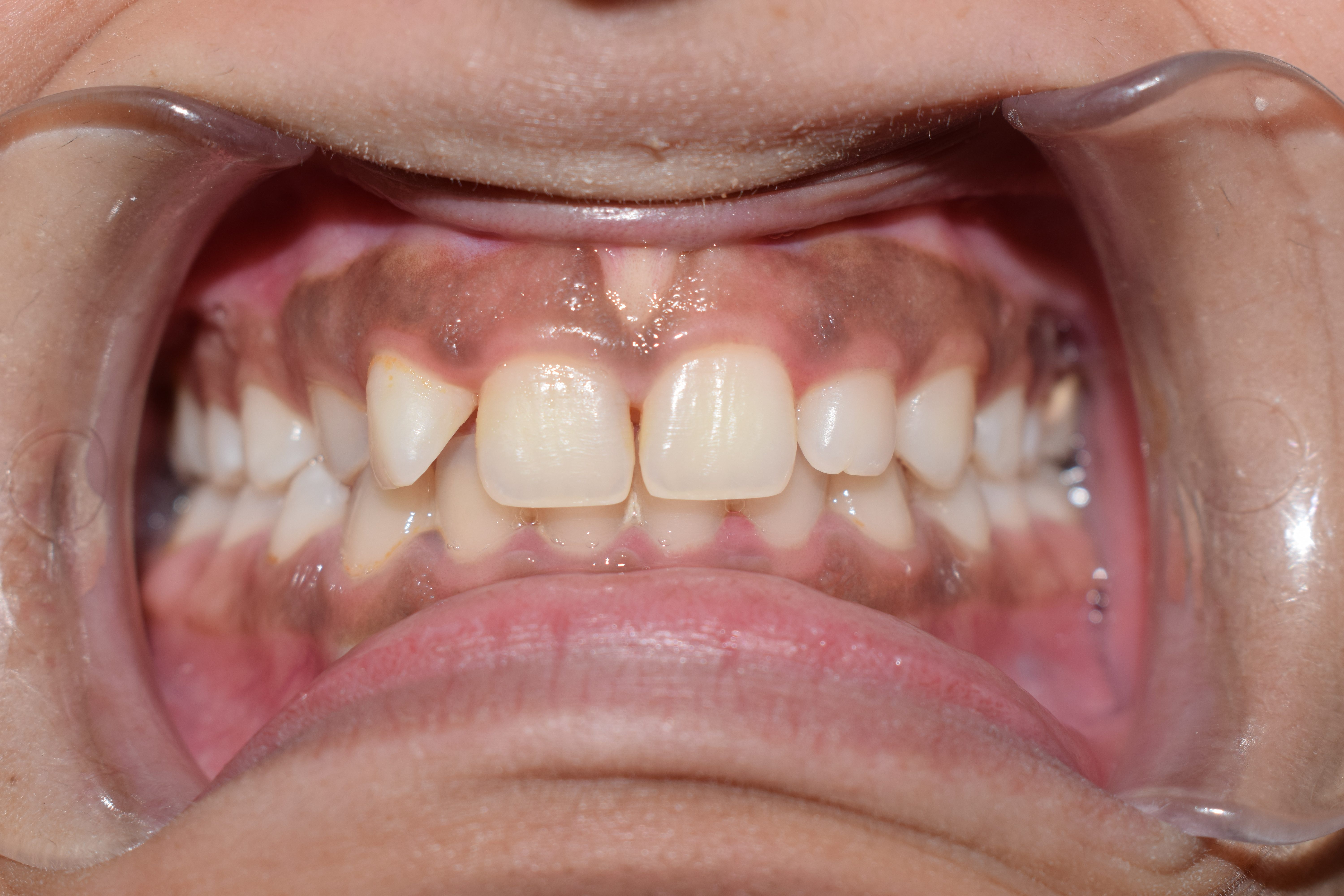
Roof Of The Mouth
The palate () is the roof of the mouth in humans and other mammals. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity. A similar structure is found in crocodilians, but in most other tetrapods, the oral and nasal cavities are not truly separated. The palate is divided into two parts, the anterior, bony hard palate and the posterior, fleshy soft palate (or velum). Structure Innervation The maxillary nerve branch of the trigeminal nerve supplies sensory innervation to the palate. Development The hard palate forms before birth. Variation If the fusion is incomplete, a cleft palate results. Function When functioning in conjunction with other parts of the mouth, the palate produces certain sounds, particularly velar, palatal, palatalized, postalveolar, alveolopalatal, and uvular consonants. History Etymology The English synonyms palate and palatum, and also the related adjective palatine (as in palatine bone), are all from the Latin ''palatum'' via Old French ''palat' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesser Palatine Arteries
The lesser palatine arteries are arteries of the head. It is a branch of the descending palatine artery. They supply the palatine tonsils and the soft palate. Structure The lesser palatine arteries are branches of the descending palatine artery. They go through the lesser palatine foramina. They anastomose with the ascending pharyngeal artery. Function The lesser palatine arteries give off tonsillary branches to supply the palatine tonsils. They also gives off mucosal branches that usually supply the soft palate The soft palate (also known as the velum, palatal velum, or muscular palate) is, in mammals, the soft tissue constituting the back of the roof of the mouth. The soft palate is part of the palate of the mouth; the other part is the hard palate. ..., and potentially the hard palate. See also * Lesser palatine nerve References Arteries of the head and neck {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Palatine Artery
The greater palatine artery is a branch of the descending palatine artery (a terminal branch of the maxillary artery) and contributes to the blood supply of the hard palate and nasal septum. Course The descending palatine artery branches off of the maxillary artery in the pterygopalatine fossa and descends through the greater palatine canal along with the greater palatine nerve (from the pterygopalatine ganglion). Once emerging from the greater palatine foramen, it changes names to the greater palatine artery and begins to supply the hard palate. As it terminates it travels through the incisive canal to anastomose with the sphenopalatine artery to supply the nasal septum The nasal septum () separates the left and right airways of the nasal cavity, dividing the two nostrils. It is depressed by the depressor septi nasi muscle. Structure The fleshy external end of the nasal septum is called the columella or col .... See also * Greater palatine nerve References E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terminologia Anatomica
''Terminologia Anatomica'' is the international standard for human anatomical terminology. It is developed by the Federative International Programme on Anatomical Terminology, a program of the International Federation of Associations of Anatomists (IFAA). The second edition was released in 2019 and approved and adopted by the IFAA General Assembly in 2020. ''Terminologia Anatomica'' supersedes the previous standard, '' Nomina Anatomica''. It contains terminology for about 7500 human anatomical structures. Categories of anatomical structures ''Terminologia Anatomica'' is divided into 16 chapters grouped into five parts. The official terms are in Latin. Although equivalent English-language terms are provided, as shown below, only the official Latin terms are used as the basis for creating lists of equivalent terms in other languages. Part I Chapter 1: General anatomy # General terms # Reference planes # Reference lines # Human body positions # Movements # Parts of human bod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascending Palatine Artery
The ascending palatine artery is an artery in the head that branches off the facial artery and runs up the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle. Structure The ascending palatine artery arises close to the origin of the facial artery and passes up between the styloglossus and stylopharyngeus to the side of the pharynx along which it is continued between the superior pharyngeal constrictor and the medial pterygoid muscle to near the base of the skull. It divides near the levator veli palatini muscle into two branches: one supplies and follows the course of this muscle, and, winding over the upper border of the superior pharyngeal constrictor, supplies the soft palate and the palatine glands, anastomosing with its fellow of the opposite side and with the descending palatine branch of the maxillary artery; the other pierces the superior pharyngeal constrictor and supplies the palatine tonsil and auditory tube, anastomosing with the tonsillar branch of the facial artery and the ascen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palatine Tonsil
Palatine tonsils, commonly called the tonsils and occasionally called the faucial tonsils, are tonsils located on the left and right sides at the back of the throat, which can often be seen as flesh-colored, pinkish lumps. Tonsils only present as "white lumps" if they are inflamed or infected with symptoms of exudates (pus drainage) and severe swelling. Tonsillitis is an inflammation of the tonsils and will often, but not necessarily, cause a sore throat and fever. In chronic cases tonsillectomy may be indicated. Structure The palatine tonsils are located in the isthmus of the fauces, between the palatoglossal arch and the palatopharyngeal arch of the soft palate. The palatine tonsil is one of the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissues (MALT), located at the entrance to the upper respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts to protect the body from the entry of exogenous material through mucosal sites. In consequence it is a site of, and potential focus for, infections, and is o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesser Palatine Canals
The lesser palatine canals (also accessory palatine canals) are passages in the palatine bone that carry the lesser and middle palatine nerves and vessels. Structure The lesser palatine canals start from the greater palatine canal, and run with them, also opening into the roof of the oral cavity. Their openings are known as the lesser palatine foramina, and they transmit the lesser palatine artery, vein, and nerve, as well as the middle palatine vessels and nerve. See also * Pterygopalatine fossa In human anatomy, the pterygopalatine fossa (sphenopalatine fossa) is a fossa in the skull. A human skull contains two pterygopalatine fossae—one on the left side, and another on the right side. Each fossa is a cone-shaped paired depression deep ... References Bones of the head and neck {{musculoskeletal-stub ro:Canale palatine mici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Palatine Canal
The greater palatine canal (or pterygopalatine canal) is a passage in the skull that transmits the descending palatine artery, vein, and greater and lesser palatine nerves between the pterygopalatine fossa and the oral cavity. Structure The greater palatine canal starts on the inferior aspect of the pterygopalatine fossa. It goes through the maxilla and palatine bones to reach the palate, ending at the greater palatine foramen. From this canal, accessory canals branch off; these are known as the lesser palatine canals. The canal is formed by a vertical groove on the posterior part of the maxillary surface of the palatine bone; it is converted into a canal by articulation with the maxilla The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The .... The canal transmits the descen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palatine Glands
The palatine glands form a continuous layer on the posterior surface of the mucous membrane of the soft palate and around the uvula The palatine uvula, usually referred to as simply the uvula, is a conic projection from the back edge of the middle of the soft palate, composed of connective tissue containing a number of racemose glands, and some muscular fibers. It also cont .... They are pure mucous glands. References External links * Glands {{Anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hard Palate
The hard palate is a thin horizontal bony plate made up of two bones of the facial skeleton, located in the roof of the mouth. The bones are the palatine process of the maxilla and the horizontal plate of palatine bone. The hard palate spans the alveolar arch formed by the alveolar process that holds the upper teeth (when these are developed). Structure The hard palate is formed by the palatine process of the maxilla and horizontal plate of palatine bone. It forms a partition between the nasal passages and the mouth. On the anterior portion of the hard palate are the plicae, irregular ridges in the mucous membrane that help facilitate the movement of food backward towards the larynx. This partition is continued deeper into the mouth by a fleshy extension called the soft palate. On the ventral surface of hard palate, some projections or transverse ridges are present which are called as palatine rugae. Function The hard palate is important for feeding and speech. Mammals with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gums
The gums or gingiva (plural: ''gingivae'') consist of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health. Structure The gums are part of the soft tissue lining of the mouth. They surround the teeth and provide a seal around them. Unlike the soft tissue linings of the lips and cheeks, most of the gums are tightly bound to the underlying bone which helps resist the friction of food passing over them. Thus when healthy, it presents an effective barrier to the barrage of periodontal insults to deeper tissue. Healthy gums are usually coral pink in light skinned people, and may be naturally darker with melanin pigmentation. Changes in color, particularly increased redness, together with swelling and an increased tendency to bleed, suggest an inflammation that is possibly due to the accumulation of bacterial plaque. Overall, the clinical appearance of the tissue reflects the underlying histology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)