|
Dental Approximant
The voiced dental fricative is a consonant sound used in some spoken languages. It is familiar to English-speakers as the ''th'' sound in ''father''. Its symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet is eth, or and was taken from the Old English and Icelandic letter eth, which could stand for either a voiced or unvoiced (inter)dental non-sibilant fricative. Such fricatives are often called " interdental" because they are often produced with the tongue between the upper and lower teeth (as in Received Pronunciation), and not just against the back of the upper teeth, as they are with other dental consonants. The letter is sometimes used to represent the dental approximant, a similar sound, which no language is known to contrast with a dental non-sibilant fricative. However, the approximant can be explicitly indicated with the lowering diacritic: . Very rarely used variant transcriptions of the dental approximant include (retracted ), (advanced ) and ( ). It has been propos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract, except for the h sound, which is pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract. Examples are and [b], pronounced with the lips; and [d], pronounced with the front of the tongue; and [g], pronounced with the back of the tongue; , pronounced throughout the vocal tract; , [v], , and [z] pronounced by forcing air through a narrow channel (fricatives); and and , which have air flowing through the nose (nasal consonant, nasals). Most consonants are Pulmonic consonant, pulmonic, using air pressure from the lungs to generate a sound. Very few natural languages are non-pulmonic, making use of Ejective consonant, ejectives, Implosive consonant, implosives, and Click consonant, clicks. Contrasting with consonants are vowels. Since the number of speech sounds in the world's languages is much greater than the number of letters in any one alphabet, Linguis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek (, ; , ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language, constituting an independent Hellenic languages, Hellenic branch within the Indo-European language family. It is native to Greece, Cyprus, Italy (in Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, Caucasus, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the list of languages by first written accounts, longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of lasting importance in the European canon. Greek is also the language in which many of the foundational texts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albanian Alphabet
The Albanian alphabet () is a variant of the Latin alphabet used to write the Albanian language. It consists of 36 letters representing all the phonemes of Standard Albanian: The vowels are shown in bold. The letters are named simply by their sounds, followed by ë for consonants (e.g. shë). to the pronunciation of the 36 letters. History The earliest known mention of Albanian writings comes from a French Catholic church document from 1332. Written either by archbishop Guillaume Adam or the monk Brocardus Monacus the report notes that ''Licet Albanenses aliam omnino linguam a latina habeant et diversam, tamen litteram latinam habent in usu et in omnibus suis libris'' ("Though the Albanians have a language entirely their own and different from Latin, they nevertheless use Latin letters in all their books"). Scholars warn that this could mean Albanians also wrote in the Latin language, not necessarily just Albanian with a Latin script. The history of the later Albanian alph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albanian Language
Albanian (Endonym and exonym, endonym: , , or ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language and the only surviving representative of the Albanoid, Albanoid branch, which belongs to the Paleo-Balkan languages, Paleo-Balkan group. It is the native language of the Albanian people. Standard Albanian is the official language of Albania and Kosovo, and a co-official language in North Macedonia and Montenegro, where it is the primary language of significant Albanian minority communities. Albanian is recognized as a minority language in Italy, Croatia, Romania, and Serbia. It is also spoken in Greece and by the Albanian diaspora, which is generally concentrated in the Americas, Europe and Oceania. Albanian is estimated to have as many as 7.5 million native speakers. Albanian and other Paleo-Balkan languages had their formative core in the Balkans after the Indo-European migrations in the region. Albanian in antiquity is often thought to have been an Illyrian language for ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Approximant Consonant
Approximants are speech sounds that involve the articulators approaching each other but not narrowly enough nor with enough articulatory precision to create turbulent airflow. Therefore, approximants fall between fricatives, which do produce a turbulent airstream, and vowels, which produce no turbulence. This class is composed of sounds like (as in ''rest'') and semivowels like and (as in ''yes'' and ''west'', respectively), as well as lateral approximants like (as in ''less''). Terminology Before Peter Ladefoged coined the term ''approximant'' in the 1960s, the terms ''frictionless continuant'' and ''semivowel'' were used to refer to non-lateral approximants. In phonology, ''approximant'' is also a distinctive feature that encompasses all sonorants except nasals, including vowels, taps, and trills. Semivowels Some approximants resemble vowels in acoustic and articulatory properties and the terms ''semivowel'' and ''glide'' are often used for these non-syllabi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sibilant
Sibilants (from 'hissing') are fricative and affricate consonants of higher amplitude and pitch, made by directing a stream of air with the tongue towards the teeth. Examples of sibilants are the consonants at the beginning of the English words ''sip'', ''zip'', ''ship'', and ''genre''. The symbols in the International Phonetic Alphabet used to denote the sibilant sounds in these words are, respectively, . Sibilants have a characteristically intense sound, which accounts for their paralinguistic use in getting one's attention (e.g. calling someone using "psst!" or quieting someone using "shhhh!"). Overview In the hissing sibilants and , the back of the tongue forms a narrow channel (is '' grooved'') to focus the stream of air more intensely, resulting in a high pitch. With the hushing sibilants (occasionally termed ''shibilants''), such as English , , , and , the tongue is flatter, and the resulting pitch lower. A broader category is stridents, which include more fricati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assyrian Neo-Aramaic
Suret ( Help:IPA for Aramaic, [ˈsuːrɪtʰ] or Help:IPA for Aramaic, [ˈsuːrɪθ]), also known as Assyrian, refers to the varieties of Northeastern Neo-Aramaic (NENA) spoken by Christians, namely Assyrian people, Assyrians.Nordhoff, Sebastian; Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2013). "Northeastern Neo-Aramaic". Glottolog 2.2. Leipzig: Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology. The various NENA dialects descend from Old Aramaic, the ''lingua franca'' in the later phase of the Assyria, Assyrian Empire, which slowly displaced the East Semitic languages, East Semitic Akkadian language beginning around the 10th century BC.Bae, C. Aramaic as a Lingua Franca During the Persian Empire (538-333 BCE). Journal of Universal Language. March 2004, 1-20. They have been further heavily influenced by Syriac language, Classical Syriac, the Aramaic#Middle Aramaic, Middle Aramaic dialect of Edessa, after its adoption as an official Sacred language, liturgi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew Language
Hebrew (; ''ʿÎbrit'') is a Northwest Semitic language within the Afroasiatic language family. A regional dialect of the Canaanite languages, it was natively spoken by the Israelites and remained in regular use as a first language until after 200 CE and as the liturgical language of Judaism (since the Second Temple period) and Samaritanism. The language was revived as a spoken language in the 19th century, and is the only successful large-scale example of linguistic revival. It is the only Canaanite language, as well as one of only two Northwest Semitic languages, with the other being Aramaic, still spoken today. The earliest examples of written Paleo-Hebrew date back to the 10th century BCE. Nearly all of the Hebrew Bible is written in Biblical Hebrew, with much of its present form in the dialect that scholars believe flourished around the 6th century BCE, during the time of the Babylonian captivity. For this reason, Hebrew has been referred to by Jews as '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varieties Of Arabic
Varieties of Arabic (or dialects or vernaculars) are the linguistic systems that Arabic speakers speak natively. Arabic is a Semitic languages, Semitic language within the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic family that originated in the Arabian Peninsula. There are considerable variations from region to region, with degrees of mutual intelligibility that are often related to geographical distance and some that are mutually unintelligible. Many aspects of the variability attested to in these modern variants can be found in the ancient Arabic dialects in the peninsula. Likewise, many of the features that characterize (or distinguish) the various modern variants can be attributed to the original settler dialects as well as local native languages and dialects. Some organizations, such as SIL International, consider these approximately 30 different varieties to be separate languages, while others, such as the Library of Congress, consider them all to be dialects of Arabic. In terms of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Standard Arabic
Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Modern Written Arabic (MWA) is the variety of Standard language, standardized, Literary language, literary Arabic that developed in the Arab world in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, and in some usages also the variety of spoken Arabic that approximates this written standard. MSA is the language used in literature, academia, print media, print and mass media, law and legislation, though it is generally not spoken as a first language, similar to Contemporary Latin. It is a Pluricentric language, pluricentric standard language taught throughout the Arab world in formal education, differing significantly from many vernacular varieties of Arabic that are commonly spoken as mother tongues in the area; these are only partially mutually intelligible with both MSA and with each other depending on their proximity in the Dialect continuum#Arabic, Arabic dialect continuum. Many linguists consider MSA to be distinct from Classical Arabic (CA; ) – t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semitic Languages
The Semitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family. They include Arabic, Amharic, Tigrinya language, Tigrinya, Aramaic, Hebrew language, Hebrew, Maltese language, Maltese, Modern South Arabian languages and numerous other ancient and modern languages. They are spoken by more than 330 million people across much of Western Asia, West Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, Malta, and in large Immigration, immigrant and Expatriate, expatriate communities in North America, Europe, and Australasia. The terminology was first used in the 1780s by members of the Göttingen school of history, who derived the name from Shem, one of the three Generations of Noah, sons of Noah in the Book of Genesis. Semitic languages List of languages by first written account, occur in written form from a very early historical date in West Asia, with East Semitic languages, East Semitic Akkadian language, Akkadian (also known as Ancient Assyrian language, Assyrian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
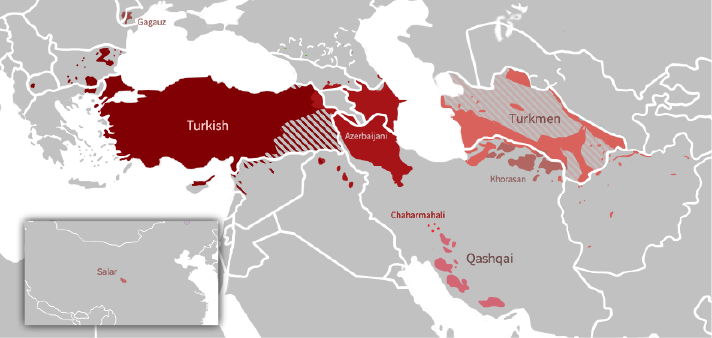
Turkmen Language
Turkmen (, , , or , , , ) is a Turkic language of the Oghuz branch spoken by the Turkmens of Central Asia. It has an estimated 4.7 million native speakers in Turkmenistan (where it is the official language), and a further 359,000 speakers in northeastern Iran and 1.2 million people in northwestern Afghanistan, where it has no official status. Turkmen is also spoken to lesser varying degrees in Turkmen communities of Uzbekistan and Tajikistan and by diaspora communities, primarily in Turkey and Russia. Turkmen is a member of the Oghuz branch of the Turkic languages. It is closely related to Azerbaijani, Gagauz, Qashqai, and Turkish, sharing varying degrees of mutual intelligibility with each of those languages. However, the closest relative of Turkmen is considered Khorasani Turkic, spoken in northeastern regions of Iran and with which it shares the eastern subbranch of Oghuz languages, as well as Khorazm, the Oghuz dialect of Uzbek spoken mainly in Khorezm along the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |