|
Demographics Of Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia had a peak population of 15.6 million, mainly composed of Czechs, Slovaks, Hungarians, Romani people, Silesians, Ruthenians, Ukrainians, Germans, Poles and Jews. The ethnic composition of Czechoslovakia changed over time from Sudeten Germans being the most prominent ethnicity to Czechs and Slovaks making up two-thirds of the demographic. Amongst this demographic there was also a diverse range of religions with Roman Catholic being the most prominent. This population has been found to have had an increasing growth rate that had a declining trajectory. The population density was approximately 121 persons per square kilometre with the highest population density being in Moravia of 154 persons per square kilometre. Population As of 1991, Czechoslovakia had a population of 15.6 million, of which by ethnicity 62.8% were Czechs (including Moravians), 31% Slovaks, 3.8% Hungarians, 0.7% Roma, and 0.4% Silesians. Smaller groups of Rusyns, Ukrainians, Germans, Austrians, Po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czechs
The Czechs (, ; singular Czech, masculine: ''Čech'' , singular feminine: ''Češka'' ), or the Czech people (), are a West Slavs, West Slavic ethnic group and a nation native to the Czech Republic in Central Europe, who share a common Bohemia, ancestry, Czech culture, culture, History of the Czech lands, history, and the Czech language. Ethnic Czechs were called Bohemians in English language, English until the early 20th century, referring to the former name of their country, Bohemia, which in turn was adapted from the late Iron Age tribe of Celtic Boii. During the Migration Period, West Slavic Bohemians (tribe), tribes settled in the area, "assimilated the remaining Celtic and Germanic populations", and formed a principality in the 9th century, which was initially part of Great Moravia, in form of Duchy of Bohemia and later Kingdom of Bohemia, the predecessors of the modern republic. The Czech diaspora is found in notable numbers in the Czech American, United States, Germany ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austrians
Austrians (, ) are the citizens and Nationality, nationals of Austria. The English term ''Austrians'' was applied to the population of Archduchy of Austria, Habsburg Austria from the 17th or 18th century. Subsequently, during the 19th century, it referred to the citizens of the Empire of Austria (1804–1867), and from 1867 until 1918 to the citizens of Cisleithania. In the closest sense, the name of Austria, term ''Austria'' originally referred to the historical March of Austria, corresponding roughly to the Vienna Basin in what is today Lower Austria. Historically, Austrians were regarded as Germans and viewed themselves as such. The Austrian lands (including Bohemia) were part of the Holy Roman Empire and the German Confederation until the Austro-Prussian War in 1866 which resulted in Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia expelling the Austrian Empire from the Confederation. Thus, when German Empire, Germany was Unification of Germany, founded as a nation-state in 1871, Austria Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpathian Ruthenia
Transcarpathia (, ) is a historical region on the border between Central and Eastern Europe, mostly located in western Ukraine's Zakarpattia Oblast. From the Hungarian Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin, conquest of the Carpathian Basin (at the end of the 9th century) to the end of World War I (Treaty of Trianon in 1920), most of this region was part of the Kingdom of Hungary. In the interwar period, it was part of the First Czechoslovak Republic, First and Second Czechoslovak Republics. Before World War II, the region was annexed by the Kingdom of Hungary (1920–46), Kingdom of Hungary once again when Germany dismembered the Second Czechoslovak Republic. After the war, it was annexed by the Soviet Union and became part of the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic. It is an ethnically diverse region, inhabited mostly by people who regard themselves as ethnic Ukrainians, Rusyns, Hungarian people, Hungarians, Romanians, Slovak people, Slovaks, and Polish people, Poles. It a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plzeň
Plzeň (), also known in English and German as Pilsen (), is a city in the Czech Republic. It is the Statutory city (Czech Republic), fourth most populous city in the Czech Republic with about 188,000 inhabitants. It is located about west of Prague, at the confluence of four rivers: Mže, Úhlava, Úslava and Radbuza, together forming the Berounka River. Founded as a royal city in the late 13th century, Plzeň became an important town for trade on routes linking Bohemia with Bavaria. By the 14th century it had grown to be the third largest city in Bohemia. The city was besieged three times during the 15th-century Hussite Wars, when it became a centre of resistance against the Hussites. During the Thirty Years' War in the early 17th century the city was temporarily occupied after the Siege of Plzeň. In the 19th century, the city rapidly industrialised and became home to the Škoda Works, which became one of the most important engineering companies in Austria-Hungary and later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Košice
Košice is the largest city in eastern Slovakia. It is situated on the river Hornád at the eastern reaches of the Slovak Ore Mountains, near the border with Hungary. With a population of approximately 230,000, Košice is the second-largest city in Slovakia, after the capital Bratislava. Being the economic and cultural centre of eastern Slovakia, Košice is the seat of the Košice Region and Košice Self-governing Region, it belongs to the :sk:Košicko-prešovská aglomerácia, Košice-Prešov agglomeration, and is home to the Constitutional Court of Slovakia, Slovak Constitutional Court, three universities, various dioceses, and many museums, galleries, and theatres. In 2013, Košice was the European Capital of Culture, together with Marseille, France. Košice is an important industrial centre of Slovakia, and the U. S. Steel Košice, s.r.o., U.S. Steel Košice steel mill is the largest employer in the city. The town has extensive railway connections and an Košice Internationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostrava
Ostrava (; ; ) is a city in the north-east of the Czech Republic and the capital of the Moravian-Silesian Region. It has about 283,000 inhabitants. It lies from the border with Poland, at the confluences of four rivers: Oder, Opava (river), Opava, Ostravice (river), Ostravice and Lučina (river), Lučina. Ostrava is the third largest city in the Czech Republic in terms of both population and area, the second largest city in the region of Moravia, and the largest city in the historical land of Czech Silesia. It straddles the border of the two historic provinces of Moravia and Silesia. The wider conurbation – which also includes the towns of Bohumín, Havířov, Karviná, Orlová, Petřvald (Karviná District), Petřvald and Rychvald – is home to about 500,000 people, making it the largest urban area in the Czech Republic apart from the capital Prague. Ostrava grew in importance due to its position at the heart of a major coalfield, becoming an important industrial engine of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brno
Brno ( , ; ) is a Statutory city (Czech Republic), city in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. Located at the confluence of the Svitava (river), Svitava and Svratka (river), Svratka rivers, Brno has about 403,000 inhabitants, making it the second-largest city in the Czech Republic after the capital, Prague, and one of the List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, 100 largest cities of the European Union. The Brno metropolitan area has approximately 730,000 inhabitants. Brno is the former capital city of Moravia and the political and cultural hub of the South Moravian Region. It is the centre of the Judiciary of the Czech Republic, Czech judiciary, with the seats of the Constitutional Court of the Czech Republic, Constitutional Court, the Supreme Court of the Czech Republic, Supreme Court, the Supreme Administrative Court of the Czech Republic, Supreme Administrative Court, and the Supreme Public Prosecutor's Office, and a number of state ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bratislava
Bratislava (German: ''Pressburg'', Hungarian: ''Pozsony'') is the Capital city, capital and largest city of the Slovakia, Slovak Republic and the fourth largest of all List of cities and towns on the river Danube, cities on the river Danube. Officially, the population of the city is about 475,000; however, some sources estimate daily number of people moving around the city based on mobile phone SIM cards is more than 570,000. Bratislava is in southwestern Slovakia at the foot of the Little Carpathians, occupying both banks of the Danube and the left bank of the Morava (river), River Morava. Bordering Austria and Hungary, it is the only national capital to border two sovereign states. The city's history has been influenced by people of many nations and religions, including Austrians, Bulgarians, Croats, Czechs, Germans, Hungarian people, Hungarians, Jews and Slovaks. It was the coronation site and legislative center and capital of the Kingdom of Hungary from 1536 to 1783; elev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prague
Prague ( ; ) is the capital and List of cities and towns in the Czech Republic, largest city of the Czech Republic and the historical capital of Bohemia. Prague, located on the Vltava River, has a population of about 1.4 million, while its Prague metropolitan area, metropolitan area is home to approximately 2.3 million people. Prague is a historical city with Romanesque architecture, Romanesque, Czech Gothic architecture, Gothic, Czech Renaissance architecture, Renaissance and Czech Baroque architecture, Baroque architecture. It was the capital of the Kingdom of Bohemia and residence of several Holy Roman Emperors, most notably Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles IV (r. 1346–1378) and Rudolf II, Holy Roman Emperor, Rudolf II (r. 1575–1611). It was an important city to the Habsburg monarchy and Austria-Hungary. The city played major roles in the Bohemian Reformation, Bohemian and the Protestant Reformations, the Thirty Years' War and in 20th-century history a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historically it could also refer to a wider area consisting of the Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the List of Bohemian monarchs, Bohemian kings, including Moravia and Czech Silesia, in which case the smaller region is referred to as Bohemia Proper as a means of distinction. Bohemia became a part of Great Moravia, and then an independent principality, which became a Kingdom of Bohemia, kingdom in the Holy Roman Empire. This subsequently became a part of the Habsburg monarchy and the Austrian Empire. After World War I and the establishment of an History of Czechoslovakia (1918–1938), independent Czechoslovak state, the whole of Bohemia became a part of Czechoslovakia, defying claims of the German-speaking inhabitants that regions with German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
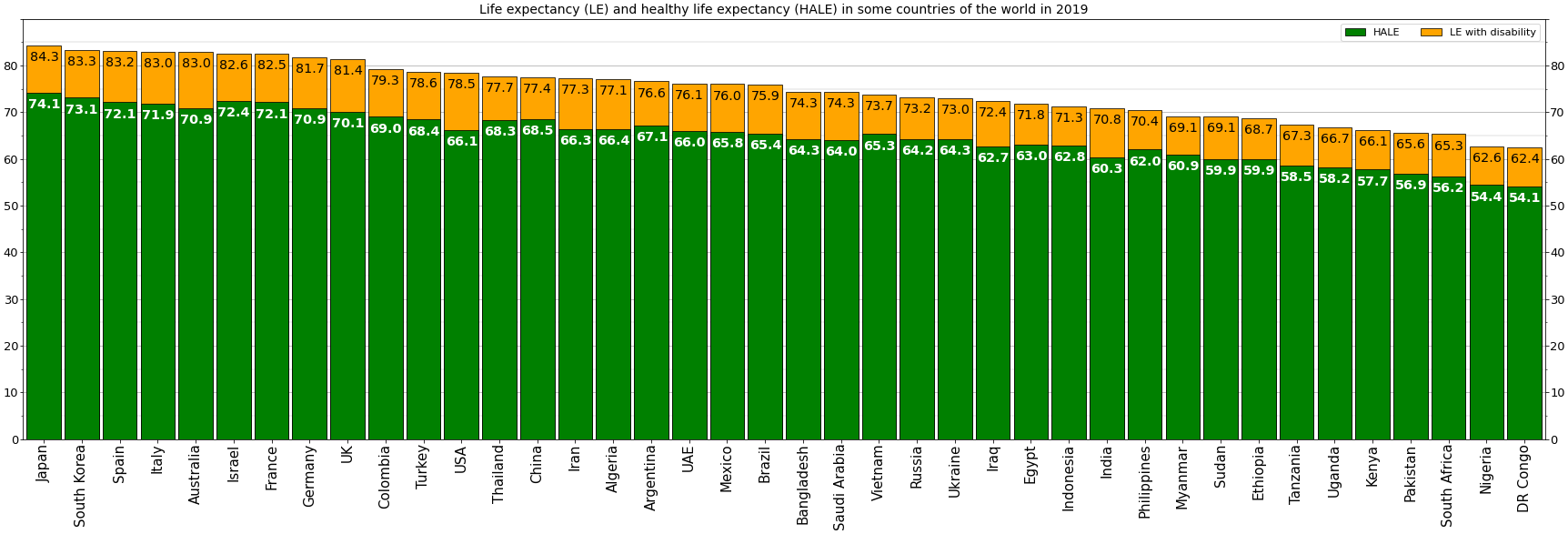
Life Expectancy
Human life expectancy is a statistical measure of the estimate of the average remaining years of life at a given age. The most commonly used measure is ''life expectancy at birth'' (LEB, or in demographic notation ''e''0, where ''e''x denotes the average life remaining at age ''x''). This can be defined in two ways. ''Cohort'' LEB is the mean length of life of a birth Cohort (statistics), cohort (in this case, all individuals born in a given year) and can be computed only for cohorts born so long ago that all their members have died. ''Period'' LEB is the mean length of life of a hypothetical cohort assumed to be exposed, from birth through death, to the mortality rates observed at a given year. National LEB figures reported by national agencies and international organizations for human populations are estimates of ''period'' LEB. Human remains from the early Bronze Age indicate an LEB of 24. In 2019, world LEB was 73.3. A combination of high infant mortality and d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovakia
Slovakia, officially the Slovak Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the west, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's mostly mountainous territory spans about , hosting a population exceeding 5.4 million. The capital and largest city is Bratislava, while the second largest city is Košice. The Slavs arrived in the territory of the present-day Slovakia in the 5th and 6th centuries. From the late 6th century, parts of modern Slovakia were incorporated into the Pannonian Avars, Avar Khaghanate. In the 7th century, the Slavs played a significant role in the creation of Samo's Empire. When the Avar Khaghanate dissolved in the 9th century, the Slavs established the Principality of Nitra before it was annexed by the Great Moravia, Principality of Moravia, which later became Great Moravia. When Great Moravia fell in the 10th century, the territory was integrated i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |