|
Deflationary Gap
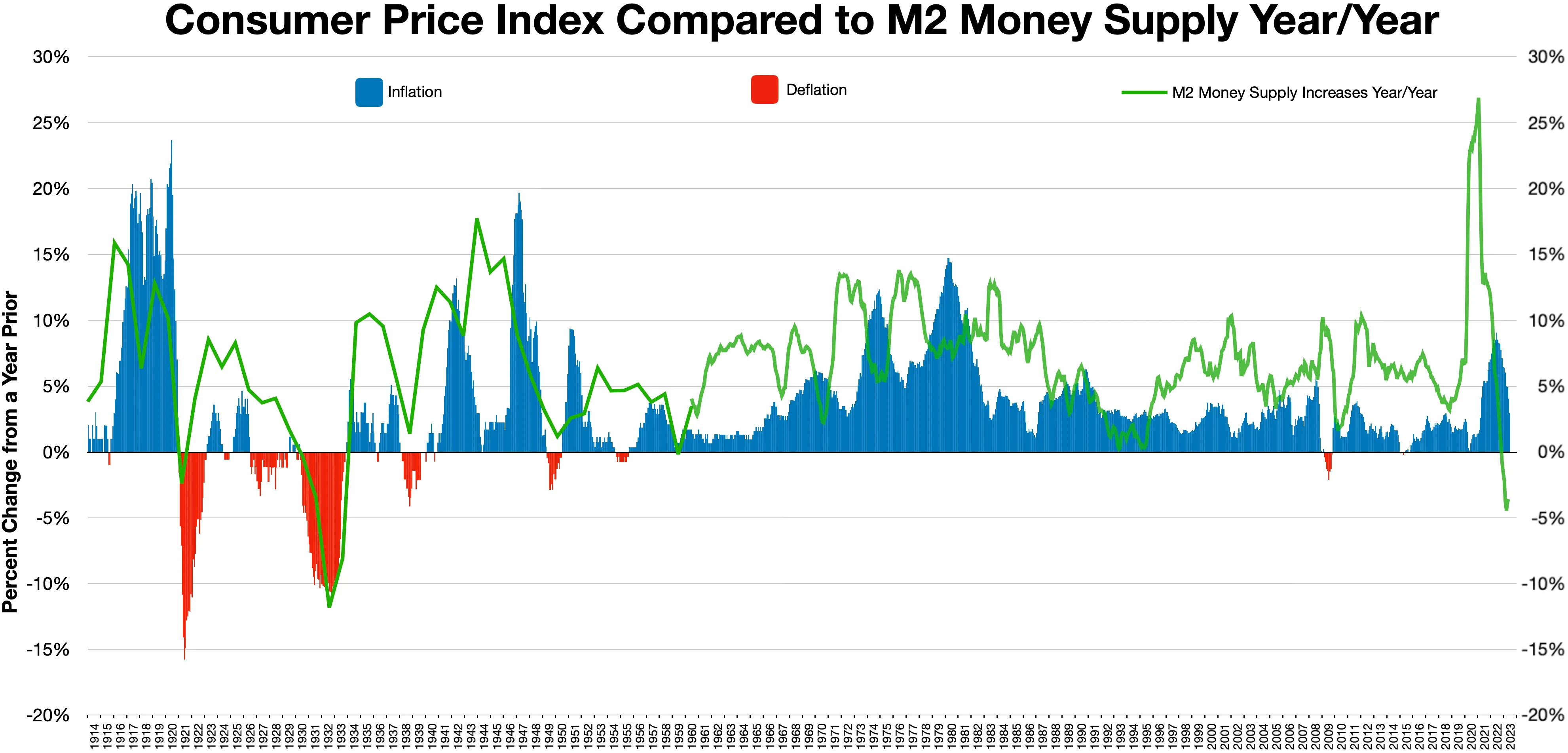
In economics, deflation is a decrease in the general price level of goods and services. Deflation occurs when the inflation rate falls below 0% and becomes negative. While inflation reduces the value of currency over time, deflation increases it. This allows more goods and services to be bought than before with the same amount of currency. Deflation is distinct from ''disinflation'', a slowdown in the inflation rate; i.e., when inflation declines to a lower rate but is still positive. Economists generally believe that a sudden deflationary shock is a problem in a modern economy because it increases the real value of debt, especially if the deflation is unexpected. Deflation may also aggravate recessions and lead to a deflationary spiral . Some economists argue that prolonged deflationary periods are related to the underlying technological progress in an economy, because as productivity increases ( TFP), the cost of goods decreases. Deflation usually happens when supply is high ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economics
Economics () is a behavioral science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of Agent (economics), economic agents and how economy, economies work. Microeconomics analyses what is viewed as basic elements within economy, economies, including individual agents and market (economics), markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyses economies as systems where production, distribution, consumption, savings, and Expenditure, investment expenditure interact; and the factors of production affecting them, such as: Labour (human activity), labour, Capital (economics), capital, Land (economics), land, and Entrepreneurship, enterprise, inflation, economic growth, and public policies that impact gloss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Competition
Competition is a rivalry where two or more parties strive for a common goal which cannot be shared: where one's gain is the other's loss (an example of which is a zero-sum game). Competition can arise between entities such as organisms, individuals, economic and social groups, etc. The rivalry can be over attainment of any exclusive goal, including recognition. Competition occurs in nature, between living organisms which co-exist in the same environment. Animals compete over water supplies, food, mates, and other biological resources. Humans usually compete for food and mates, though when these needs are met deep rivalries often arise over the pursuit of wealth, power, prestige, and fame when in a static, repetitive, or unchanging environment. Competition is a major tenet of market economies and business, often associated with business competition as companies are in competition with at least one other firm over the same group of customers. Competition inside a compan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Productivity Improving Technologies (historical)
The productivity-improving technologies are the technological innovations that have historically increased productivity. Productivity is often measured as the ratio of (aggregate) output to (aggregate) input in the production of goods and services. Productivity is increased by lowering the amount of labor, capital, energy or materials that go into producing any given amount of economic goods and services. Increases in productivity are largely responsible for the increase in per capita living standards. History Productivity-improving technologies date back to antiquity, with rather slow progress until the late Middle Ages. Important examples of early to medieval European technology include the water wheel, the horse collar, the spinning wheel, the three-field system (after 1500 the four-field system—see crop rotation) and the blast furnace. Technological progress was aided by literacy and the diffusion of knowledge that accelerated after the spinning wheel spread to Western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Competition
Competition is a rivalry where two or more parties strive for a common goal which cannot be shared: where one's gain is the other's loss (an example of which is a zero-sum game). Competition can arise between entities such as organisms, individuals, economic and social groups, etc. The rivalry can be over attainment of any exclusive goal, including recognition. Competition occurs in nature, between living organisms which co-exist in the same environment. Animals compete over water supplies, food, mates, and other biological resources. Humans usually compete for food and mates, though when these needs are met deep rivalries often arise over the pursuit of wealth, power, prestige, and fame when in a static, repetitive, or unchanging environment. Competition is a major tenet of market economies and business, often associated with business competition as companies are in competition with at least one other firm over the same group of customers. Competition inside a compan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Efficiency
Efficiency is the often measurable ability to avoid making mistakes or wasting materials, energy, efforts, money, and time while performing a task. In a more general sense, it is the ability to do things well, successfully, and without waste. In more mathematical or scientific terms, it signifies the level of performance that uses the least amount of inputs to achieve the highest amount of output. It often specifically comprises the capability of a specific application of effort to produce a specific outcome with a minimum amount or quantity of waste, expense, or unnecessary effort.Sickles, R., and Zelenyuk, V. (2019).Measurement of Productivity and Efficiency: Theory and Practice. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. . Efficiency refers to very different inputs and outputs in different fields and industries. In 2019, the European Commission said: "Resource efficiency means using the Earth's limited resources in a sustainable procent manner while minimising impacts on the envi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purchasing Power
Purchasing power refers to the amount of products and services available for purchase with a certain currency unit. For example, if you took one unit of cash to a store in the 1950s, you could buy more products than you could now, showing that the currency had more purchasing power back then. If one's income remains constant but prices rise, their purchasing power decreases. Inflation does not always result in decreased purchasing power, especially if income exceeds price levels. A larger real income means more purchasing power, as it corresponds to the income itself. Traditionally, the purchasing power of money depended heavily upon the local value of gold and silver, but was also made subject to the availability and demand of certain goods on the market. Most modern fiat currencies, like US dollars, are traded against each other and commodity money in the secondary market for the purpose of international Balance transfer, transfer of payment for goods and services. Scottish ec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carry (investment)
The carry of an asset is the return obtained from holding it (if positive), or the cost of holding it (if negative) (see also Cost of carry). For instance, commodities are usually negative carry assets, as they incur storage costs or may suffer from depreciation. (Imagine corn or wheat sitting in a silo somewhere, not being sold or eaten.) But in some circumstances, appropriately hedged commodities can be positive carry assets if the forward/futures market is willing to pay sufficient premium for future delivery. This can also refer to a trade with more than one leg, where you earn the spread between borrowing a low carry asset and lending a high carry one; such as gold during a financial crisis, due to its safe haven quality. Carry trades are not usually arbitrages: pure arbitrages make money no matter what; carry trades make money only if nothing changes against the carry's favor. Interest rates carry trade/maturity transformation For instance, the traditional revenue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autarky
Autarky is the characteristic of self-sufficiency, usually applied to societies, communities, states, and their economic systems. Autarky as an ideology or economic approach has been attempted by a range of political ideologies and movements, particularly leftist ones like African socialism, mutualism, war communism, communalism, swadeshi, syndicalism (especially anarcho-syndicalism), and left-wing populism, generally in an effort to build alternative economic structures or to control resources against structures a particular movement views as hostile. However, some right-wing ones, like nationalism, conservatism, and anti-globalism, along with even some centrist movements, have also adopted autarky, generally on a more limited scale, to develop a particular industry, to gain independence from other national entities or to preserve part of an existing social order. Proponents of autarky have argued for national self-sufficiency to reduce foreign economic, polit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquidity Trap
A liquidity trap is a situation, described in Keynesian economics, in which, "after the rate of interest has fallen to a certain level, liquidity preference may become virtually absolute in the sense that almost everyone prefers holding cash rather than holding a debt (financial instrument) which yields so low a rate of interest."John Maynard Keynes, Keynes, John Maynard (1936) ''The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money'', United Kingdom: Palgrave Macmillan, 2007 edition, A liquidity trap is caused when people hold cash because they Expectation (epistemic), expect an adverse event such as deflation, insufficient aggregate demand, or war. Among the characteristics of a liquidity trap are interest rates that are close to zero lower bound and changes in the money supply that fail to translate into changes in inflation.Paul R. Krugman, Krugman, Paul R. (1998)"It's baack: Japan's Slump and the Return of the Liquidity Trap," Brookings Institution, Brookings Papers on Economi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risk Aversion
In economics and finance, risk aversion is the tendency of people to prefer outcomes with low uncertainty to those outcomes with high uncertainty, even if the average outcome of the latter is equal to or higher in monetary value than the more certain outcome. Risk aversion explains the inclination to agree to a situation with a lower average payoff that is more predictable rather than another situation with a less predictable payoff that is higher on average. For example, a risk-averse investor might choose to put their money into a bank account with a low but guaranteed interest rate, rather than into a stock that may have high expected returns, but also involves a chance of losing value. Example A person is given the choice between two scenarios: one with a guaranteed payoff, and one with a risky payoff with same average value. In the former scenario, the person receives $50. In the uncertain scenario, a coin is flipped to decide whether the person receives $100 or nothing. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Money Supply
In macroeconomics, money supply (or money stock) refers to the total volume of money held by the public at a particular point in time. There are several ways to define "money", but standard measures usually include currency in circulation (i.e. physical cash) and demand deposits (depositors' easily accessed assets on the books of financial institutions). Money supply data is recorded and published, usually by the national statistical agency or the central bank of the country. Empirical money supply measures are usually named M1, M2, M3, etc., according to how wide a definition of money they embrace. The precise definitions vary from country to country, in part depending on national financial institutional traditions. Even for narrow aggregates like M1, by far the largest part of the money supply consists of deposits in commercial banks, whereas currency (banknotes and coins) issued by central banks only makes up a small part of the total money supply in modern economies. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
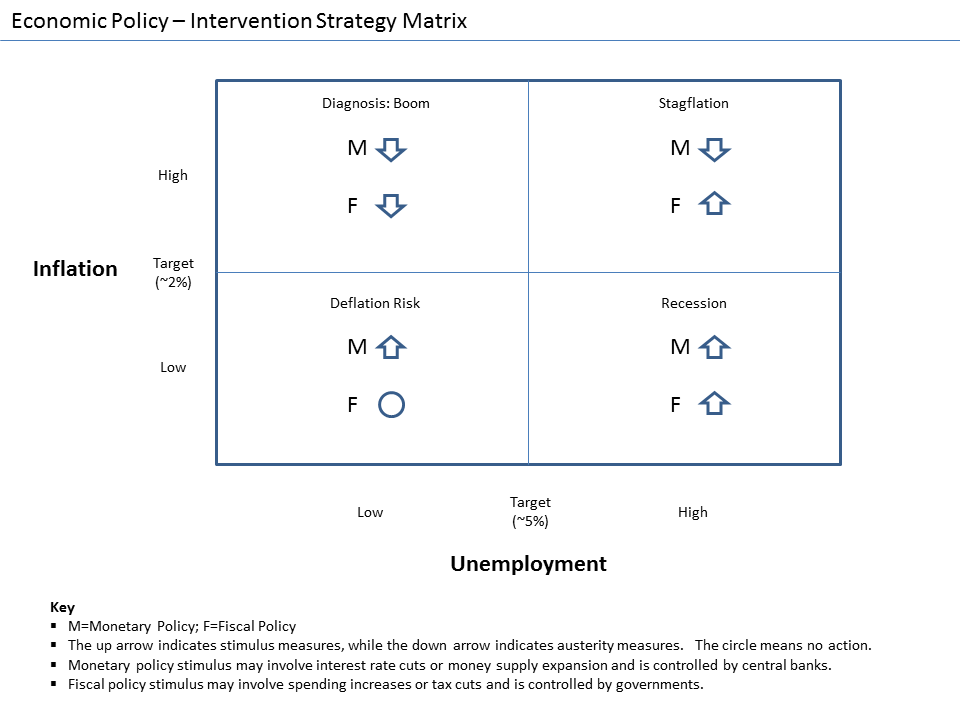
Stimulus (economic)
In economics, stimulus refers to attempts to use monetary policy or fiscal policy (or stabilization policy in general) to stimulate the economy. Stimulus can also refer to monetary policies such as lowering interest rates and quantitative easing. A stimulus is sometimes colloquially referred to as "priming the pump" or "pump priming". Concept During a recession, production and employment are far below their sustainable potential due to lack of demand. It is hoped that increasing demand will stimulate growth and that any adverse side effects from stimulus will be mild. Fiscal stimulus refers to increasing government consumption or transfers or lowering taxes, increasing the rate of growth of public debt. Supporters of Keynesian economics assume the stimulus will cause sufficient economic growth to fill that gap partially or completely via the multiplier effect. Monetary stimulus refers to lowering interest rates, quantitative easing, or other ways of increasing the amount of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |