|
December 22 (Eastern Orthodox Liturgics)
December 21 - Eastern Orthodox liturgical calendar - December 23 All fixed commemorations below celebrated on January 4 by Eastern Orthodox Churches on the Old Calendar. For December 22nd, Orthodox Churches on the Old Calendar commemorate the Saints listed on December 9. Feasts * Forefeast of the Nativity of Christ.December 22/January 4 Orthodox Calendar (PRAVOSLAVIE.RU). Saints * Great Martyr , Deliverer from Bonds, and: :* her teacher Martyr |
Anastasia The Roman
Anastasia the Roman (died 250) was 3rd-century Christian saint and nun who was martyred during the reign of Roman emperor Decius. Anastasia was orphaned at the age of three and was raised in a convent, where she became renowned for her asceticism. During the persecutions under the Emperor Decius, she was apprehended, tortured, and beheaded by a city administrator named Probus. Her feast day is celebrated on 29 October. This St. Anastasia should not be confused with another St. Anastasia of Rome who was martyred with St. Basilissa in 68 AD. See also *List of saints named Anastasia Saint Anastasia or Santa Anastasia may refer to one of several saints, including: * Basilissa and Anastasia of Rome (died AD 68), martyrs * Anastasia the Roman (died ), virgin martyr * Anastasia of Sirmium (died 304), virgin martyr who is comm ... References BibliographySaint Anastasia The Great Martyrfrom Jehanne d'ArcOrthodox Wiki Year of birth unknown 250 deaths Saints from Roman It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
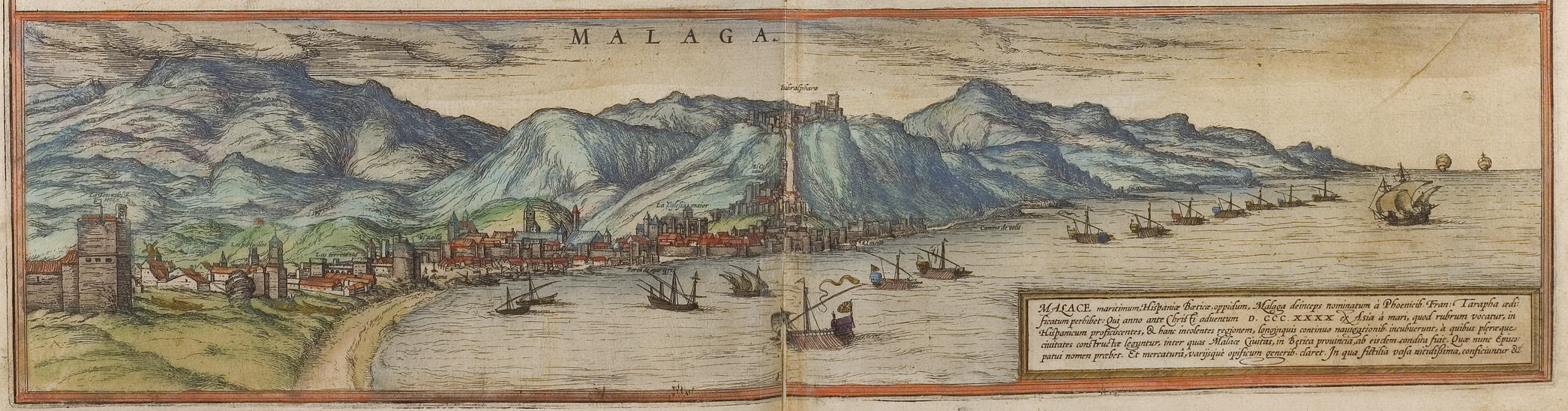
Málaga
Málaga (; ) is a Municipalities in Spain, municipality of Spain, capital of the Province of Málaga, in the Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Andalusia. With a population of 591,637 in 2024, it is the second-most populous city in Andalusia and the Ranked lists of Spanish municipalities#By population, sixth most populous in the country. It lies in Southern Iberian Peninsula, Iberia on the Costa del Sol ("Coast of the Sun") of the Mediterranean, primarily in the left bank of the Guadalhorce. The urban core originally developed in the space between the Gibralfaro, Gibralfaro Hill and the Guadalmedina. Málaga's history spans about 2,800 years, making it one of the List of cities by time of continuous habitation#Europe, oldest continuously inhabited cities in Western Europe. According to most scholars, it was founded about 770BC by the Phoenicians from Tyre, Lebanon, Tyre as ''Malaka''. From the 6th centuryBC the city was under the hegemony of Ancient Cartha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prüm
Prüm () is a town in the Westeifel (Rhineland-Palatinate), Germany. Formerly a district capital, today it is the administrative seat of the ''Verbandsgemeinde'' ("collective municipality") Prüm (Verbandsgemeinde), Prüm. Geography Prüm lies on the river Prüm (river), Prüm (a tributary of the Sauer) at the southeastern end of the Schneifel, which is 697 m high. Prüm is eponymous for the Prüm syncline (Ger. ''Prümer Kalkmulde''), the largest of the Eifel-lime-synclines. Here, the only Global Boundary Stratotype Section and Point, GSSP-point in Germany identifies the geological border between the lower Devonian Emsian and the middle Devonian Eifelian. History See main article on the town's former monastery, Prüm Abbey. In 2005, the Prüm Convention was signed in the city by several European countries. Ninety-two percent of the town was destroyed by bombing and ground fighting during the Second World War. In 1949, it was wrecked again by an Prüm explosion, explosion on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archdiocese Of Utrecht (695–1580)
The archdiocese, archbishopric, diocese or Bishopric of Utrecht may refer to: * Diocese of Utrecht (695–1580) The historic Diocese of Utrecht was a diocese of the Latin Church (or Western) of the Catholic Church from 695 to 1580, and from 1559 archdiocese in the Low Countries before and during the Protestant Reformation. History Diocese According to th ..., the historic diocese and after 1559 archdiocese before and during the Protestant Reformation ** Prince-Bishopric of Utrecht (1024–1528), the temporal jurisdiction of the bishops * Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Utrecht (1853 – present), the current archdiocese in the Netherlands within the Catholic Church * Old Catholic Archdiocese of Utrecht (1723 – present), the current archdiocese within the Old Catholic Church of the Netherlands See also * List of bishops and archbishops of Utrecht {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Hunger
Hunger (died 866), also known as , was the Bishop of Utrecht from 854 to 866. He is a saint of the Catholic and Eastern Orthodox Churches. Born around 800, Hunger became a Benedictine. After the death of his predecessor Liudger of Utrecht, Liudger's nephew Craft was offered the seat. However, Craft, a very wealthy person, refused because he was afraid that he would attract Viking raids. Instead, Canon Hunger was appointed. At first his relations with the Vikings were peaceful, but eventually Utrecht was threatened by the Vikings, which caused the bishop and the entire clergy of Utrecht to flee to Sint Odiliënberg, near Roermond. In 858, the Lotharingian king Lothair II made a monastery available for them. Later the bishop settled in Prüm and then in Deventer. Hunger seems to have been a godly man who, unlike his predecessors, did not engage in nepotism. In the case of the childless marriage between Lothair II and his wife Teutberga, he defended the sanctity of their marriage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julian The Apostate
Julian (; ; 331 – 26 June 363) was the Caesar of the West from 355 to 360 and Roman emperor from 361 to 363, as well as a notable philosopher and author in Greek. His rejection of Christianity, and his promotion of Neoplatonic Hellenism in its place, caused him to be remembered as Julian the Apostate in the Christian tradition. A nephew of Constantine the Great, Julian was one of few in the imperial family to survive the purges and civil wars during the reign of Constantius II, his cousin. Julian became an orphan as a child after his father was executed in 337, and spent much of his life under Constantius's close supervision. However, the emperor allowed Julian freedom to pursue an education in the Greek-speaking east. In 355, Constantius II summoned Julian to court and appointed him to rule Roman Gaul, Gaul. Julian was successful in his rule, defeating and counterattacking Germanic peoples, Germanic raids across the Rhine and encouraging the provinces' return to prosperi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acquapendente
Acquapendente is a city and ''comune'' in the province of Viterbo, in Lazio (Italy). Acquapendente is a centre for the agricultural production of vegetables and wine, and has a tradition of pottery craftsmanship. Its ''frazione'' of Torre Alfina is one of I Borghi più belli d'Italia ("The most beautiful villages of Italy"). History The area of modern Acquapendente was settled by Etruscan civilization, Etruscans in ancient Rome, Roman times, as archaeological finds have shown. However, the first historical document of the modern city dates from the 9th century AD, with a town named ''Farisa'' or ''Arisa'' along the Via Francigena. A document from Emperor Otto I, Holy Roman Emperor, Otto I, dated 964, contains the first recorded use of the name ''Acquapendentem'' which means "hanging water", from several small waterfalls in the Paglia (river), Paglia river on the boundary between Lazio and Tuscany. Acquapendente was the first stop in Italy in the travels of Saint Roch in the ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praefectus Urbi
The ''praefectus urbanus'', also called ''praefectus urbi'' or urban prefect in English, was prefect of the city of Rome, and later also of Constantinople. The office originated under the Roman kings, continued during the Republic and Empire, and held high importance in late Antiquity. The office survived the collapse of the Western Roman Empire, and the last urban prefect of Rome, named Iohannes, is attested in 599. Lançon (2000), p. 45 In the East, in Constantinople, the office survived until the 13th century. Regal period According to Roman tradition, in 753 BC when Romulus founded the city of Rome and instituted the monarchy, he also created the office of ''custos urbis'' (guardian of the city) to serve as the king's chief lieutenant. Appointed by the king to serve for life, the ''custos urbis'' served concurrently as the '' princeps Senatus''. As the second highest office of state, the ''custos urbis'' was the king's personal representative. In the absence of the king fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
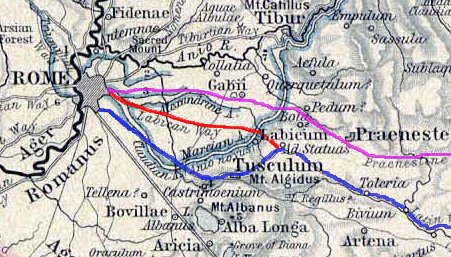
Via Lavicana
The Via Labicana was an ancient road of Italy, leading east-southeast from Rome. The course after the first six miles from Rome is not taken by any modern road, but it can be clearly traced from remains of pavement and buildings. It seems possible that the road at first led to Tusculum, was then extended to Labici, and later became a road for through traffic. As the preferred way to the southeast, the Via Labicana may even have superseded the Via Latina. The Via Labicana's summit just west of the Mount Algidus pass, calls for some less of a climb overall. Beyond the two roads' reunion, the route was probably called Via Latina rather than Via Labicana. Ashby cites his own contribution to ''Papers of the British School at Rome'', i .215 sqq. Via Labicana entered Rome through the Aurelian walls via the ancient monumental gate of Porta Prenestina, and reached, after an internal part, the Servian Wall, entering through the Porta Esquilina, decorated with the arch of Gallienus. The se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
November 21 (Eastern Orthodox Liturgics)
November 20 - Eastern Orthodox liturgical calendar - November 22 All fixed commemorations below are observed on December 4 by Eastern Orthodox Churches on the Old Calendar. For November 21, Orthodox Churches on the Old Calendar commemorate the Saints listed on November 8. Feasts *The Entry of the Most Holy Theotokos into the Temple.November 21 / December 4 Orthodox Calendar (PRAVOSLAVIE.RU).December 4 / November 21 Holy Trinity Russian Orthodox Church (A parish of the Patriarchate of Moscow). Συναξαριστής. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostia Antica
Ostia Antica () is an ancient Roman city and the port of Rome located at the mouth of the Tiber. It is near modern Ostia, southwest of Rome. Due to silting and the invasion of sand, the site now lies from the sea. The name ''Ostia'' (the plural of ''ostium'') derives from Latin ''os'' 'mouth'. Ostia is now a large archaeological site noted for the excellent preservation of its ancient buildings, magnificent frescoes and impressive mosaics. The city's decline after antiquity led to harbor deterioration, marshy conditions, and reduced population. Sand dunes covering the site aided its preservation. Its remains provide insights into a city of commercial importance. As in Pompeii, Ostia's ruins provide details about Roman urbanism that are not accessible within the city of Rome itself. History Origins Ostia may have been Rome's first '' colonia''. According to legend, Ancus Marcius, the fourth king of Rome, was the first to destroy Ficana, an ancient town that was only fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |