|
Davul
The davul, dhol, tapan, atabal or tabl is a large double-headed drum that is played with mallets. It has many names depending on the country and region. These drums are commonly used in the music of the Middle East and the Balkans. These drums have both a deep bass drum, bass sound and a thin treble (sound), treble sound due to their construction and playing style, where different heads and sticks are used to produce different sounds on the same drum. Names Some names of davuls include: *''dhol'' () *''dawola/tabla'' () *''dohol'' () *''doli'' ( ka, დოლი doli) *''davul'' () *''dahol'' (, ) *''davil'' () *''davula'' (Sinhala language, Sinhala: දවුල) *''tupan'' (Gora dialect, Goranian: tupan) *''daul'', ''tǎpan'', ''tupan'' () *''goč'', ''tapan'', ''tupan'' () *''tapan, tupan'' () *''tobă/dobă'' () *''tabl'' ( or ''tabl baladi'') *''tof'' () *''taoul(in)'' () *''lodra'', ''tupana'', ''daulle'', ''taborre'' () *''moldvai dob'' () Other Greek language, Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bass Drum
The bass drum is a large drum that produces a note of low definite or indefinite pitch. The instrument is typically cylindrical, with the drum's diameter usually greater than its depth, with a struck head at both ends of the cylinder. The heads may be made of calfskin or plastic and there is normally a means of adjusting the tension, either by threaded taps or by strings. Bass drums are built in a variety of sizes, but size does not dictate the volume produced by the drum. The pitch and the sound can vary much with different sizes,Norman Del Mar, Del Mar, Norman (1981). ''Anatomy of the Orchestra''. . but the size is also chosen based on convenience and aesthetics. Bass drums are percussion instruments that vary in size and are used in several musical genres. Three major types of bass drums can be distinguished. * The type usually seen or heard in orchestral, ensemble or concert band music is the orchestral, or concert bass drum (in Italian: gran cassa, gran tamburo). It is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
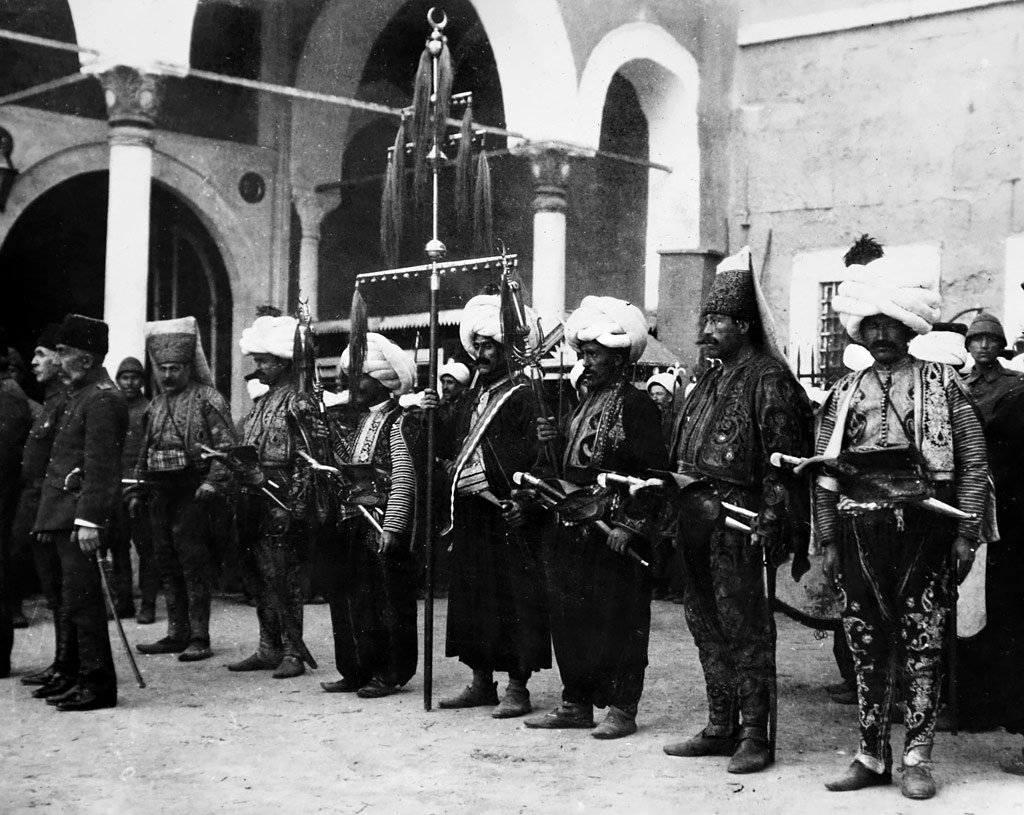
Mehter
Ottoman military bands were the first-recorded military marching bands. Though often known as the ''mehter'', this term refers only to a single musician in the band. In the Ottoman Empire, the band was generally known in the plural as ''mehterân'', though those bands used in the retinue of a vizier or prince were generally known as ''mehterhâne''. The band as a whole is often termed ''mehter bölüğü'' (' company roop) or ''mehter takımı'' (' platoon'). In Western Europe, the band's music is also often called Janissary music because the janissaries formed the core of the bands. History Such military bands as the ''mehter''s, were not definitively mentioned until the 13th century. It is believed that the first "mehter" was sent to Osman I by the Seljuk Sultan Alaeddin Kayqubad III as a present along with a letter that salutes the newly formed state. From then on every day after the afternoon prayer; "mehter" played for the Ottoman ruler. The notion of a military marching ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zurla (instrument)
The zurna is a double reed wind instrument played in Central Asia, West Asia, the Caucasus, Southeast Europe and parts of North Africa. It is also used in Sri Lanka. It is usually accompanied by a davul (bass drum) in Armenian, Anatolian and Assyrian folk music. The zurna is largely played in Turkey. Etymology and terminology A folk etymology explains that the name is derived from Persian "" (''surnāy''), composed of "" (''sūr'') meaning "banquet, feast", and (''nāy'') meaning "reed, pipe". The term is attested in the oldest Turkic records, as "''suruna''" in the 12th and 13th century Codex Cumanicus (CCM fol. 45a). Zurna has also been suggested as a possible borrowing from Hittite or Luwian into the Armenian language, where Arm. զուռնա ''zuṙna'' is compared to Luwian ''zurni'' "horn". Origins The zurna was said to originate from Central Asia and ancient Asia Minor (Anatolia). Images of the zurna are visible in stone reliefs and artwork by the Hittites, who were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assyrian People
Assyrians (, ) are an ethnic group Indigenous peoples, indigenous to Mesopotamia, a geographical region in West Asia. Modern Assyrians Assyrian continuity, share descent directly from the ancient Assyrians, one of the key civilizations of Mesopotamia. While they are distinct from other Mesopotamian groups, such as the Babylonians, they share in the broader cultural heritage of the Mesopotamian region. Modern Assyrians may culturally self-identify as Terms for Syriac Christians#Syriac identity, Syriacs, Chaldean Catholics, Chaldeans, or Terms for Syriac Christians#Aramean identity, Arameans for religious, geographic, and tribal identification. Assyrians speak various dialects of Neo-Aramaic, specifically those known as Suret and Turoyo, which are among the oldest continuously spoken and written languages in the world. Aramaic was the lingua franca of West Asia for centuries and was the language spoken by historical Jesus, Jesus. It has influenced other languages such as Hebrew an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Janissary
A janissary (, , ) was a member of the elite infantry units that formed the Ottoman sultan's household troops. They were the first modern standing army, and perhaps the first infantry force in the world to be equipped with firearms, adopted during the reign of Murad II (r. 1421–1444, 1446–1451). The corps was established under either Orhan or Murad I, and dismantled by Mahmud II in 1826. Janissaries began as elite corps made up through the ''devşirme'' system of Ghilman, child levy enslavement, by which Ethnic groups in Europe, indigenous European Christians, Christian boys, chiefly from the Balkans, were taken, levied, subjected to forced circumcision and Forced conversion#Islam, forced conversion to Islam, and incorporated into the Ottoman army in the 15th–19th centuries, Ottoman army. They became famed for internal cohesion cemented by strict discipline and order. Unlike typical History of slavery in the Muslim world, slaves, they were paid regular salaries. Forbidden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percussion Instrument
A percussion instrument is a musical instrument that is sounded by being struck or scraped by a percussion mallet, beater including attached or enclosed beaters or Rattle (percussion beater), rattles struck, scraped or rubbed by hand or struck against another similar instrument. Excluding Zoomusicology, zoomusicological instruments and the human voice, the percussion family is believed to include the oldest musical instruments.''The Oxford Companion to Music'', 10th edition, p.775, In spite of being a very common term to designate instruments, and to relate them to their players, the percussionists, percussion is not a systematic classificatory category of instruments, as described by the scientific field of organology. It is shown below that percussion instruments may belong to the organological classes of idiophone, membranophone, aerophone and String instrument, chordophone. The percussion section of an orchestra most commonly contains instruments such as the timpani, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assyrian Folk Dance
Assyrian folk dances are sets of dances that are performed throughout the world by Assyrians, mostly on occasions such as weddings, community parties and other jubilant events. Assyrian folk dances are mainly made up of circle dances like ballet that are performed in a line, which may be straight, curved, or both. Most of the dances allow unlimited number of participants, with the exception of the ''Sabre Dance'', which require three at most. Assyrian dances would vary from weak to strong, depending on the mood and tempo of a song. Assyrian folk dances belong to five metric groups: (10 dances), (6 dances), (13 dances), (1 dance), (1 dance). The tempo would usually range from slow (70 beats per minute) to very fast (140 beats). Technique All Assyrian dances, with the exception of the ''Sabre Dance'', are done in a connected circle. Most Assyrian circle dances are lateral, vining and open-ended, where more and more participants can join the dance. In an open floor space, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assyrian Folk/pop Music
Assyrian folk/pop music, also known as Assyrian folk-pop, is the musical style of the Assyrian people derived from traditional music that includes a broad range of stylistic varieties, which would also encompass fusions of Western genres such as pop, electronic, Latin, jazz and/or classical music, with a melodic basis of Assyrian folk. Background Assyrian folk music claims to be the descendant of the music of their ancient Upper Mesopotamian ancestors that has survived in the liturgical music of the Syriac Churches. Assyrian songs are generally sung in Iraqi Koine, a standard variety of Assyrian Neo-Aramaic. However, older songs mostly had an Urmian dialect and tribal-folk music tend to contain Tyari dialects. Themes tend to focus on longing, melancholy, strife and love issues. Assyrian songs are usually lengthy, tending to be around 5 minutes long on average. Composition Assyrian folk can also be found in traditional Middle Eastern makams, and it has similarities to other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duduk
The duduk ( ; ) or tsiranapogh (, meaning "apricot-made wind instrument"), is a double reed woodwind instrument made of apricot wood originating from Armenia. Variations of the Armenian duduk appear throughout the Caucasus, the Balkans, and the Middle East, including Bulgaria, Azerbaijan, Georgia (country), Georgia, Kurdistan, Turkey, and Iran. Duduk, Balaban (instrument), Balaban, and Mey (instrument), Mey are almost identical, except for historical and geographical differences. It is commonly played in pairs: while the first player plays the melody, the second plays a steady drone called ''dum'', and the sound of the two instruments together creates a richer, more haunting sound. The unflattened reed and cylindrical body produce a sound closer to the English horn than the oboe or bassoon. Unlike other double reed instruments like the oboe or shawm, the duduk has a very large reed proportional to its size. UNESCO proclaimed the Armenian duduk and its music as a Masterpieces of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goblet Drum
The goblet drum (also chalice drum, tarabuka, tarabaki, darbuka, darabuka, derbake, debuka, doumbek, dumbec, dumbeg, dumbelek, toumperleki, tumbak, or zerbaghali; / Romanized: ) is a single-head membranophone with a goblet-shaped body. It is most commonly used in the traditional music of Egypt, where it is considered the national symbol of Egyptian Shaabi Music. The instrument is also featured in traditional music from West Asia, North Africa, South Asia, and Eastern Europe. The West African djembe is also a goblet membranophone. This article focuses on the Middle Eastern and North African goblet drum. History The origin of the term ''Darbuka'' lies in the rural Egyptian Arabic slang word that changed "darb" meaning "to strike" into "darabuka". Goblet drums have been around for thousands of years and were used in Mesopotamian and Ancient Egyptian cultures. They were also seen in Babylonia and Sumer from as early as 1100 BCE. On Sulawesi, large goblet drums are used as temple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sring
The sring (, also transliterated as ) is a shepherd's flute originating in Armenia. Sring is also the common term for end-blown flutes in general. These flutes are made either of a stork bone, bamboo, wood from the apricot tree or cane and have or eight finger holes, producing a diatonic scale. The Armenian Armenian may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia * Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent ** Armenian diaspora, Armenian communities around the ... musicologist Komitas believed that the sring was the most characteristic among the Armenian instruments. Blul The ' instrument is a particular variety of the sring family of flutes. It is often considered a modern evolution of the medieval sring, with the primary differences being the presence of ring-shaped zones, both ends being thickened, and the resulting sound being characterized as velvety and slightly muted. Reference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |