|
David Urie
Prior to June 2007, David Urie was Vice-President and Program Manager of Rocketplane Limited, Inc., where he managed the design of the Rocketplane XP. Prior to joining the Rocketplane team, Urie served as president of Concept Fusion, Inc., providing technical development services to established companies and start-up organizations. During his 30-year career with the Lockheed Martin Corporation, Urie led teams on Lockheed’s X-30 National Aerospace Plane and the HL-20 Personnel Launch System. He was Chief Engineer and then Program Manager of the SR-71 Blackbird reconnaissance system before initiating and heading the Single Stage to Orbit (SSTO) and X-33 Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) Programs at Lockheed. Urie's work as the program manager for the previously classified Have Region project demonstrated that rocket-powered single-stage-to-orbit vehicles were technically feasible, which led to the Lockheed Martin SSTO design approach. As a Director of the Lockheed-Martin Skunk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oklahoma Gazette
The ''Oklahoma Gazette'' is a free alt-weekly online website featuring mostly news of Greater Oklahoma City restaurants, clubs, music and local trends. The Gazette was formerly a print weekly newspaper distributed throughout the Oklahoma City Oklahoma City (), officially the City of Oklahoma City, and often shortened to OKC, is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Oklahoma, most populous city of the U.S. state of Oklahoma. The county seat ... metro area via more than 800 now defunct rack locations and via its official website. It covers local and statewide news dealing with city government, education, politics, sustainability, food, restaurants, theater, and music. A notable feature of the ''Oklahoma Gazette'' is its Chicken-Fried News, where interesting, weird and obscure news from around the state is highlighted. On June 14, 2023, the Gazette announced their ceasing of print publication to focus on digital media. It appears the dig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skunk Works
Skunk Works is an official pseudonym for Lockheed Martin's Advanced Development Programs (ADP), formerly called Lockheed Advanced Development Projects. It is responsible for a number of aircraft designs, highly classified research and development programs, and exotic aircraft platforms. Known locations include United States Air Force Plant 42 (Palmdale, California), United States Air Force Plant 4 (Fort Worth, Texas), and Marietta, Georgia. Skunk Works' history started with the P-38 Lightning in 1939 and the P-80 Shooting Star in 1943. Skunk Works engineers subsequently developed the U-2, SR-71 Blackbird, F-117 Nighthawk, F-22 Raptor, and F-35 Lightning II, the latter being used in the air forces of several countries. The Skunk Works name was taken from the "Skonk Oil" factory in the comic strip ''Li'l Abner''. Derived from the Lockheed use of the term, the designation "skunk works" or "skunkworks" is now widely used in business, engineering, and technical fields to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Purpose: Because living persons may suffer personal harm from inappropriate information, we should watch their articles carefully. By adding an article to this category, it marks them with a notice about sources whenever someone tries to edit them, to remind them of WP:BLP (biographies of living persons) policy that these articles must maintain a neutral point of view, maintain factual accuracy, and be properly sourced. Recent changes to these articles are listed on Special:RecentChangesLinked/Living people. Organization: This category should not be sub-categorized. Entries are generally sorted by family name In many societies, a surname, family name, or last name is the mostly hereditary portion of one's personal name that indicates one's family. It is typically combined with a given name to form the full name of a person, although several give .... Maintenance: Individuals of advanced age (over 90), for whom there has been no new documentation in the last ten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vince Weldon
Vincent A. Weldon is an American aerospace engineer who has designed critical components for both the Apollo Moon missions and the Space Shuttle. In 2006 Weldon called the Boeing 787 ''Dreamliner'' unsafe, and Boeing fired Weldon under disputed circumstances. Aerospace career Weldon joined Boeing in 1960, beginning a 46-year career with the firm. He was first involved with the wing design of the Boeing 727 airliner, a design that incorporated high-lift devices such as triple-slotted flaps, which enabled the 727 to be one of the first jet aircraft capable of operating from relatively short runways.Eden, Paul. (Ed). ''Civil Aircraft Today.'' 2008: Amber Books, pp. 72-3. In mid-1962, Weldon was assigned to the Apollo program, where he designed the support and release system for the Lunar Module. He was also tasked to design a new thrust structure for the Apollo Service module's main engine, which would be 100% stiffer, yet not increase the weight of the Service module. Weight was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Salvay
Melvin Eugene Salvay (November 15, 1919 – April 8, 2016) was an American aircraft engineer. Early life Salvay was born in Kansas City, Missouri. Gene's father, Israel David Salvay (b:1889 in Veisiejai, Lithuania) was a fashion designer and pattern maker; his mother, Anna (Kiansky) Salvay (b:1895 in Starodub Russia) worked as a seamstress in order to get her sons, Seymour Nathan Salvay (b:1916; Hump Pilot in WWII and, later, Vice President of Milgram Food Stores, Kansas City, MO) and Gene through high school and training as aeronautical engineers. Education Salvay graduated Central High School, Kansas City, Missouri, in 1936. That same year, he won 1st place nationally in the Fisher Body coach-building contest with a model of a horse-drawn carriage. The next year, he won 2nd place nationally in the Fisher Body auto-design contest. He continued his education at Curtiss-Wright Technical School, Glendale Airport, California from which he received his engineering degree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Institute Of Aeronautics And Astronautics
The American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (AIAA) is a professional society for the field of aerospace engineering Aerospace engineering is the primary field of engineering concerned with the development of aircraft and spacecraft. It has two major and overlapping branches: aeronautical engineering and astronautical engineering. Avionics engineering is s .... The AIAA is the U.S. representative on the International Astronautical Federation and the International Council of the Aeronautical Sciences. In 2015, it had more than 30,000 members among aerospace professionals worldwide (a majority are American or live in the United States). History The AIAA was founded in 1963 from the merger of two earlier societies: the American Rocket Society (ARS), founded in 1930 as the American Interplanetary Society (AIS), and the Institute of the Aerospace Sciences (IAS), founded in 1932 as the Institute of the Aeronautical Sciences. Paul Johnston was the first executive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States's civil list of government space agencies, space program, aeronautics research and outer space, space research. National Aeronautics and Space Act, Established in 1958, it succeeded the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) to give the American space development effort a distinct civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. It has since led most of America's space exploration programs, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968–1972 Apollo program missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. Currently, NASA supports the International Space Station (ISS) along with the Commercial Crew Program and oversees the development of the Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft and the Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lifting Body
A lifting body is a fixed-wing aircraft or spacecraft configuration in which the body itself produces lift (force), lift. In contrast to a flying wing, which is a wing with minimal or no conventional fuselage, a lifting body can be thought of as a fuselage with little or no conventional wing. Whereas a flying wing seeks to maximize cruise efficiency at Subsonic flight, subsonic speeds by eliminating non-lifting surfaces, lifting bodies generally minimize the drag and structure of a wing for subsonic, supersonic and hypersonic flight, or spacecraft re-entry. All of these flight regimes pose challenges for proper flight safety. Lifting bodies were a major area of research in the 1960s and 1970s as a means to build a small and lightweight crewed spacecraft. The US built a number of lifting body rocket planes to test the concept, as well as several rocket-launched re-entry vehicles that were tested over the Pacific. Interest waned as the US Air Force lost interest in the crewed missio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
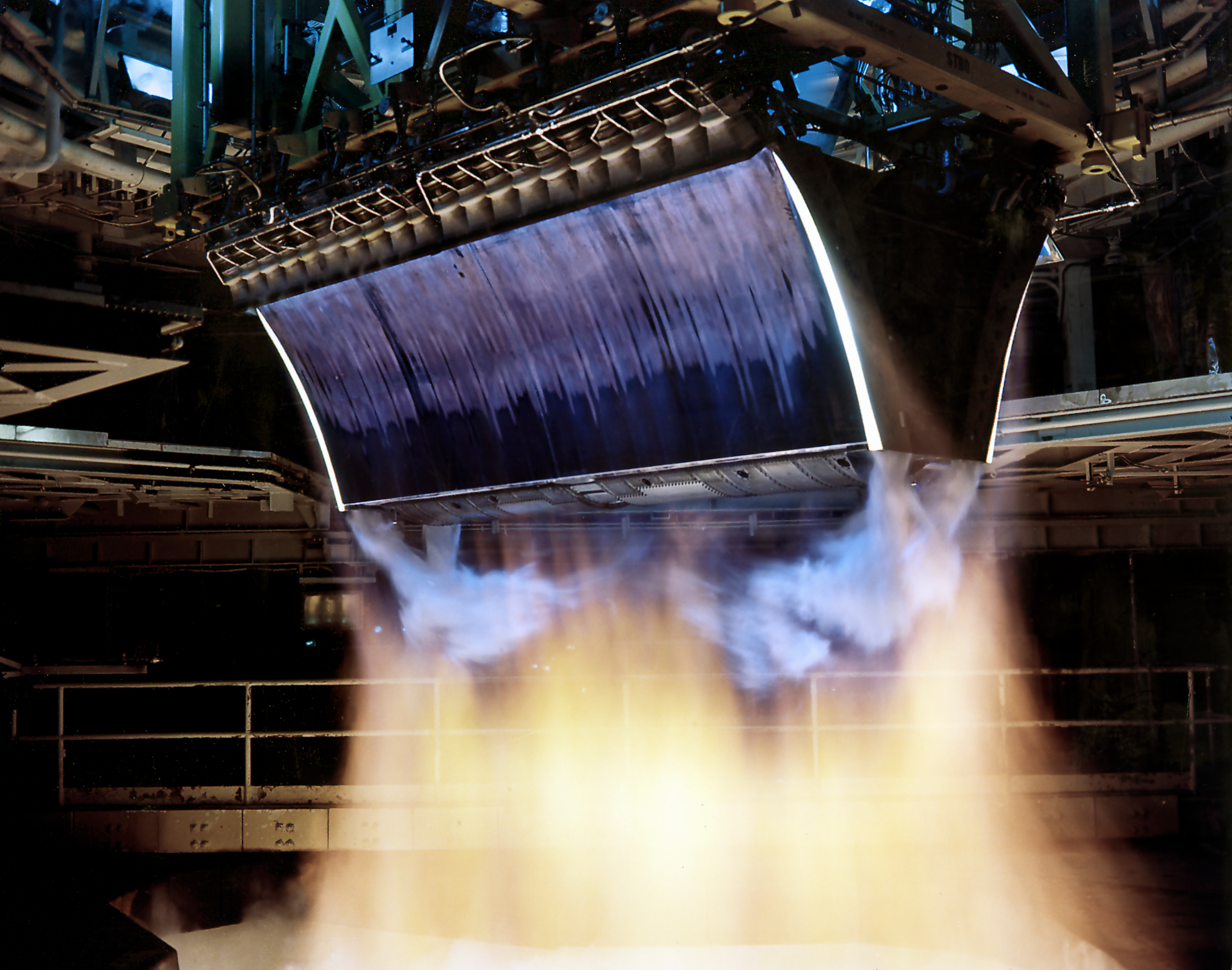
Aerospike Engine
The aerospike engine is a type of rocket engine that maintains its aerodynamic efficiency across a wide range of altitudes. It belongs to the class of altitude compensating nozzle engines. Aerospike engines were proposed for many single-stage-to-orbit (SSTO) designs. They were a contender for the Space Shuttle main engine. However, as of 2023 no such engine was in commercial production, although some large-scale aerospikes were in testing phases. The term ''aerospike'' was originally used for a truncated plug nozzle#In rockets, plug nozzle with a rough conical taper and some gas injection, forming an "air spike" to help make up for the absence of the plug tail. However, a full-length plug nozzle may also be called an aerospike. Principles The purpose of any engine bell is to direct the exhaust of a rocket engine in one direction, generating thrust in the opposite direction. The exhaust, a high-temperature mix of gases, has an effectively random momentum distribution (i.e., the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Have Region
Have or having may refer to: * the concept of ownership * any concept of ''possession'' * the English verb "to " is used: ** to express possession linguistically, in a broad sense ** as an auxiliary verb ** in constructions such as ''have something done'' * ''Having'' (album), a 2006 album by the band Trespassers William * Having (SQL), a clause in the SQL programming-language * Having (inlet), on Rügen island in Germany * HAVE, a United States military code-word designating projects developed by the Air Force Systems Command, such as the Lockheed Have Blue * ''Have'', a grammatically incorrect variation of the Latin salute ''Ave'' * Peter Have, Danish politician * Stefan Haves, American clown and director See also * Has (other) HAS or Has may refer to: Organizations * Hawaii Audubon Society, bird conservation organization in Hawaii * Hellenic Actuarial Society, association of actuaries in Greece * Hubbard Association of Scientologists International, corporati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oklahoma City
Oklahoma City (), officially the City of Oklahoma City, and often shortened to OKC, is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Oklahoma, most populous city of the U.S. state of Oklahoma. The county seat of Oklahoma County, Oklahoma, Oklahoma County, its population ranks List of United States cities by population, 20th among United States cities and 8th in the Southern United States. The population grew following the 2010 Census and reached 681,054 in the 2020 United States census. The Oklahoma City metropolitan area had a population of 1,396,445, and the Oklahoma City–Shawnee, Oklahoma, Shawnee Combined Statistical Area had a population of 1,469,124, making it Oklahoma's largest municipality and metropolitan area by population. Oklahoma City's city limits extend somewhat into Canadian County, Oklahoma, Canadian, Cleveland County, Oklahoma, Cleveland, and Pottawatomie County, Oklahoma, Pottawatomie counties. However, much of those areas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |