|
David Snoke
David W. Snoke is a Distinguished Professor of Physics at the University of Pittsburgh and co-director of the Pittsburgh Quantum Institute . In 2006 he was elected a Fellow of the American Physical Society "for his pioneering work on the experimental and theoretical understanding of dynamical optical processes in semiconductor systems." In 2004 he co-wrote a controversial paper with prominent intelligent design proponent Michael Behe. In 2007, his research group was the first to report Bose-Einstein condensation of polaritons in a trap. David Snoke and theoretical physicist Jonathan Keeling recently published an article announcing a new era for polariton condensates saying that polaritons are arguably the "...best hope for harnessing the strange effects of quantum condensation and superfluidity in everyday applications." Academic career Snoke received his bachelor's degree in physics from Cornell University and his PhD in physics from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." It is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physics. (...) You will come to see physics as a towering achievement of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Review Letters
''Physical Review Letters'' (''PRL''), established in 1958, is a peer-reviewed, scientific journal that is published 52 times per year by the American Physical Society. The journal is considered one of the most prestigious in the field of physics. Over a quarter of Physics Nobel Prize-winning papers between 1995 and 2017 were published in it. ''PRL'' is published both online and as a print journal. Its focus is on short articles ("letters") intended for quick publication. The Lead Editor is Hugues Chaté. The Managing Editor is Robert Garisto. History The journal was created in 1958. Samuel Goudsmit, who was then the editor of '' Physical Review'', the American Physical Society's flagship journal, organized and published ''Letters to the Editor of Physical Review'' into a new standalone journal'','' which became ''Physical Review Letters''. It was the first journal intended for the rapid publication of short articles, a format that eventually became popular in many other fiel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David W
David (; , "beloved one") was a king of ancient Israel and Judah and the third king of the United Monarchy, according to the Hebrew Bible and Old Testament. The Tel Dan stele, an Aramaic-inscribed stone erected by a king of Aram-Damascus in the late 9th/early 8th centuries BCE to commemorate a victory over two enemy kings, contains the phrase (), which is translated as " House of David" by most scholars. The Mesha Stele, erected by King Mesha of Moab in the 9th century BCE, may also refer to the "House of David", although this is disputed. According to Jewish works such as the '' Seder Olam Rabbah'', '' Seder Olam Zutta'', and '' Sefer ha-Qabbalah'' (all written over a thousand years later), David ascended the throne as the king of Judah in 885 BCE. Apart from this, all that is known of David comes from biblical literature, the historicity of which has been extensively challenged,Writing and Rewriting the Story of Solomon in Ancient Israel; by Isaac Kalimi; pag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Journal
In academic publishing, a scientific journal is a periodical publication designed to further the progress of science by disseminating new research findings to the scientific community. These journals serve as a platform for researchers, scholars, and scientists to share their latest discoveries, insights, and methodologies across a multitude of scientific disciplines. Unlike professional or trade magazines, the articles are mostly written by scientists rather than staff writers employed by the journal. Scientific journals are characterized by their rigorous peer review process, which aims to ensure the validity, reliability, and quality of the published content. In peer review, submitted articles are reviewed by active scientists (peers) to ensure scientific rigor. With origins dating back to the 17th century, the publication of scientific journals has evolved significantly, advancing scientific knowledge, fostering academic discourse, and facilitating collaboration within ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Center For Science And Culture
The Center for Science and Culture (CSC), formerly known as the Center for the Renewal of Science and Culture (CRSC), is part of the Discovery Institute (DI), a conservative Christian think tank in the United States. The CSC lobbies for the inclusion of creationism in the form of intelligent design (ID) in public-school science curricula as an explanation for the origins of life and the universe while trying to cast doubt on the theory of evolution. These positions have been rejected by many in the scientific community, which identifies intelligent design as pseudoscientific neo-creationism, whereas the theory of evolution is the accepted scientific consensus. The Center for Science and Culture serves as the hub of the intelligent design movement. Nearly all of prominent proponents of intelligent design are either CSC advisors, officers, or fellows. Stephen C. Meyer, a former vice president of the Discovery Institute and founder of the CSC, serves as a Senior Fellow, and Phil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discovery Institute
The Discovery Institute (DI) is a conservatism in the United States, politically conservative think tank that advocates the pseudoscience, pseudoscientific concept Article available froUniversiteit Gent of intelligent design (ID). It was founded in 1991 in Seattle as a Nonprofit organization, non-profit offshoot of the Hudson Institute. Its "Teach the Controversy" campaign aims to permit the teaching of anti-evolution, intelligent-design beliefs in United States State school#United States, public high school Science education, science courses in place of accepted Scientific theory, scientific theories, positing that a scientific controversy exists over whether evolution is a reality, when in fact there is none. History The institute was cofounded in 1991 by Bruce Chapman and George Gilder as a non-profit educational foundation and think tank. It was started as a branch organization of the Hudson Institute, an Indianapolis-based conservatism in the United States, conservative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
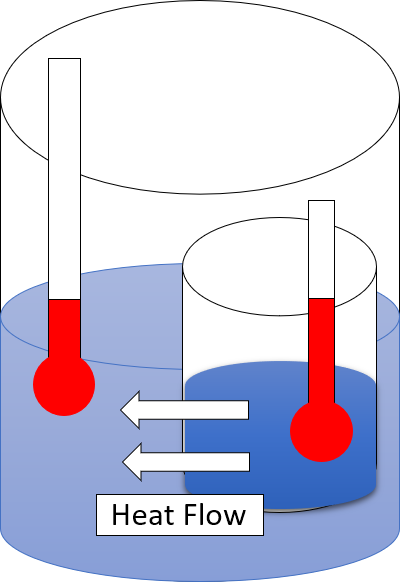
Second Law Of Thermodynamics
The second law of thermodynamics is a physical law based on Universal (metaphysics), universal empirical observation concerning heat and Energy transformation, energy interconversions. A simple statement of the law is that heat always flows spontaneously from hotter to colder regions of matter (or 'downhill' in terms of the temperature gradient). Another statement is: "Not all heat can be converted into Work (thermodynamics), work in a cyclic process."Young, H. D; Freedman, R. A. (2004). ''University Physics'', 11th edition. Pearson. p. 764. The second law of thermodynamics establishes the concept of entropy as a physical property of a thermodynamic system. It predicts whether processes are forbidden despite obeying the requirement of conservation of energy as expressed in the first law of thermodynamics and provides necessary criteria for spontaneous processes. For example, the first law allows the process of a cup falling off a table and breaking on the floor, as well as allowi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Boltzmann Equation
The quantum Boltzmann equation, also known as the Uehling–Uhlenbeck equation, is the quantum mechanical modification of the Boltzmann equation, which gives the nonequilibrium time evolution of a gas of quantum-mechanically interacting particles. Typically, the quantum Boltzmann equation is given as only the “collision term” of the full Boltzmann equation, giving the change of the momentum distribution of a locally homogeneous gas, but not the drift and diffusion in space. It was originally formulated by L.W. Nordheim (1928), and by and E. A. Uehling and George Uhlenbeck (1933). In full generality (including the p-space and x-space drift terms, which are often neglected) the equation is represented analogously to the Boltzmann equation. \left frac + \mathbf \cdot \nabla_x + \mathbf \cdot \nabla_p \rightf(\mathbf,\mathbf,t) = \mathcal \mathbf,\mathbf) where \mathbf represents an externally applied potential acting on the gas' p-space distribution and \mathcal is the collisio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boltzmann
Ludwig Eduard Boltzmann ( ; ; 20 February 1844 – 5 September 1906) was an Austrian mathematician and theoretical physicist. His greatest achievements were the development of statistical mechanics and the statistical explanation of the second law of thermodynamics. In 1877 he provided the current definition of entropy, S = k_ \ln \Omega, where Ω is the number of microstates whose energy equals the system's energy, interpreted as a measure of the statistical disorder of a system. Max Planck named the constant the Boltzmann constant. Statistical mechanics is one of the pillars of modern physics. It describes how macroscopic observations (such as temperature and pressure) are related to microscopic parameters that fluctuate around an average. It connects thermodynamic quantities (such as heat capacity) to microscopic behavior, whereas, in classical thermodynamics, the only available option would be to measure and tabulate such quantities for various materials. Biography ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrow Of Time
An arrow is a fin-stabilized projectile launched by a bow. A typical arrow usually consists of a long, stiff, straight shaft with a weighty (and usually sharp and pointed) arrowhead attached to the front end, multiple fin-like stabilizers called fletchings mounted near the rear, and a slot at the rear end called a nock for engaging the bowstring. A container or bag carrying additional arrows for convenient reloading is called a quiver. The use of bows and arrows by humans predates recorded history and is common to most cultures. A craftsman who makes arrows is a fletcher, and one who makes arrowheads is an arrowsmith.Paterson ''Encyclopaedia of Archery'' p. 56 History The oldest evidence of likely arrowheads, dating to years ago, were found in Sibudu Cave, current South Africa.Backwell L, d'Errico F, Wadley L.(2008). Middle Stone Age bone tools from the Howiesons Poort layers, Sibudu Cave, South Africa. Journal of Archaeological Science, 35:1566–1580. Backwell L, B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bose–Einstein Condensation
Bose–Einstein may refer to: * Bose–Einstein condensate, a phase of matter in quantum mechanics ** Bose–Einstein condensation (network theory), the application of this model in network theory ** Bose–Einstein condensation of polaritons ** Bose–Einstein condensation of quasiparticles * Bose–Einstein correlations * Bose–Einstein integral * Bose–Einstein statistics, in particle statistics See also *Bose (other) *Einstein (other) *Boson (other) *Satyendra Nath Bose Satyendra Nath Bose (; 1 January 1894 – 4 February 1974) was an Indian theoretical physicist and mathematician. He is best known for his work on quantum mechanics in the early 1920s, in developing the foundation for Bose–Einstein statist ..., Indian physicist * Albert Einstein (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |