|
David Saharuni
David Saharuni (, ''Davit' Saharuni'') was ''sparapet'', ''curopalates'', '' ishkhan'', and presiding prince of Byzantine-controlled Armenia from 635 to 638. In an unprecedented move, his remit also included Byzantine-controlled Syria, which was likely driven by the efforts of the emperor Heraclius to attract Armenian military support against the advancing Muslim armies. Biography David was a nakharar from the princely noble House of Saharuni. When the marzpan of Persarmania Varaztirots II Bagratuni was in the Byzantine imperial court in Osroene, he entered into a plot against emperor Heraclius organized by his illegitimate son John Athalarichos. David was also part of this plot. The attempt ultimately failed and Varaztirots was deported to an island near the coast of North Africa. David Saharuni was attacked by the general and ruler of Byzantine Armenia, Mzhezh Gnuni but managed to evade capture and killed Mzhezh Gnuni, with the help of Gnuni's own troops, many of whom were Arm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sparapet
' () was a military title and office in ancient and medieval Armenia. Under the Arsacid dynasty of Armenia, the ' was the supreme commander of the kingdom's armed forces. During the Arsacid period and for some time afterwards, the office was held hereditarily by the senior member of the House of Mamikonian. Later in history, the title was held by members of other noble houses, such as the Bagratuni Dynasty, Bagratuni and Pahlavuni dynasties. The title was used in the medieval Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia, where the bearer of the title was also called ' (), from the Byzantine and Western title of constable. Etymology The word is of Iranian origin, ultimately deriving from Proto-Iranian language, Proto-Iranian ''*spādapati-'' (“commander of the army”), which is composed of ''*cwáHdaH'' (“army”) and ''*pati-'' (“lord”).Anahit Perikhanian, Perikhanyan, A. G. (1993). ''Материалы к этимологическому словарю древнеармянского ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mjej II Gnuni
Mzhezh or Mjej Gnuni (, ''Mžēž Gnuni''), was an Armenian sparapet of Byzantine Armenia. Initially serving under Heraclius, the contingent of Armenian troops under his command were instrumental in the Byzantine success against the Sassanids during the Byzantine-Persian Wars that culminated in the overthrow of Khosrau II in 628. He also served as the sparapet (commander in chief) of Byzantine Armenia from about 630 to 638, and during this time may have been responsible for the founding of the Cathedral of Mren. He was succeeded in this position by David Saharuni David Saharuni (, ''Davit' Saharuni'') was ''sparapet'', ''curopalates'', '' ishkhan'', and presiding prince of Byzantine-controlled Armenia from 635 to 638. In an unprecedented move, his remit also included Byzantine-controlled Syria, which was li ..., from the middle-ranking Armenian nobility, after the latter was accused of plotting against the life of Heraclius. While being sent into exile, David escaped and made his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
7th-century Armenian People
The 7th century is the period from 601 through 700 in accordance with the Julian calendar in the Christian Era. The spread of Islam and the Muslim conquests began with the unification of Arabia by the Islamic prophet Muhammad starting in 622. After Muhammad's death in 632, Islam expanded beyond the Arabian Peninsula under the Rashidun Caliphate (632–661) and the Umayyad Caliphate (661–750). The Muslim conquest of Persia in the 7th century led to the downfall of the Sasanian Empire. Also conquered during the 7th century were Syria, Palestine, Armenia, Egypt, and North Africa. The Byzantine Empire suffered setbacks during the rapid expansion of the Caliphate and a mass incursion of Slavs in the Balkans which reduced its territorial limits. The decisive victory at the Siege of Constantinople in the 670s led the empire to retain Asia Minor, which ensured the existence of the empire. In the Iberian Peninsula, the 7th century was known as the ''Siglo de Concilios'' (century o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Governors
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th centuryAD, it endured until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. The term 'Byzantine Empire' was coined only after its demise; its citizens used the term 'Roman Empire' and called themselves 'Romans'. During the early centuries of the Roman Empire, the western provinces were Romanization (cultural), Latinised, but the eastern parts kept their Hellenistic culture. Constantine the Great, Constantine I () legalised Christianity and moved the capital to Constantinople. Theodosius I, Theodosius I () made Christianity the state religion and Greek gradually replaced Latin for official use. The empire adopted a defensive strategy and, throughout its remaining history, expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
7th-century Monarchs In Asia
The 7th century is the period from 601 through 700 in accordance with the Julian calendar in the Christian Era. The spread of Islam and the Muslim conquests began with the unification of Arabia by the Islamic prophet Muhammad starting in 622. After Muhammad's death in 632, Islam expanded beyond the Arabian Peninsula under the Rashidun Caliphate (632–661) and the Umayyad Caliphate (661–750). The Muslim conquest of Persia in the 7th century led to the downfall of the Sasanian Empire. Also conquered during the 7th century were Syria, Palestine, Armenia, Egypt, and North Africa. The Byzantine Empire suffered setbacks during the rapid expansion of the Caliphate and a mass incursion of Slavs in the Balkans which reduced its territorial limits. The decisive victory at the Siege of Constantinople in the 670s led the empire to retain Asia Minor, which ensured the existence of the empire. In the Iberian Peninsula, the 7th century was known as the ''Siglo de Concilios'' (century o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Death Unknown
A year is a unit of time based on how long it takes the Earth to orbit the Sun. In scientific use, the tropical year (approximately 365 solar days, 5 hours, 48 minutes, 45 seconds) and the sidereal year (about 20 minutes longer) are more exact. The modern calendar year, as reckoned according to the Gregorian calendar, approximates the tropical year by using a system of leap years. The term 'year' is also used to indicate other periods of roughly similar duration, such as the lunar year (a roughly 354-day cycle of twelve of the Moon's phasessee lunar calendar), as well as periods loosely associated with the calendar or astronomical year, such as the seasonal year, the fiscal year, the academic year, etc. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by changes in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sebeos
Sebeos () was the reputed author of a 7th-century Armenian history. As this authorship attribution is widely accepted to be false (pseudepigraphical), the author is frequently referred to as Pseudo-Sebeos. Though his name is not known, he was likely a member of the clergy. It is the primary source for Armenian history in the 6th and 7th centuries. It is valued as the earliest surviving major account of the rise of Islam and the early Muslim conquests and as one of the very few non-Islamic sources on the Muslim conquests Authorship The history attributed to Sebeos has survived in a manuscript written in Bitlis in 1672 (now held at the Matenadaran in Armenia), in which it is included as an anonymous, untitled history in a collection of Armenian sources.Sebeos 1999, p. xxxi. The name ''Sebeos'', which is a shortened form of the name ''Eusebius'', appears as the name of one of the Armenian bishops who signed the resolution of the Fourth Council of Dvin in 645: "Bishop Sebeos of the Bag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodoros Rshtuni
Theodore or Theodoros Rshtuni (, ; AD 590–655 or 656), equated with Pasagnathes (), the "''patrikios'' of the Armenians" from the chronicle of Theophanes the Confessor, at, '' of the Byzantine Empire 641-867'' (PBE I) online edition, . Accessed 2021-09-16. was an (magnate), famous for resisting the first Arab invasions of Armenia. After the previous (prince) [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dionysius Of Tell Mahre
Dionysius I Telmaharoyo (Latin: ''Dionysius Telmaharensis'', Syriac: ܕܝܘܢܢܘܣܝܘܣ ܬܠܡܚܪܝܐ, Arabic: مار ديونيسيوس التلمحري), also known as Dionysius of Tel Mahre, was the Patriarch of Antioch, and head of the Syriac Orthodox Church from 818 until his death in 845.Barsoum (2003) Biography Dionysius was born in Tal Mahre, near the city of Raqqa, into a wealthy family from Edessa, and became a monk at the Monastery of Qenneshre, where he studied philology, jurisprudence, philosophy, and theology. He also studied at the Monastery of Mar Jacob at Kayshum.Hoyland (1997), p. 416 In 818, Dionysius was elected Patriarch of Antioch unanimously by a synod of forty-eight bishops. After his consecration, he issued a proclamation and held three councils in Raqqa in the same year, at which he issued twelve canons. Dionysius restored the Monastery of Qenneshre in 822 after it was damaged by fire caused by dissenters. In 826, Dionysius visited Egypt in the com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
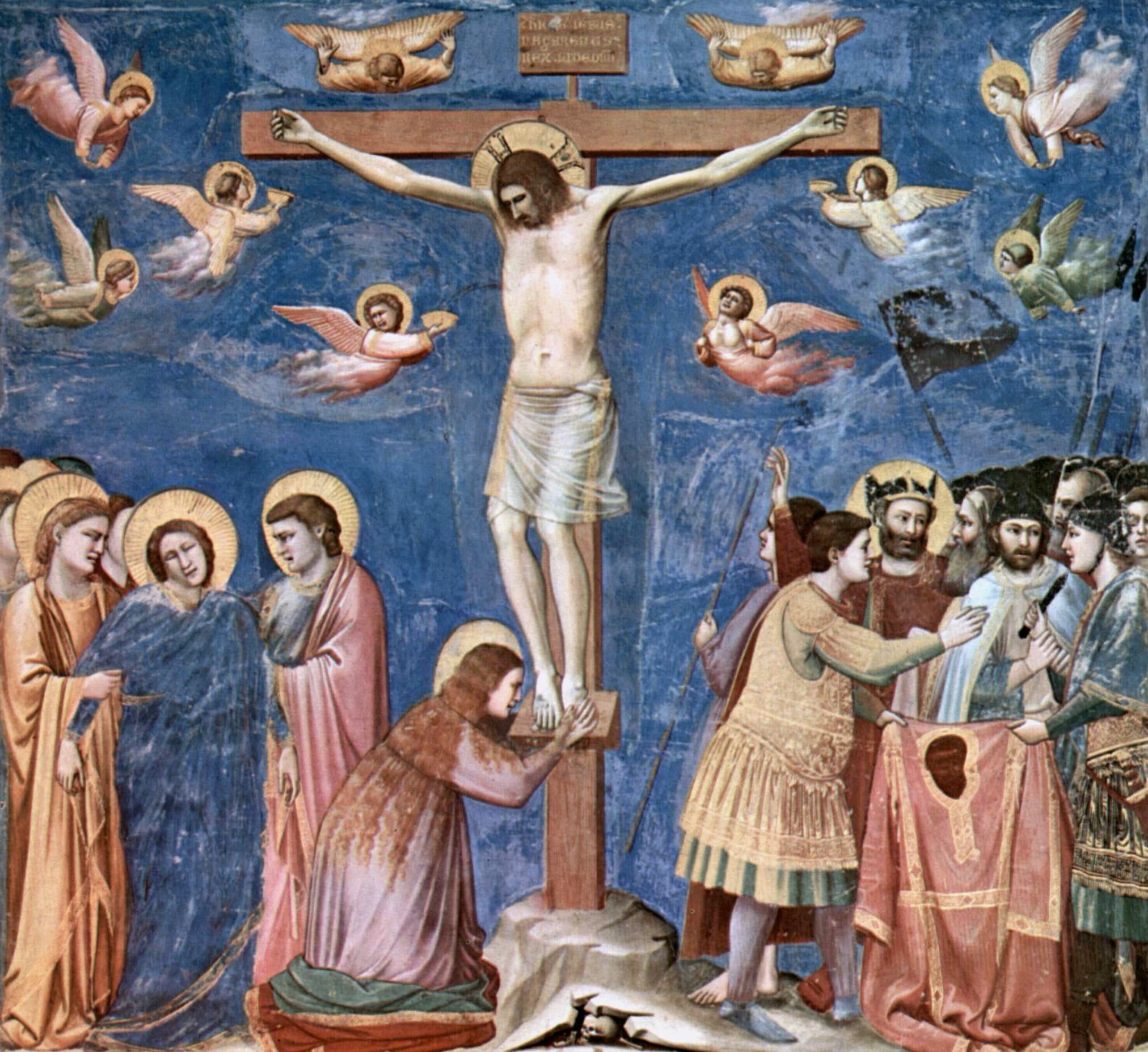
True Cross
According to Christian tradition, the True Cross is the real instrument of Jesus' crucifixion, cross on which Jesus of Nazareth was Crucifixion of Jesus, crucified. It is related by numerous historical accounts and Christian mythology, legends that Helena, mother of Constantine I, Helen, the mother of Roman emperor Constantine the Great, recovered the True Cross at the Holy Sepulchre in Jerusalem, when she travelled to the Holy Land in the years 326–328. The late fourth-century historians Gelasius of Caesarea and Tyrannius Rufinus wrote that while Helen was there, she discovered the hiding place of three crosses that were believed to have been used at the crucifixion of Jesus and the two thieves, Penitent thief, Dismas and Impenitent thief, Gestas, who were executed with him. To one cross was affixed the Titulus (inscription), titulus bearing Jesus' name, but according to Rufinus, Helen was unsure of its legitimacy until a miracle revealed that it was the True Cross. This event ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |