|
David Hostetler
David L. Hostetler (December 27, 1926 – November 18, 2015) was a wood carver and bronze sculptor of works capturing the female form. He was also a professor emeritus of Ohio University. Biography Early life Born in Beach City, Ohio, on December 27, 1926, Hostetler had a close relationship with his Amish grandfather, an influence which stayed with him throughout his career. His interest in art came by accident: during World War II, while studying as an engineer in the US Army, he suffered a Shrapnel shell, shrapnel wound in the leg during a training exercise in California. While recuperating for six months, he became interested in art after receiving drawing materials from a Red Cross volunteer. He received his art degree from Indiana University in 1948 and in 1949 was awarded a Master's of Fine Arts from Ohio University, where he taught for 38 years. Career His art career spanned more than 60 years, progressing from Folk art, folk images to stylized forms and including guest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
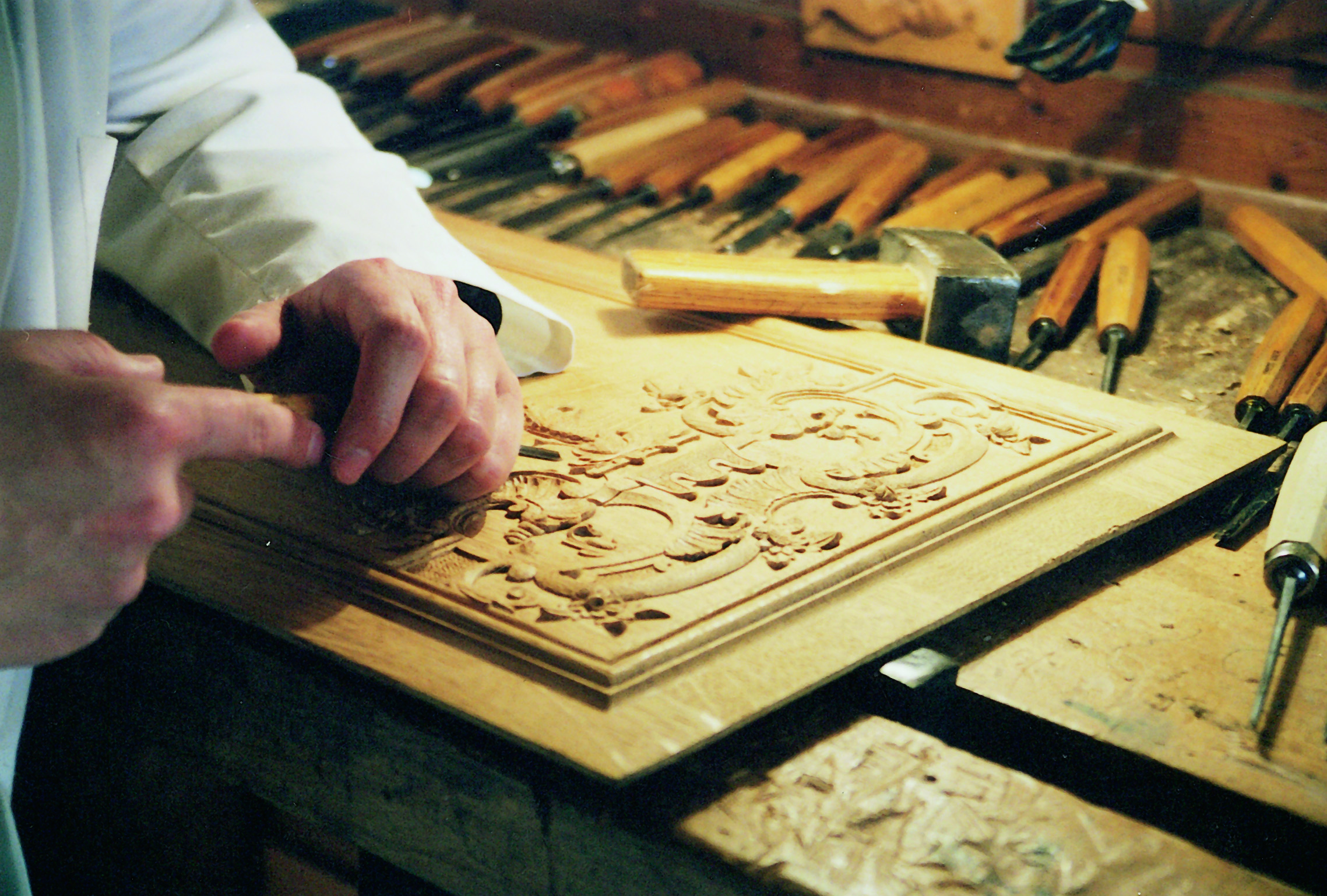
Wood Carver
Wood carving is a form of woodworking by means of a cutting tool (knife) in one hand or a chisel by two hands or with one hand on a chisel and one hand on a mallet, resulting in a wooden figure or figurine, or in the sculptural ornamentation of a wooden object. The phrase may also refer to the finished product, from individual sculptures to hand-worked mouldings composing part of a tracery. The making of sculpture in wood has been extremely widely practised, but doesn't survive undamaged as well as the other main materials like stone and bronze, as it is vulnerable to decay, insect damage, and fire. Therefore, it forms an important hidden element in the art history of many cultures. Outdoor wood sculptures do not last long in most parts of the world, so it is still unknown how the totem pole tradition developed. Many of the most important sculptures of China and Japan, in particular, are in wood, and so are the great majority of African sculpture and that of Oceania an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denver Art Museum
The Denver Art Museum (DAM) is an art museum located in the Civic Center of Denver, Colorado. With encyclopedic collections of more than 70,000 diverse works from across the centuries and world, the DAM is one of the largest art museums between the West Coast and Chicago. It is known for its collection of American Indian art, as well as The Petrie Institute of Western American Art, which oversees the museum's Western art collection. and its other collections of more than 70,000 diverse works from across the centuries and world. The museum's iconic Martin Building (formerly known as the North Building) was designed by famed Italian architect Gio Ponti in 1971. In 2018, the museum began a transformational $150 million renovation project to unify the campus and revitalize Ponti's original structure, including the creation of new exhibition spaces, two new dining options, and a new welcome center. History 1893–1923 The museum's origins can be traced back to the founding of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yousuf Karsh
Yousuf Karsh, FRPS (December 23, 1908 – July 13, 2002) was a Canadian-Armenian photographer known for his portraits of notable individuals. He has been described as one of the greatest portrait photographers of the 20th century. An Armenian genocide survivor, Karsh migrated to Canada as a refugee. By the 1930s he established himself as a significant photographer in Ottawa, where he lived most of his adult life, though he traveled extensively for work. His iconic 1941 photograph of Winston Churchill was a breakthrough point in his 60-year career, through which he took numerous photos of known political leaders, men and women of arts and sciences. Over 20 photos by Karsh appeared on the cover of ''Life'' magazine, until he retired in 1993. Early life and arrival in Canada Yousuf Karsh was born to Armenian parents Amsih Karsh (1872–1962), a merchant, and Bahia Nakash (1883–1958), on December 23, 1908, in Mardin, Diyarbekir Vilayet, Ottoman Empire. His father was Catholic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pink Ivory
Pink ivory (''Phyllogeiton zeyheri'', syn. ''Berchemia zeyheri''), also called purple ivory, red ivory, umnini or umgoloty, is an African hardwood used to make a variety of products (for example: billiard cues and knife handles). The pink ivory tree grows predominantly in Zimbabwe, Mozambique, Northern Botswana and South Africa. The tree is protected and sustainably maintained in South Africa, only felled by very limited permit. The wood is extremely hard, with a density of 990 g/dm3. Pink ivory was the royal tree of the Zulu people and only members of the royal family were allowed to possess it until the Anglo-Zulu War The Anglo-Zulu War was fought in 1879 between the British Empire and the Zulu Kingdom. Following the passing of the British North America Act of 1867 forming a federation in Canada, Lord Carnarvon thought that a similar political effort, coup ... of 1879. Before the Anglo-Zulu War, the Zulu king (and prior to 1818, Zulu chiefs) would possess a pink ivory '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cordia
''Cordia'' is a genus of flowering plants in the borage family, Boraginaceae. It contains about 300 species of shrubs and trees, that are found worldwide, mostly in warmer regions. Many of the species are commonly called manjack, while ''bocote'' may refer to several Central American species in Spanish. The generic name honours German botanist and pharmacist Valerius Cordus (1515–1544). Like most other Boraginaceae, the majority have trichomes (hairs) on the leaves. Taxonomy The taxonomy of ''Cordia'' is complex and controversial. Gottschling et al. (2005) say this is partly due to "extraordinarily high intraspecific variability" in some groups of species, making identification difficult, and partly due to new taxa having been "airily described on the basis of poorly preserved herbarium specimens". Selected species *'' Cordia africana'' Lam. – White manjack *'' Cordia alliodora'' ( Ruiz & Pav.) Oken – Spanish elm, Ecuador laurel, salmwood, bocote (Neotropics) *''Cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purpleheart
''Peltogyne'', commonly known as purpleheart, violet wood, amaranth and other local names (often referencing the colour of the wood) is a genus of 23 species of flowering plants in the family Fabaceae; native to tropical rainforests of Central and South America; from Guerrero, Mexico, through Central America, and as far as south-eastern Brazil. They are medium-sized to large trees growing to tall, with trunk diameters of up to . The leaves are alternate, divided into a symmetrical pair of large leaflets long and broad. The flowers are small, with five white petals, produced in panicles. The fruit is a pod containing a single seed. The timber is desirable, but difficult to work. Distribution The species of the genus range from southeastern Brazil through northern South America, Panama, Costa Rica, and Trinidad, with the majority of species in the Amazon Basin. ''P. mexicana'' is a geographic outlier, native to the Mexican state of Guerrero. Overharvesting has caused several s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maple
''Acer'' () is a genus of trees and shrubs commonly known as maples. The genus is placed in the family Sapindaceae.Stevens, P. F. (2001 onwards). Angiosperm Phylogeny Website. Version 9, June 2008 nd more or less continuously updated since http://www.mobot.org/MOBOT/research/APweb/. There are approximately 132 species, most of which are native to Asia, with a number also appearing in Europe, northern Africa, and North America. Only one species, '' Acer laurinum'', extends to the Southern Hemisphere.Gibbs, D. & Chen, Y. (2009The Red List of Maples Botanic Gardens Conservation International (BGCI) The type species of the genus is the sycamore maple, '' Acer pseudoplatanus'', the most common maple species in Europe.van Gelderen, C. J. & van Gelderen, D. M. (1999). ''Maples for Gardens: A Color Encyclopedia'' Maples usually have easily recognizable palmate leaves ('' Acer negundo'' is an exception) and distinctive winged fruits. The closest relatives of the maples are the hor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walnut
A walnut is the edible seed of a drupe of any tree of the genus '' Juglans'' (family Juglandaceae), particularly the Persian or English walnut, '' Juglans regia''. Although culinarily considered a "nut" and used as such, it is not a true botanical nut. After full ripening, the shell is discarded and the kernel is eaten. Nuts of the eastern black walnut ('' Juglans nigra'') and butternuts ('' Juglans cinerea'') are less commonly consumed. Characteristics Walnuts are rounded, single-seeded stone fruits of the walnut tree commonly used for food after fully ripening between September and November, in which the removal of the husk at this stage reveals a browning wrinkly walnut shell, which is usually commercially found in two segments (three or four-segment shells can also form). During the ripening process, the husk will become brittle and the shell hard. The shell encloses the kernel or meat, which is usually made up of two halves separated by a membranous partition. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
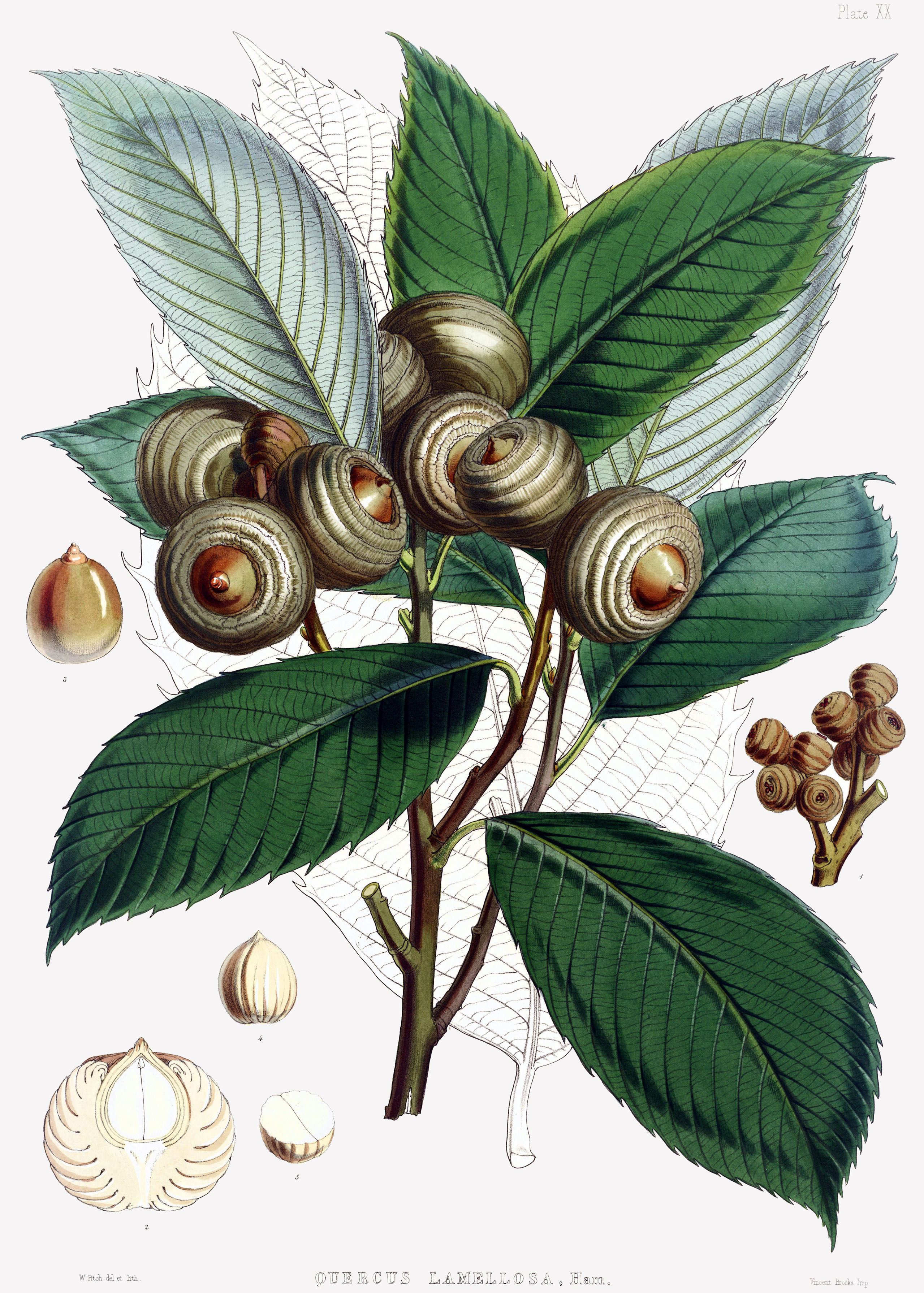
White Oak
The genus ''Quercus'' contains about 500 species, some of which are listed here. The genus, as is the case with many large genera, is divided into subgenera and sections. Traditionally, the genus ''Quercus'' was divided into the two subgenera ''Cyclobalanopsis'', the ring-cupped oaks, and ''Quercus'', which included all the other sections. However, a comprehensive revision in 2017 identified different relationships. Now the genus is commonly divided into a subgenus ''Quercus'' and a sugenus ''Cerris'', with ''Cyclobalanopsis'' included in the latter. The sections of subgenus ''Quercus'' are mostly native to the New World, with the notable exception of the white oaks of sect. ''Quercus'' and the endemic Quercus pontica. In contrast, the sections of the subgenus ''Cerris'' are exclusively native to the Old World. Legend Species with evergreen foliage (" live oaks") are tagged '#'. Species in the genus have been recategorized between deciduous and evergreen on numerous occasions, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hardwoods
Hardwood is wood from dicot trees. These are usually found in broad-leaved temperate and tropical forests. In temperate and boreal latitudes they are mostly deciduous, but in tropics and subtropics mostly evergreen. Hardwood (which comes from angiosperm trees) contrasts with softwood (which is from gymnosperm trees). Characteristics Hardwoods are produced by angiosperm trees that reproduce by flowers, and have broad leaves. Many species are deciduous. Those of temperate regions lose their leaves every autumn as temperatures fall and are dormant in the winter, but those of tropical regions may shed their leaves in response to seasonal or sporadic periods of drought. Hardwood from deciduous species, such as oak, normally shows annual growth rings, but these may be absent in some tropical hardwoods. Hardwoods have a more complex structure than softwoods and are often much slower growing as a result. The dominant feature separating "hardwoods" from softwoods is the presence o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religious Conversion
Religious conversion is the adoption of a set of beliefs identified with one particular religious denomination to the exclusion of others. Thus "religious conversion" would describe the abandoning of adherence to one denomination and affiliating with another. This might be from one to another denomination within the same religion, for example, from Baptist to Catholic Christianity or from Sunni Islam to Shi’a Islam. In some cases, religious conversion "marks a transformation of religious identity and is symbolized by special rituals". People convert to a different religion for various reasons, including active conversion by free choice due to a change in beliefs, secondary conversion, deathbed conversion, conversion for convenience, marital conversion, and forced conversion. Proselytism is the act of attempting to convert by persuasion another individual from a different religion or belief system. Apostate is a term used by members of a religion or denomination to refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The people of the Kingdom of Israel and the ethnic and religious group known as the Jewish people that descended from them have been subjected to a number of forced migrations in their history" and Hebrews of historical History of ancient Israel and Judah, Israel and Judah. Jewish ethnicity, nationhood, and religion are strongly interrelated, "Historically, the religious and ethnic dimensions of Jewish identity have been closely interwoven. In fact, so closely bound are they, that the traditional Jewish lexicon hardly distinguishes between the two concepts. Jewish religious practice, by definition, was observed exclusively by the Jewish people, and notions of Jewish peoplehood, nation, and community were suffused with faith in the Jewish God, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)