|
David H. Turner
David Howe Turner is a professor of Anthropology at the University of Toronto, and a Fellow at Trinity College and the Netherlands Institute for Advanced Study. He has worked with Indigenous Australians since 1969 and has worked with indigenous peoples in Bali, North India, Japan, and Canada. At Toronto, his main area of focus is comparative religion and the role of music in the indigenous societies of Australia, North America, Africa, and India. While conducting his Ph.D. at the University of Western Australia, Turner began his fieldwork with the people of Groote Eylandt, in order to better understand Aboriginal social organization and symbolism. Since then, he has challenged common notions of hunter-gatherer social and spiritual life and sought to bring a deeper understanding of the Australian Aboriginal way of life to the modern world. Indeed, in 1986, after undergoing the second stage of initiation by the Aboriginal people of Groote Eylandt, he was told by his hosts to go ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthropology
Anthropology is the scientific study of humanity, concerned with human behavior, human biology, cultures, society, societies, and linguistics, in both the present and past, including archaic humans. Social anthropology studies patterns of behaviour, while cultural anthropology studies cultural meaning, including norms and values. The term sociocultural anthropology is commonly used today. Linguistic anthropology studies how language influences social life. Biological anthropology, Biological (or physical) anthropology studies the biology and evolution of Human evolution, humans and their close primate relatives. Archaeology, often referred to as the "anthropology of the past," explores human activity by examining physical remains. In North America and Asia, it is generally regarded as a branch of anthropology, whereas in Europe, it is considered either an independent discipline or classified under related fields like history and palaeontology. Etymology The abstract noun ''wikt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
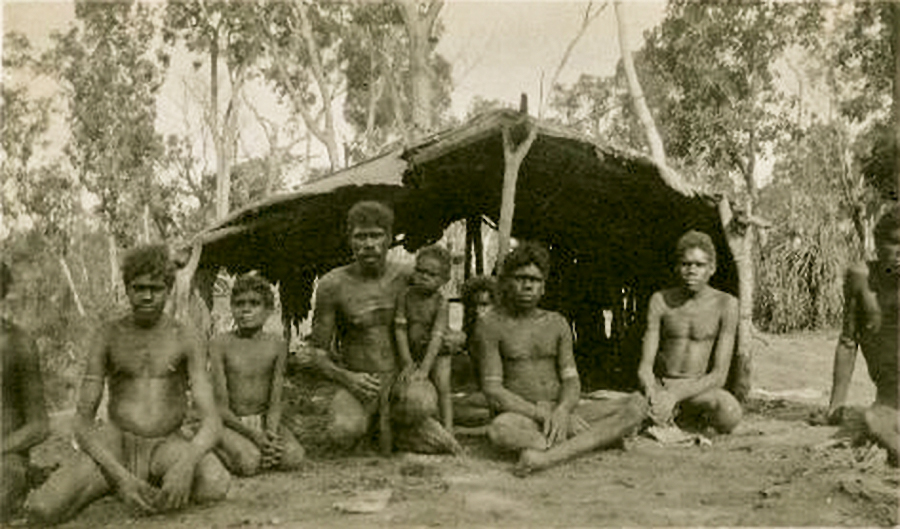
Groote Eylandt
Groote Eylandt ( Anindilyakwa: ''Ayangkidarrba''; meaning "island" ) is the largest island in the Gulf of Carpentaria and the fourth largest island in Australia. It was named by the explorer Abel Tasman in 1644 and is Dutch for "large island" in archaic spelling. The modern Dutch spelling is ''Groot Eiland''. The original inhabitants of Groote Eylandt are the Anindilyakwa people (also known as Warnindhilyagwa), an Aboriginal Australian people, who speak the Anindilyakwa language (also known as Amamalya Ayakwa). They consist of 14 clan groups which make up the two moieties on the island. The clans maintain their traditions and have strong ties with the people in the community of Numbulwar and on Bickerton Island. The island's population was 2,811 in the 2016 census. There are four communities on Groote Eylandt. The mining company GEMCO established the township of Alyangula for its workers. The three main Aboriginal communities are Angurugu and Umbakumba, and Milyakbu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academic Staff Of The University Of Toronto
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of tertiary education. The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, founded approximately 386 BC at Akademia, a sanctuary of Athena, the goddess of wisdom and skill, north of Athens, Greece. The Royal Spanish Academy defines academy as scientific, literary or artistic society established with public authority and as a teaching establishment, public or private, of a professional, artistic, technical or simply practical nature. Etymology The word comes from the ''Academy'' in ancient Greece, which derives from the Athenian hero, ''Akademos''. Outside the city walls of Athens, the gymnasium was made famous by Plato as a center of learning. The sacred space, dedicated to the goddess of wisdom, Athena, had formerly been an olive grove, hence the expression "the groves of Academe". In these gardens, the philosopher Plato conversed with followers. Plato developed his sessions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Anthropologists
Canadians () are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of their being ''Canadian''. Canada is a multilingual and multicultural society home to people of groups of many different ethnic, religious, and national origins, with the majority of the population made up of Old World immigrants and their descendants. Following the initial period of French and then the much larger British colonization, different waves (or peaks) of immigration and settlement of non-indigenous peoples took place over the course of nearly two centuries and continue today. Elements of Indigenous, French, British, and more recent immigrant customs, languages, and religions have combined to form the culture of Canada, and thus a Canadian identity and Canadian values. Canada has also been strongly influenced by its linguistic, geographic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creation Myth
A creation myth or cosmogonic myth is a type of cosmogony, a symbolic narrative of how the world began and how people first came to inhabit it., "Creation myths are symbolic stories describing how the universe and its inhabitants came to be. Creation myths develop through oral traditions and therefore typically have multiple versions." While in popular usage the term ''myth'' often refers to false or fanciful stories, members of cultures often ascribe varying degrees of truth to their creation myths. In the society in which it is told, a creation myth is usually regarded as conveying profound truthsmetaphorically, symbolically, historically, or literally. They are commonly, although not always, considered cosmogonical mythsthat is, they describe the ordering of the cosmos from a state of chaos or amorphousness. Creation myths often share several features. They often are considered sacred accounts and can be found in nearly all known religious traditions. They are all storie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bickerton Island
Bickerton Island is 13 km west of Groote Eylandt and 8 km east of the mouth of Blue Mud Bay in eastern Arnhem Land, in the Northern Territory of Australia. It is about 21 by 21 kilometres in size, with deep bays and indentations, and has an area of 215 km2. The largest bays are South Bay and North Bay. Bickerton Island was named by Matthew Flinders for Admiral Sir Richard Bickerton, Bt. Flinders actually called it "Bickerton's Island", and noted as follows in Voyage to Terra Australis II: "In passing the south side of Bickerton's Island, we observed in it a deep bight or bay which would afford shelter in the north-west monsoon, if there be depth sufficient for a ship; and the hills at the back being high and woody, there was a probability of its receiving a stream of fresh water. The country round the entrance of the bight, had the appearance of being sandy and sterile." The Aboriginal community of Milyakburra was established in 1975 as a family outstation. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Lang (publishing Company)
Peter Lang is an academic publisher specializing in the humanities and social sciences. It has its headquarters in Lausanne, Switzerland, with offices in Berlin, Brussels, Chennai, New York, and Oxford. Peter Lang publishes over 1,100 academic titles annually, both in print and digital formats, with a backlist of over 40,000 books. It has its complete online journals collection available on Ingentaconnect, and distributes its digital textbooks globally through Kortext. Areas of publication The company specializes in the following twelve subject areas: History The company was founded in Frankfurt am Main in 1970 by Swiss editor Peter Lang. Since 1982 it has an American subsidiary, Peter Lang Publishing USA, specializing in textbooks for classroom use in education, media and communication, and Black studies, as well as monographs in the humanities and social sciences. Academic journals Peter Lang publishers 22 academic journals. Former journals published by Peter Lang * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reciprocal Altruism
In evolutionary biology, reciprocal altruism is a behaviour whereby an organism acts in a manner that temporarily reduces its fitness while increasing another organism's fitness, with the expectation that the other organism will act in a similar manner at a later time. The concept was initially developed by Robert Trivers to explain the evolution of cooperation as instances of mutually altruistic acts. The concept is close to the strategy of " tit for tat" used in game theory. In 1987, Trivers presented at a symposium on reciprocity, noting that he initially titled his article "The Evolution of Delayed Return Altruism," but reviewer W. D. Hamilton suggested renaming it "The Evolution of Reciprocal Altruism." While Trivers adopted the new title, he retained the original examples, causing confusion about reciprocal altruism for decades. Rothstein and Pierotti (1988) addressed this issue at the symposium, proposing new definitions that clarified the concepts. They argued that Delayed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Culture
Western culture, also known as Western civilization, European civilization, Occidental culture, Western society, or simply the West, refers to the Cultural heritage, internally diverse culture of the Western world. The term "Western" encompasses the social norms, ethical values, Tradition, traditional customs, belief systems, political systems, Cultural artifact, artifacts and technology, technologies primarily rooted in History of Europe, European and History of the Mediterranean region, Mediterranean histories. A broad concept, "Western culture" does not relate to a region with fixed members or geographical confines. It generally refers to the classical era cultures of Ancient Greece and Ancient Rome that expanded across the Mediterranean basin and Europe, and later circulated around the world predominantly through colonization and globalization. Historically, scholars have closely associated the idea of Western culture with the classical era of Greco-Roman antiquity. Howeve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primitive Culture
Urgesellschaft (meaning "primal society" in German) is a term that, according to Friedrich Engels,Friedrich Engels: '' Der Ursprung der Familie, des Privateigentums und des Staats'' (1884), in: MEW 21, Seit36-84/ref> refers to the original coexistence of humans in prehistoric times, before recorded history. Here, a distinction is made between the kind of ''Homo sapiens'' as humans, who hardly differed from modern humans biologically (an assertion disputed by anthropology), and other representatives of the genus ''Homo'' such as the ''Homo erectus'' or the ''Neanderthal''. Engels claimed "that animal family dynamics and human primitive society are incompatible things" because "the primitive humans that developed out of animalism either knew no family at all or at most one that does not occur among animals". The U.S. anthropologist Lewis Henry Morgan and translations of his books also make use of the term. In specificity, this long period of time is not directly accessible throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Initiation
Initiation is a rite of passage marking entrance or acceptance into a group or society. It could also be a formal admission to adulthood in a community or one of its formal components. In an extended sense, it can also signify a transformation in which the initiate is 'reborn' into a new role. Examples of initiation ceremonies might include Christian baptism or confirmation, Jewish bar or bat mitzvah, acceptance into a fraternal organization, secret society or religious order, or graduation from school or recruit training. A person taking the initiation ceremony in traditional rites, such as those depicted in these pictures, is called an ''initiate''. Characteristics William Ian Miller notes the role of ritual humiliation in comic ordering and testing. Mircea Eliade discussed initiation as a principal religious act by classical or traditional societies. He defined initiation as "a basic change in existential condition", which liberates man from profane time and histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
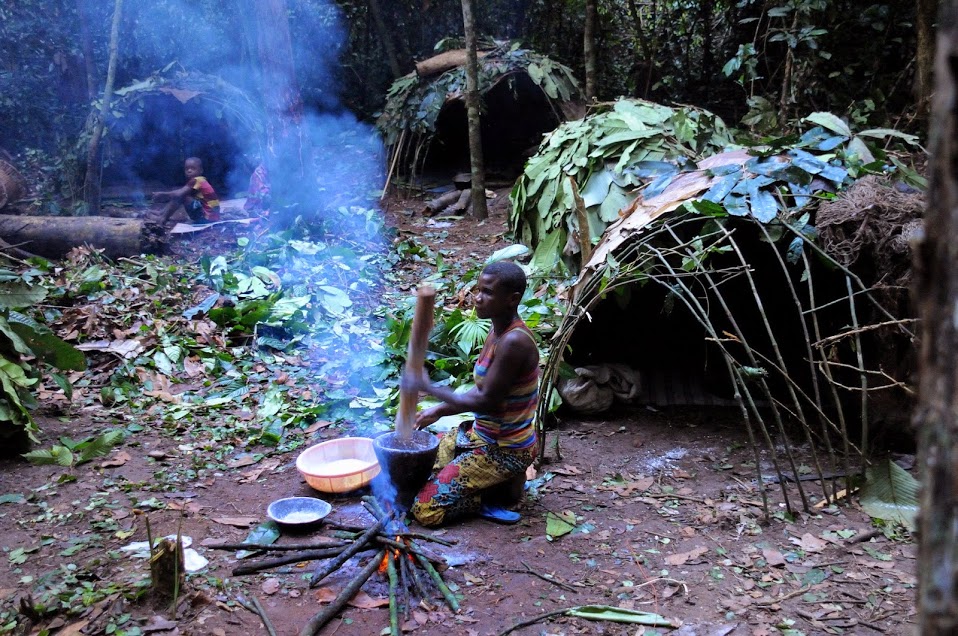
Hunter-gatherer
A hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living in a community, or according to an ancestrally derived Lifestyle, lifestyle, in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local naturally occurring sources, especially wild edible plants but also insects, Fungus, fungi, Honey hunting, honey, Eggs as food, bird eggs, or anything safe to eat, or by hunting game (pursuing or trapping and killing Wildlife, wild animals, including Fishing, catching fish). This is a common practice among most vertebrates that are omnivores. Hunter-gatherer Society, societies stand in contrast to the more Sedentism, sedentary Agrarian society, agricultural societies, which rely mainly on cultivating crops and raising domesticated animals for food production, although the boundaries between the two ways of living are not completely distinct. Hunting and gathering was humanity's original and most enduring successful Competition (biology), competitive adaptation in the nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |