|
Datu Mastura
''Datu'' is a title which denotes the rulers (variously described in historical accounts as chiefs, sovereign princes, and monarchs) of numerous Indigenous peoples throughout the Philippine archipelago. The title is still used today, though not as much as early Philippine history. It is a cognate of ''datuk'', ''dato'', and ''ratu'' in several other Austronesian languages. Overview In early Philippine history, ''datus'' and a small group of their close relatives formed the "apex stratum" of the traditional three-tier social hierarchy of lowland Philippine societies. Only a member of this birthright aristocracy (called ''maginoo'', ''nobleza'', ''maharlika'', or ''timagua'' by various early chroniclers) could become a ''datu''; members of this elite could hope to become a ''datu'' by demonstrating prowess in war or exceptional leadership. In large coastal polities such as those in Maynila, Tondo, Pangasinan, Cebu, Panay, Bohol, Butuan, Cotabato, Lanao, and Sulu, several ''d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lakan
In History of the Philippines (900–1521), early Philippine history, the Filipino styles and honorifics, rank of ''lakan'' denoted a "paramount ruler" (or more specifically, "''paramount datu''") of one of the large coastal barangays (known as a "bayan") on the central and southern regions of the island of Luzon. Overview The ''lakan'' was democratically selected by other ruling datus from among themselves to serve as their "''pangulo''" (head). Writers such as William Henry Scott (historian), William Henry Scott have suggested that this rank is equivalent to that of rajah, and that different ethnic groups either used one term or the other, or used the two words interchangeably.Scott, William Henry, Barangay: Sixteenth-Century Philippine Culture and Society, Quezon City: Ateneo de Manila University Press, 1994. But other writers such as Nick Joaquin have suggested that the usage of the term "rajah" specifically indicates leadership of a bayan or barangay which has extensive tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke
Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of Royal family, royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, grand dukes, and above sovereign princes. As royalty or nobility, they are ranked below grand dukes and above or below princes, depending on the country or specific title. The title comes from French ''duc'', itself from the Latin language, Latin ''dux'', 'leader', a term used in Roman Republic, republican Rome to refer to a military commander without an official rank (particularly one of Germanic peoples, Germanic or Celts, Celtic origin), and later coming to mean the leading military commander of a province. In most countries, the word ''duchess'' is the female equivalent. Following the reforms of the emperor Diocletian (which separated the civilian and military administrations of the Roman provinces), a ''dux'' became the military commander in each province. The title ''dux'', Hellenised to ''do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobility
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy. It is normally appointed by and ranked immediately below royalty. Nobility has often been an estate of the realm with many exclusive functions and characteristics. The characteristics associated with nobility may constitute substantial advantages over or relative to non-nobles or simply formal functions (e.g., precedence), and vary by country and by era. Membership in the nobility, including rights and responsibilities, is typically hereditary and patrilineal. Membership in the nobility has historically been granted by a monarch or government, and acquisition of sufficient power, wealth, ownerships, or royal favour has occasionally enabled commoners to ascend into the nobility. There are often a variety of ranks within the noble class. Legal recognition of nobility has been much more common in monarchies, but nobility also existed in such regimes as the Dutch Republic (1581–1795), the Republic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visayas
The Visayas ( ), or the Visayan Islands (Bisayan languages, Visayan: ''Kabisay-an'', ; Filipino language, Filipino: ''Kabisayaan'' ), are one of the three Island groups of the Philippines, principal geographical divisions of the Philippines, along with Luzon and Mindanao. Located in the central part of the archipelago, it consists of several islands, primarily surrounding the Visayan Sea, although the Visayas are also considered the northeast extremity of the entire Sulu Sea. Its inhabitants are predominantly the Visayan peoples. The major islands of the Visayas are Panay, Negros, Cebu Island, Cebu, Bohol Island, Bohol, Leyte and Samar. The region may also include the provinces of Palawan, Romblon, and Masbate, whose populations identify as Visayan and whose languages are more closely related to other Visayan languages than to the major languages of Luzon. There are four administrative Regions of the Philippines, regions in the Visayas: Western Visayas (pop. 4.73 million), Neg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luzon
Luzon ( , ) is the largest and most populous List of islands in the Philippines, island in the Philippines. Located in the northern portion of the List of islands of the Philippines, Philippine archipelago, it is the economic and political center of the nation, being home to the country's capital city, Manila, as well as Quezon City, the country's most populous city. With a population of 64 million , it contains 52.5% of the country's total population and is the List of islands by population, 4th most populous island in the world. It is the List of islands by area, 15th largest island in the world by land area. ''Luzon'' may also refer to one of the three primary Island groups of the Philippines, island groups in the country. In this usage, it includes the Luzon Mainland, the Batanes and Babuyan Islands, Babuyan groups of islands to the north, Polillo Islands to the east, and the outlying islands of Catanduanes, Marinduque and Mindoro, among others, to the south. The islands o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palawan
Palawan (, ), officially the Province of Palawan (; ), is an archipelagic province of the Philippines that is located in the region of Mimaropa. It is the largest province in the country in terms of total area of . The capital and largest city is Puerto Princesa which is geographically grouped with but administered independently from the province. Palawan is known as the Philippines' ''Last Frontier'' and as the Philippines' ''Best Island''. The islands of Palawan stretch between Mindoro island in the northeast and Borneo in the southwest. It lies between the South China Sea and the Sulu Sea. The province is named after its largest island, Palawan Island (), measuring long, and wide."Palawan – the Philippines' Last Frontier" ''WowPhilippines''. Acce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulu
Sulu (), officially the Province of Sulu (Tausug language, Tausūg: ''Wilaya' sin Lupa' Sūg''; ), is a Provinces of the Philippines, province of the Philippines in the Sulu Archipelago. It was part of the Bangsamoro, Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (BARMM), until the Supreme Court of the Philippines on September 9, 2024 declared its inclusion to be unconstitutional because of the province's simple majority vote against it during the 2019 Bangsamoro autonomy plebiscite. Its capital is Jolo, Sulu, Jolo on the Jolo, island of the same name. Maimbung, the royal capital of the Sultanate of Sulu, is also located in the province. Sulu is along the southern border of the Sulu Sea and the northern boundary of the Celebes Sea. Out of all 82 provinces in the Philippines, it is the poorest, as evidenced by it having the highest poverty rate. According to the Philippine Statistics Authority, poverty incidence in Sulu had reduced in 2021 with 51 percent compared to 75.3 p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
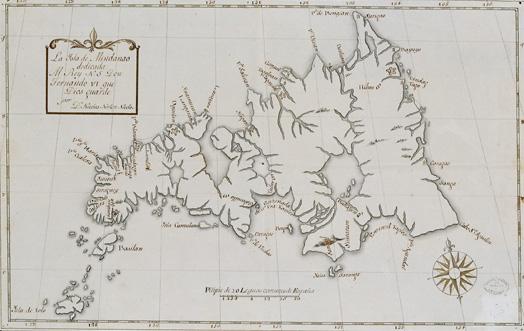
Mindanao
Mindanao ( ) is the List of islands of the Philippines, second-largest island in the Philippines, after Luzon, and List of islands by population, seventh-most populous island in the world. Located in the southern region of the archipelago, the island is part of an island group of the same name that also includes its adjacent islands, notably the Sulu Archipelago. According to the 2020 census, Mindanao had a population of 26,252,442, while the entire island group had an estimated population of 27,021,036. Mindanao is divided into six administrative regions: the Zamboanga Peninsula, Northern Mindanao, the Caraga region, the Davao Region, Davao region, Soccsksargen, and the autonomous region of Bangsamoro. According to the 2020 census, Davao City is the most populous city on the island, with 1,776,949 people, followed by Zamboanga City (pop. 977,234), Cagayan de Oro (pop. 728,402), General Santos (pop. 697,315), Butuan (pop. 372,910), Iligan (pop. 363,115) and Cotabato City (pop. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince
A prince is a male ruler (ranked below a king, grand prince, and grand duke) or a male member of a monarch's or former monarch's family. ''Prince'' is also a title of nobility (often highest), often hereditary, in some European states. The female equivalent is a princess. The English word derives, via the French word ''prince'', from the Latin noun , from (first) and (head), meaning "the first, foremost, the chief, most distinguished, noble ruler, prince". In a related sense, now not commonly used, all more or less sovereign rulers over a state, including kings, were "princes" in the language of international politics. They normally had another title, for example king or duke. Many of these were Princes of the Holy Roman Empire. Historical background The Latin word (older Latin *prīsmo-kaps, ), became the usual title of the informal leader of the Roman senate some centuries before the transition to empire, the '' princeps senatus''. Emperor Augustus establishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord
Lord is an appellation for a person or deity who has authority, control, or power (social and political), power over others, acting as a master, chief, or ruler. The appellation can also denote certain persons who hold a title of the Peerage of the United Kingdom, peerage in the United Kingdom, or are entitled to courtesy titles. The collective "Lords" can refer to a group or body of Peerages in the United Kingdom, peers. Etymology According to the ''Oxford Dictionary of English'', the etymology of the word can be traced back to the Old English language, Old English word ''hlāford'' which originated from ''hlāfweard'' meaning "loaf-ward" or "bread-keeper", reflecting the Germanic tribes, Germanic tribal custom of a Germanic chieftain, chieftain providing food for his followers. The appellation "lord" is primarily applied to men, while for women the appellation "lady" is used. This is no longer universal: the Lord of Mann, a title previously held by Elizabeth II, the Queen o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vicente De Cadenas Y Vicent
Vicente de Cadenas y Vicent (29 April 1915 – 21 December 2005) was a '' Cronista Rey de Armas'' ("Chronicler King of Arms") of the Kingdom of Spain. Biography A native of Madrid, Spain, Cadenas was born on 29 April 1915, the son of Francisco de Cadenas y Gaztañaga and Vicenta Vicent y Nogués. Beginning in 1932, he studied the fields of history and journalism, at the University of Madrid. He maintained dual professions as both the Chronicler of Arms and as a journalist. He was for many years a member of the Deputation of the Constantinian Order, of which he was Secretary and which he joined in 1960 upon the succession of the Infante D. Alfonso as Grand Master. Cadenas founded the ''Asociación de Hidalgos a Fuero de España'' in 1954 to obtain the recognition of the untitled nobility''(nobleza llana)''. In 1953 he founded the review ''Hidalguía'' (with the particular aim of challenging false genealogies, fake titles and pseudo orders of chivalry) and the ''Instituto Inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |