|
Danubian Culture
The term Danubian culture was coined by the Australian archaeologist Vere Gordon Childe to describe the first agrarian society in Central Europe and Eastern Europe. It covers the Linear Pottery culture (Linearbandkeramik, LBK), stroked pottery and Rössen cultures. The beginning of the Linear Pottery culture dates to around 5500 BC. It appears to have spread westwards along the valley of the river Danube and interacted with the cultures of Atlantic Europe when they reached the Paris Basin. Danubian I peoples cleared forests and cultivated fertile loess soils from the Balkans to the Low Countries and the Paris Basin. They made LBK pottery and kept domesticated cows, pigs, dogs, sheep, and goats. The characteristic tool of the culture is the shoe-last celt, a kind of long thin stone adze which was used to fell trees and sometimes as a weapon, evidenced by the skulls found at Talheim, Neckar in Germany and Schletz in Austria. Settlements consisted of longhouses. According to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Culture
An archaeological culture is a recurring assemblage of types of artifacts, buildings and monuments from a specific period and region that may constitute the material culture remains of a particular past human society. The connection between these types is an empirical observation. Their interpretation in terms of ethnic or political groups is based on archaeologists' understanding. However, this is often subject to long-unresolved debates. The concept of the archaeological culture is fundamental to culture-historical archaeology. Concept Different cultural groups have material culture items that differ both functionally and aesthetically due to varying cultural and social practices. This notion is observably true on the broadest scales. For example, the equipment associated with the brewing of tea varies greatly across the world. Social relations to material culture often include notions of identity and status. Advocates of culture-historical archaeology use the notion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
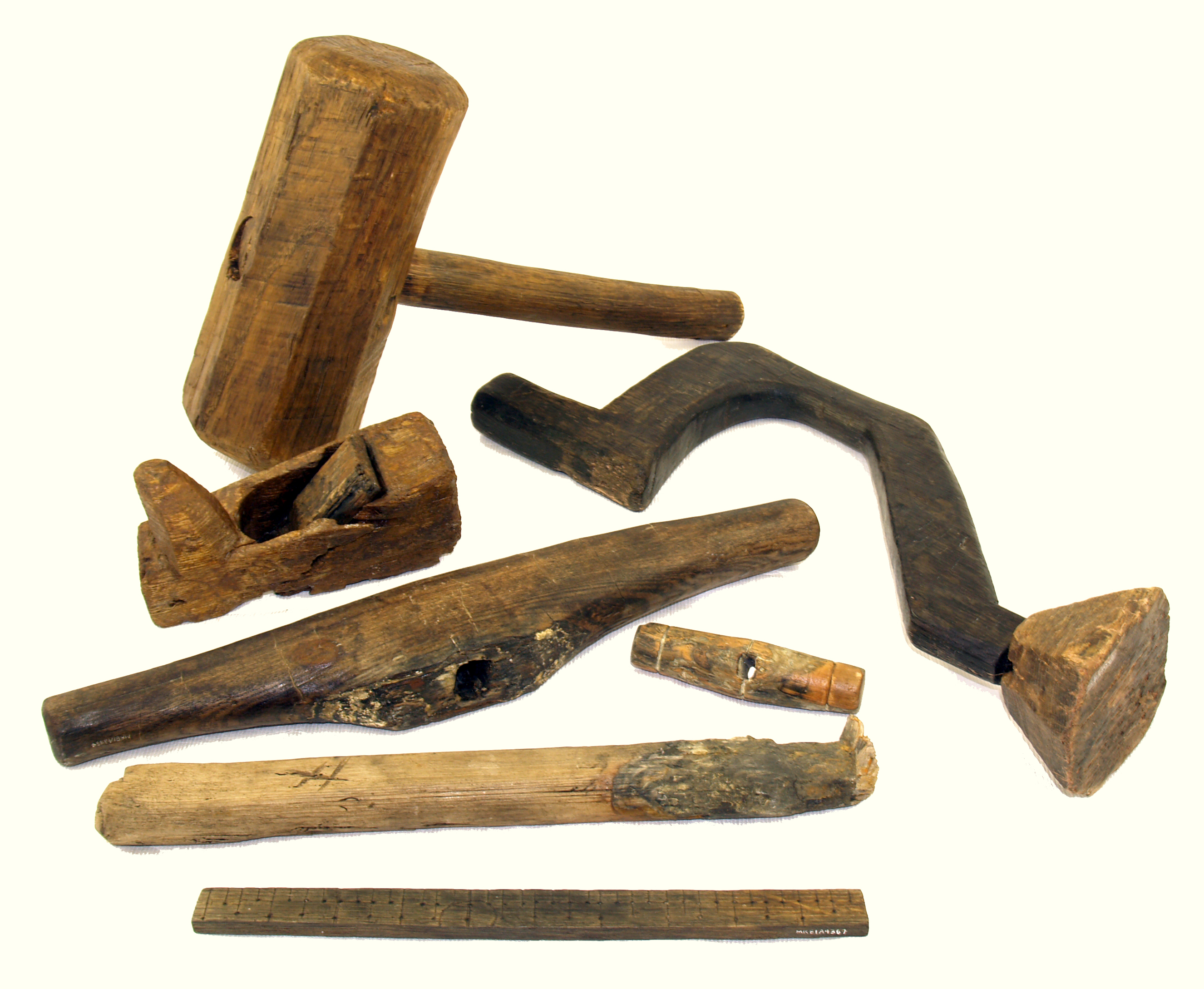
Tool
A tool is an Physical object, object that can extend an individual's ability to modify features of the surrounding environment or help them accomplish a particular task. Although many Tool use by animals, animals use simple tools, only human beings, whose use of stone tools dates back hundreds of millennia, have been observed using tools to make other tools. Early human tools, made of such materials as Rock (geology), stone, bone, and wood, were used for the preparation of food, hunting, the manufacture of weapons, and the working of materials to produce clothing and useful Cultural artifact, artifacts and crafts such as pottery, along with the construction of housing, businesses, infrastructure, and transportation. The development of metalworking made additional types of tools possible. Harnessing energy sources, such as Working animal, animal power, wind, or steam, allowed increasingly complex tools to produce an even larger range of items, with the Industrial Revolution markin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stroke-ornamented Ware
The Stroke-ornamented ware (culture) or (German) Stichbandkeramik (abbr. STK or STbK), Stroked Pottery culture, Danubian Ib culture of V. Gordon Childe, or Middle Danubian culture is the successor of the Linear Pottery culture, a major archaeological horizon of the European Neolithic in Central Europe. The STK flourishes during approximately 4900-4400 BC. Centered on Silesia in Poland, eastern Germany, and the northern Czech Republic, it overlaps with the Lengyel horizon to the south and the Rössen culture to the west. Description The STbK and the Notenkopfkeramik (Musical Note pottery) are a development of the LBK. Much it features incised zig-zag bands going around the pot, with punctures at the line segment junctions. The STK abandons incision in favor bands of small punctures, also in zig-zag patterns, with a vertical band dividing each angle. The effect is a band pattern of contiguous A-frames. Where the Musical Note pottery expanded east over the Bug River, the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which has long been home to the majority of the human population, was the site of many of the first civilisations. Its 4.7 billion people constitute roughly 60% of the world's population. Asia shares the landmass of Eurasia with Europe, and of Afro-Eurasia with both Europe and Africa. In general terms, it is bounded on the east by the Pacific Ocean, on the south by the Indian Ocean, and on the north by the Arctic Ocean. The border of Asia with Europe is a social constructionism, historical and cultural construct, as there is no clear physical and geographical separation between them. A commonly accepted division places Asia to the east of the Suez Canal separating it from Africa; and to the east of the Turkish straits, the Ural Mountains an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Europe, on the south by North Africa, and on the west almost by the Morocco–Spain border. The Mediterranean Sea covers an area of about , representing 0.7% of the global ocean surface, but its connection to the Atlantic via the Strait of Gibraltar—the narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates the Iberian Peninsula in Europe from Morocco in Africa—is only wide. Geological evidence indicates that around 5.9 million years ago, the Mediterranean was cut off from the Atlantic and was partly or completely desiccated over a period of some 600,000 years during the Messinian salinity crisis before being refilled by the Zanclean flood about 5.3 million years ago. The sea was an important rout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spondylus
''Spondylus'' is a genus of bivalve molluscs, the only genus in the family Spondylidae and subfamily Spondylinae. They are known in English as spiny oysters or thorny oysters (although they are not, in fact, true oysters, but are related to scallops). Description The many species of ''Spondylus'' vary considerably in appearance. They are grouped in the same superfamily as the scallops. They are not closely related to true oysters (family Ostreidae); however, they do share some habits such as cementing themselves to rocks rather than attaching themselves by a byssus. The two halves of their shells are joined with a ball-and-socket type of hinge, rather than with a toothed hinge as is more common in other bivalves. They also still retain vestigial anterior and posterior ''auricles'' ("ears", triangular shell flaps) along the hinge line, a characteristic feature of scallops, although not of oysters. As is the case in all scallops, ''Spondylus'' spp. have multiple eyes around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jens Lüning
Jens may refer to: * Jens (given name), a list of people with the name * Jens (surname), a list of people * Jens, Switzerland, a municipality * 1719 Jens, an asteroid See also * Jensen (other) Jensen may refer to: People and fictional characters * Jensen (surname), a list of people and fictional characters * Jensen (given name), a list of people * Jensen (gamer), Danish professional ''League of Legends'' player Places * Jensen, Que ... * Jenssi {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Modderman
Peter may refer to: People * List of people named Peter, a list of people and fictional characters with the given name * Peter (given name) ** Saint Peter (died 60s), apostle of Jesus, leader of the early Christian Church * Peter (surname), a surname (including a list of people with the name) Culture * Peter (actor) (born 1952), stage name Shinnosuke Ikehata, a Japanese dancer and actor * ''Peter'' (1934 film), a film directed by Henry Koster * ''Peter'' (2021 film), a Marathi language film * "Peter" (''Fringe'' episode), an episode of the television series ''Fringe'' * ''Peter'' (novel), a 1908 book by Francis Hopkinson Smith * "Peter" (short story), an 1892 short story by Willa Cather * ''Peter'' (album), a 1972 album by Peter Yarrow * ''Peter'', a 1993 EP by Canadian band Eric's Trip * "Peter", 2024 song by Taylor Swift from '' The Tortured Poets Department: The Anthology'' Animals * Peter (Lord's cat), cat at Lord's Cricket Ground in London * Peter (chief mouser), Chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fallow
Fallow is a farming technique in which arable land is left without sowing for one or more vegetative cycles. The goal of fallowing is to allow the land to recover and store Organic compound, organic matter while retaining moisture and disrupting pest life cycles and soil borne pathogens by temporarily removing their Host (biology), hosts. Crop rotation systems typically called for some of a farmer's fields to be left fallow each year. The increase in intensive farming, including the use of cover crops in lieu of fallow practices, has caused a loss of acreage of fallow land, as well as field margins, hedges, and wasteland. This has reduced biodiversity; fallows have been the primary habitat for farmland bird populations. Fallow syndrome Fallow syndrome is when a crop has insufficient nutrient uptake due to the lack of arbuscular mycorhizae (AM fungi) in the soil following a fallow period. Crops such as corn that are prone to fallow syndrome should not follow a period of fallow, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eduard Sangmeister
Eduard Model Accessories is a Czech manufacturer of plastic models and finescale model accessories. History Formed in 1989 in the city of Most, Eduard began in a rented cellar as a manufacturer of photoetched brass model components. Following the success of their early products, the company branched off into plastic models in 1993. As of 2006, Eduard's product line contained some 30 plastic kits and more than 800 individual photoetch detail sets. To the plastic modeller community at large, Eduard has become a household word in the field of photoetched parts, and their products are available worldwide. Product lines Eduard aircraft kits range from World War I to the present day. Some notable ones include: most of the famous World War I fighters are: Fokker D.VII, Pfalz D.III, Albatros D.III and the Sopwith Pup, while World War II had the: Yakovlev Yak-3, Hawker Hurricane, Spitfire and the Messerschmitt Bf 109 The Messerschmitt Bf 109 is a monoplane fighter aircraft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic Long House
The Neolithic long house was a long, narrow timber dwelling built by the Old Europeans in Europe beginning at least as early as the period 6000 to 5000 BC. They first appeared in central Europe in connection with the early Neolithic cultures such as the Linear Pottery culture or Cucuteni culture. This type of architecture represents the largest free-standing structure in the world in its era. Long houses are present across numerous regions and time periods in the archaeological record. The long house was a rectangular structure, wide, of variable length, around up to . Outer walls were wattle and daub, sometimes alternating with split logs, with pitched, thatched roofs, supported by rows of poles, three across.The numbers are from Gimbutas (1991) pages 39–41. However, they are approximately the same as the numbers given by other researchers and can therefore be taken as true measurements within a tolerance. The exterior walls would have been quite short beneath the large r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |