|
Danisco (building)
Danisco A/S is a Danish bio-based company with activities in food production, enzymes and other bioproducts as well as a wide variety of pharmaceutical grade excipients. It was formed in 1989 from the largest Danish industrial merger ever of the two old C.F. Tietgen companies Danish Sugar (founded 1872), and Dansk Handels- og Industri Company (Danisco A/S).Nordic Sugar History Shared history Danisco is one of the world's leading producers of ingredients for food and other consumer products and was also one of the biggest sugar producers in Europe until the divestment of its sugar division to [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DuPont
DuPont de Nemours, Inc., commonly shortened to DuPont, is an American multinational chemical company first formed in 1802 by French-American chemist and industrialist Éleuthère Irénée du Pont de Nemours. The company played a major role in the development of Delaware and first arose as a major supplier of gunpowder. DuPont developed many polymers such as Vespel, neoprene, nylon, Corian, Polytetrafluoroethylene, Teflon, Mylar, Kapton, Kevlar, Zemdrain, M5 fiber, Nomex, Tyvek, Sorona, Artificial Leather#Corfam, Corfam and Lycra in the 20th century, and its scientists developed many chemicals, most notably Freon (chlorofluorocarbons), for the refrigerant industry. It also developed synthetic pigments and paints including ChromaFlair. In 2015, DuPont and the Dow Chemical Company agreed to a reorganization plan in which the two companies would merge and split into three. As a merged entity, DuPont simultaneously acquired Dow and renamed itself to DowDuPont on August 31, 2017, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OMX Copenhagen 20
The OMX Copenhagen 25 (), formerly KFX and OMXC20) is the top-tier stock market index for Nasdaq Copenhagen, which is part of the Nasdaq Nordic Nasdaq Nordic is the common name for the subsidiaries of Nasdaq, Inc. that provide financial services and operate marketplaces for securities in the Nordic and Baltic regions of Europe. Historically, the operations were known by the compan ..., prior being replaced (as of December 2017) was known as OMX Copenhagen 20 index. It is a market value weighted index that consists of the 25 most-traded stock classes. Components The following 25 listings make up the index as of January 2021. Footnotes External links Bloomberg page for KFX:IND [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biofuel
Biofuel is a fuel that is produced over a short time span from biomass, rather than by the very slow natural processes involved in the formation of fossil fuels, such as oil. According to the United States Energy Information Administration (EIA), biofuels are mostly used for transportation, but can also be used for heating and electricity. Biofuel can be produced from plants or from agricultural, domestic or industrial biowaste. The greenhouse gas mitigation potential of biofuel varies considerably, from emission levels comparable to fossil fuels in some scenarios to negative emissions in others. See the biomass article for more on this particular subject. The two most common types of biofuel are Ethanol#Fuel, bioethanol and biodiesel. The U.S. is the largest producer of bioethanol, while the EU is the largest producer of biodiesel. The energy content in the global production of bioethanol and biodiesel is 2.2 and 1.8 EJ per year, respectively. * Bioethanol is an Alcohol (chem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DuPont Danisco
DuPont Danisco Cellulosic Ethanol LLC is a 50/50 joint venture between DuPont and Genencor, a subsidiary of Danisco. The company is accelerating development and deployment of cellulosic ethanol, which is made from non-food biomass. DDCE plans to license its technology and also will engage in limited operations of cellulosic ethanol biorefineries. The company's collaborations include work with Genera Energy and the University of Tennessee Research Foundation DDCE has constructed a demonstration-scale biorefinery and research and development facility for cellulosic ethanol in Vonore, Tennessee Vonore is a town in Monroe County, which is located on the southeast border of the U.S. state of Tennessee. The population was 1,574 as of the 2020 census. The city hall, library, community center, police department, and fire department are locat .... The plant went into operation at the end of 2009. DDCE was founded in 2008, but was eventually dissolved in 2011 due to the acquisition of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbohydrate
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or may not be different from ''n''), which does not mean the H has covalent bonds with O (for example with , H has a covalent bond with C but not with O). However, not all carbohydrates conform to this precise stoichiometric definition (e.g., uronic acids, deoxy-sugars such as fucose), nor are all chemicals that do conform to this definition automatically classified as carbohydrates (e.g. formaldehyde and acetic acid). The term is most common in biochemistry, where it is a synonym of saccharide (), a group that includes sugars, starch, and cellulose. The saccharides are divided into four chemical groups: monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides. Monosaccharides and disaccharides, the smallest (lower molecul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a hydroxyl group). Ethanol is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid with a characteristic wine-like odor and pungent taste. It is a psychoactive recreational drug, the active ingredient in alcoholic drinks. Ethanol is naturally produced by the fermentation process of sugars by yeasts or via petrochemical processes such as ethylene hydration. It has medical applications as an antiseptic and disinfectant. It is used as a chemical solvent and in the synthesis of organic compounds, and as a fuel source. Ethanol also can be dehydrated to make ethylene, an important chemical feedstock. As of 2006, world production of ethanol was , coming mostly from Brazil and the U.S. Etymology ''Ethanol'' is the systematic name defined by the Internat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Household Cleaner
A detergent is a surfactant or a mixture of surfactants with cleansing properties when in dilute solutions. There are a large variety of detergents, a common family being the alkylbenzene sulfonates, which are soap-like compounds that are more soluble in hard water, because the polar sulfonate (of detergents) is less likely than the polar carboxylate (of soap) to bind to calcium and other ions found in hard water. Definitions The word ''detergent'' is derived from the Latin adjective ''detergens'', from the verb ''detergere'', meaning to wipe or polish off. Detergent is a surfactant or a mixture of surfactants with cleansing properties when in dilute solutions. However, conventionally, detergent is used to mean synthetic cleaning compounds as opposed to ''soap'' (a salt of the natural fatty acid), even though soap is also a detergent in the true sense. In domestic contexts, the term ''detergent'' refers to household cleaning products such as ''laundry detergent'' or ''dish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Biotechnology
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used by Károly Ereky in 1919, meaning the production of products from raw materials with the aid of living organisms. Definition The concept of biotechnology encompasses a wide range of procedures for modifying living organisms according to human purposes, going back to domestication of animals, cultivation of the plants, and "improvements" to these through breeding programs that employ artificial selection and hybridization. Modern usage also includes genetic engineering as well as cell and tissue culture technologies. The American Chemical Society defines biotechnology as the application of biological organisms, systems, or processes by various industries to learning about the science of life and the improvement of the value of materia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genencor
Genencor is a biotechnology company based in Palo Alto, CA and a subsidiary of IFF. Genencor is a producer of Industrial enzymes and low-priced bulk protein. The name Genencor originates with Genencor, Inc., the original joint venture between Genentech and Corning Incorporated, which was founded in 1982. It is considered to have pioneered the field of industrial biotechnology, as distinct from traditional applications of biotechnology to health care and agriculture. In 2005 Genencor was acquired by Danisco. In 2008 Genencor entered a joint venture with DuPont, called DuPont Danisco Cellulosic Ethanol LLC, to develop and commercialize low cost technology for the production of cellulosic ethanol. In 2008, Genencor and Goodyear announced they were working to develop BioIsoprene. In 2011, Dupont acquired Danisco for $6.3 billion. In 2021, portions of Dupont including the Genencor division were acquired by International Flavors & Fragrances International Flavors & Fragranc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sweetener
{{Wiktionary, sweetener A sweetener is a substance added to food or drink to impart the flavor of sweetness, either because it contains a type of sugar, or because it contains a sweet-tasting sugar substitute. Many artificial sweeteners have been invented and are now used in commercially produced food and drink. Natural non-sugar sweeteners also exist, such as glycyrrhizin found in licorice. List of sweeteners * Sugar **Sugar alcohol **Sucrose, or glucose-fructose, commonly called ''table sugar'' ***Fructose, or ''fruit sugar'' ***Glucose, or dextrose * Sugar substitute, or ''artificial sweetener'' *Syrups ** Agave syrup, or ''agave nectar'' **Maple syrup **Corn syrup ***High-fructose corn syrup (HFCS), used industrially *Honey * Unrefined sweetener See also * Sweet (other) * Sweetness (other) * Sugar free (other) Sugar free foods use sugar substitutes for sweetness. Sugar free may also refer to: *Sugarfree (Filipino band), a Filipino Indiep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbiological Culture
A microbiological culture, or microbial culture, is a method of multiplying microbial organisms by letting them reproduce in predetermined culture medium under controlled laboratory conditions. Microbial cultures are foundational and basic diagnostic methods used as a research tool in molecular biology. The term ''culture'' can also refer to the microorganisms being grown. Microbial cultures are used to determine the type of organism, its abundance in the sample being tested, or both. It is one of the primary diagnostic methods of microbiology and used as a tool to determine the cause of infectious disease by letting the agent multiply in a predetermined medium. For example, a throat culture is taken by scraping the lining of tissue in the back of the throat and blotting the sample into a medium to be able to screen for harmful microorganisms, such as ''Streptococcus pyogenes'', the causative agent of strep throat. Furthermore, the term culture is more generally used informall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
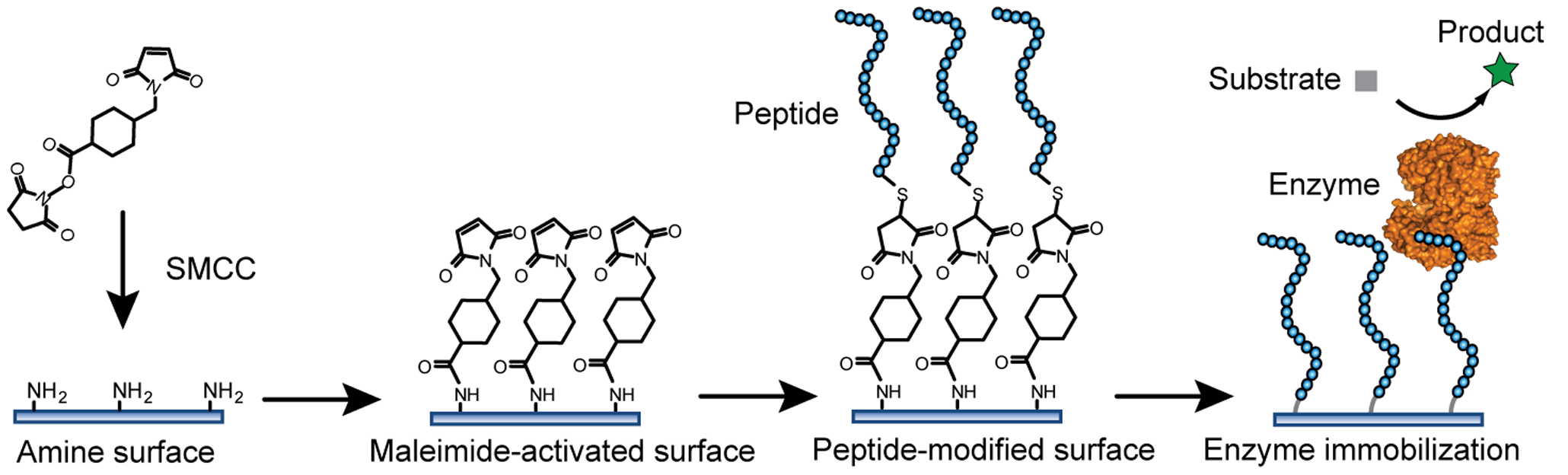
Industrial Enzymes
Industrial enzymes are enzymes that are commercially used in a variety of industries such as pharmaceuticals, chemical production, biofuels, food & beverage, and consumer products. Due to advancements in recent years, biocatalysis through isolated enzymes is considered more economical than use of whole cells. Enzymes may be used as a unit operation within a process to generate a desired product, or may be the product of interest. Industrial biological catalysis through enzymes has experienced rapid growth in recent years due to their ability to operate at mild conditions, and exceptional chiral and positional specificity, things that traditional chemical processes lack. Isolated enzymes are typically used in hydrolytic and isomerization reactions. Whole cells are typically used when a reaction requires a co-factor. Although co-factors may be generated in vitro, it is typically more cost-effective to use metabolically active cells. Enzymes as a unit of operation Immobilization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |