|
Danicopan
Danicopan, sold under the brand name Voydeya, is a medication used for the treatment of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. It is a Complement system, complement inhibitor which reversibly binds to factor D to prevent alternative pathway-mediated hemolysis and deposition of complement C3 proteins on red blood cells. Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged. The most common side effects include fever, headache, increased levels of liver enzymes (a sign of possible liver problems) and pain in the extremities (arms and legs). Danicopan was approved for medical use in Japan in January 2024, in the United States in March 2024, and in the European Union in April 2024. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) considers it to be a first-in-class medication. Medical uses Danicopan is indicated as add-on therapy to ravulizumab or eculizumab for the treatment of extravascular hemolys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
By Mouth
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are intended to have a systemic effect, reaching different parts of the body via the bloodstream, for example. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes, such as injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients willing and able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eculizumab
Eculizumab, sold under the brand name Soliris among others, is a medication used to treat paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH), atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS), generalized myasthenia gravis, and neuromyelitis optica. In people with PNH, it reduces both the destruction of red blood cells and need for blood transfusion, but does not appear to affect the risk of death. Eculizumab was the first drug approved for each of its uses, and its approval was granted based on small trials. It is given in a clinic by intravenous (IV) infusion. Side effects include a risk for meningococcal infections and it is only prescribed to those who have enrolled in and follow a risk evaluation and mitigation strategy, which involves counseling people and ensuring that they are vaccinated. It is a humanized monoclonal antibody functioning as a terminal complement inhibitor. It has been developed, manufactured, and marketed by Alexion Pharmaceuticals, which had patent exclusivity un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunosuppressants
Immunosuppressive drugs, also known as immunosuppressive agents, immunosuppressants and antirejection medications, are drugs that inhibit or prevent activity of the immune system. Classification Immunosuppressive drugs can be classified into five groups: * glucocorticoids * cytostatics * antibodies * drugs acting on immunophilins * other drugs Glucocorticoids In pharmacologic (supraphysiologic) doses, glucocorticoids, such as prednisone, dexamethasone, and hydrocortisone are used to suppress various allergic, inflammatory, and autoimmune disorders. They are also administered as posttransplantory immunosuppressants to prevent the acute transplant rejection and graft-versus-host disease. Nevertheless, they do not prevent an infection and also inhibit later reparative processes. Immunosuppressive mechanism Glucocorticoids suppress cell-mediated immunity. They act by inhibiting genes that code for the cytokines Interleukin 1 (IL-1), IL-2, IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hematology
Hematology ( always spelled haematology in British English) is the branch of medicine concerned with the study of the cause, prognosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases related to blood. It involves treating diseases that affect the production of blood and its components, such as blood cells, hemoglobin, blood proteins, bone marrow, platelets, blood vessels, spleen, and the mechanism of coagulation. Such diseases might include hemophilia, blood clots ( thrombus), other bleeding disorders, and blood cancers such as leukemia, multiple myeloma, and lymphoma. The laboratory analysis of blood is frequently performed by a medical technologist or medical laboratory scientist. Specialization Physicians specialized in hematology are known as hematologists or haematologists. Their routine work mainly includes the care and treatment of patients with hematological diseases, although some may also work at the hematology laboratory viewing blood films and bone marrow sli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) is a rare, acquired, life-threatening disease of the blood characterized by destruction of red blood cells by the complement system, a part of the body's innate immune system. This destructive process occurs due to deficiency of the red blood cell surface protein DAF, which normally inhibits such immune reactions. Since the complement cascade attacks the red blood cells within the blood vessels of the circulatory system, the red blood cell destruction (hemolysis) is considered an ''intravascular'' hemolytic anemia. Other key features of the disease, such as the high incidence of venous blood clot formation, are incompletely understood. PNH is the only hemolytic anemia caused by an ''acquired'' (rather than inherited) intrinsic defect in the cell membrane (deficiency of glycophosphatidylinositol or GPI) leading to the absence of protective exterior surface proteins that normally attach via a GPI anchor. It may develop on its own ("primary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Institute For Health And Care Excellence
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) is an executive non-departmental public body of the Department of Health and Social Care in England that publishes guidelines in four areas: * the use of health technologies within England's National Health Service (NHS) and NHS Wales (such as the use of new and existing medicines, treatments and procedures) * clinical practice (guidance on the appropriate treatment and care of people with specific diseases and conditions) * guidance for public sector workers on health promotion and ill-health avoidance * guidance for social care services and users. These appraisals are based primarily on evidence-based evaluations of efficacy, safety and cost-effectiveness in various circumstances. It serves both the English NHS and the Welsh NHS. It was set up as the National Institute for Clinical Excellence in 1999, and on 1 April 2005 joined with the Health Development Agency to become the new National Institute for Healt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Medicines Agency
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) is an agency of the European Union (EU) in charge of the evaluation and supervision of medicinal products. Prior to 2004, it was known as the European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products or European Medicines Evaluation Agency (EMEA).Set up by EC Regulation No. 2309/93 as the European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products, and renamed by EC Regulation No. 726/2004 to the European Medicines Agency, it had the acronym EMEA until December 2009. The European Medicines Agency does not call itself EMA either – it has no official acronym but may reconsider if EMA becomes commonly accepted (secommunication on new visual identity an). The EMA was set up in 1995, with funding from the European Union and the pharmaceutical industry, as well as indirect subsidy from member states, its stated intention to harmonise (but not replace) the work of existing national medicine regulatory bodies. The hope was that this plan would not o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Committee For Medicinal Products For Human Use
The Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), formerly known as Committee for Proprietary Medicinal Products (CPMP), is the European Medicines Agency's committee A committee or commission is a body of one or more persons subordinate to a deliberative assembly. A committee is not itself considered to be a form of assembly. Usually, the assembly sends matters into a committee as a way to explore them more ... responsible for elaborating the agency's opinions on all issues regarding medicinal products for human use. See also * Committee for Medicinal Products for Veterinary Use References External links Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) Health and the European Union {{eu-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breakthrough Therapy
Breakthrough therapy is a United States Food and Drug Administration designation that expedites drug development that was created by Congress under Section 902 of the 9 July 2012 Food and Drug Administration Safety and Innovation Act. The FDA's "breakthrough therapy" designation is not intended to imply that a drug is actually a "breakthrough" or that there is high-quality evidence of treatment efficacy for a particular condition; rather, it allows the FDA to grant priority review to drug candidates if preliminary clinical trials indicate that the therapy may offer substantial treatment advantages over existing options for patients with serious or life-threatening diseases. The FDA has other mechanisms for expediting the review and approval process for promising drugs, including fast track designation, accelerated approval, and priority review. Requirements A breakthrough therapy designation can be assigned to a drug if "it is a drug which is intended alone or in combinatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ravulizumab
Ravulizumab, sold under the brand name Ultomiris, is a humanized monoclonal antibody complement inhibitor medication designed for the treatment of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) and atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. It is designed to bind to and prevent the activation of Complement component 5 (C5). Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria is characterized by red blood cell destruction, anemia (red blood cells unable to carry enough oxygen to tissues), blood clots, and impaired bone marrow function (not making enough blood cells). In paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria, proteins known as the 'complement system', which is part of the immune system, become overactive because of a genetic mutation and start to attack the patients' own red blood cells. Ravulizumab, is a monoclonal antibody (a type of protein) designed to attach to the C5 protein, which is part of the complement system. By attaching to the C5 protein, the medicine blocks its effect and thereby reduces the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
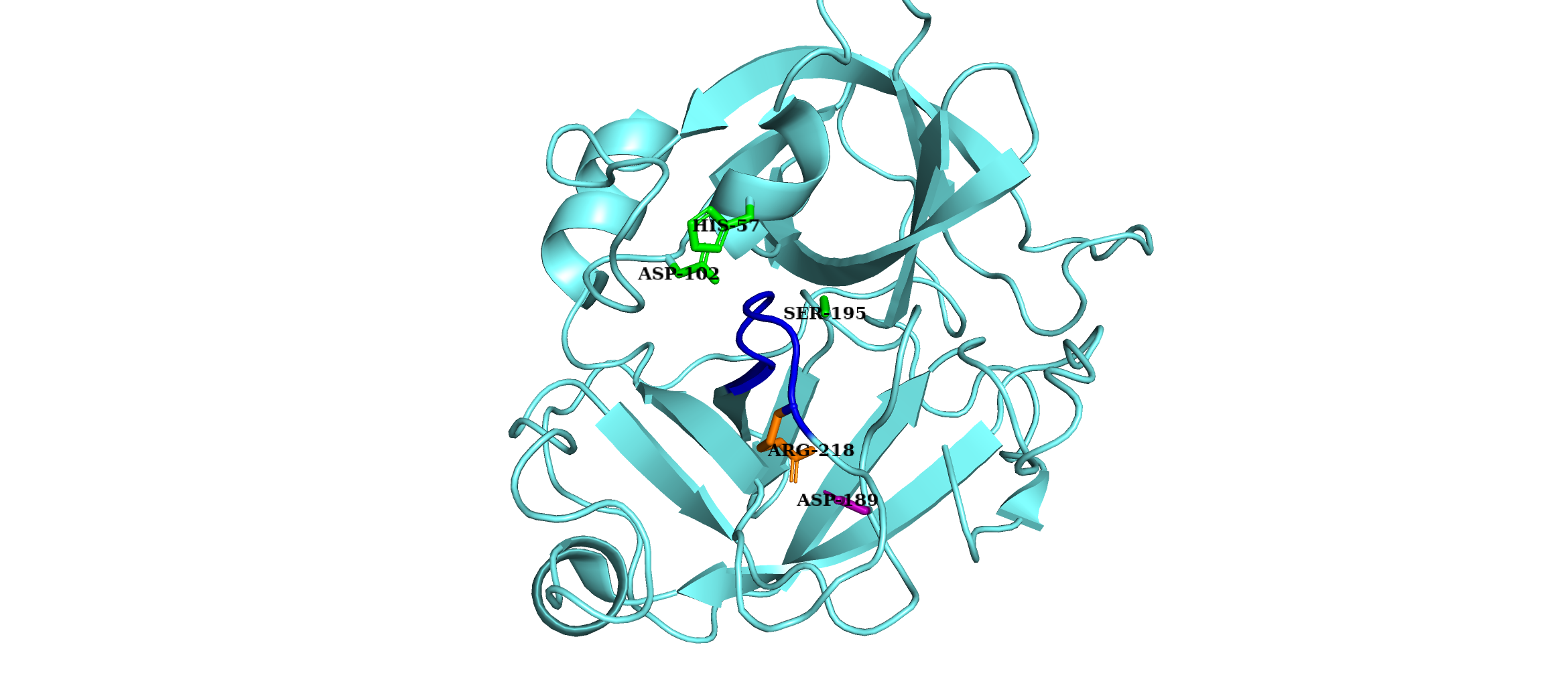
Complement Factor D
Factor D (, ''C3 proactivator convertase'', ''properdin factor D esterase'', ''factor D (complement)'', ''complement factor D'', ''CFD'', ''adipsin'') is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''CFD'' gene. Factor D is involved in the alternative complement pathway of the complement system where it cleaves factor B. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the trypsin family of serine proteases secreted by adipocytes into the bloodstream. The encoded protein is a component of the alternative complement pathway best known for its role in humoral suppression of infectious agents. Finally, the encoded protein has a high level of expression in fat, suggesting a role for adipose tissue in immune system biology. Factor D is a serine protease that stimulates glucose transport for triglyceride accumulation in fats cells and inhibits lipolysis. Clinical significance The level of Factor D is decreased in obese patients. This reduction may be due to high activit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |