|
Damasta Sabotage
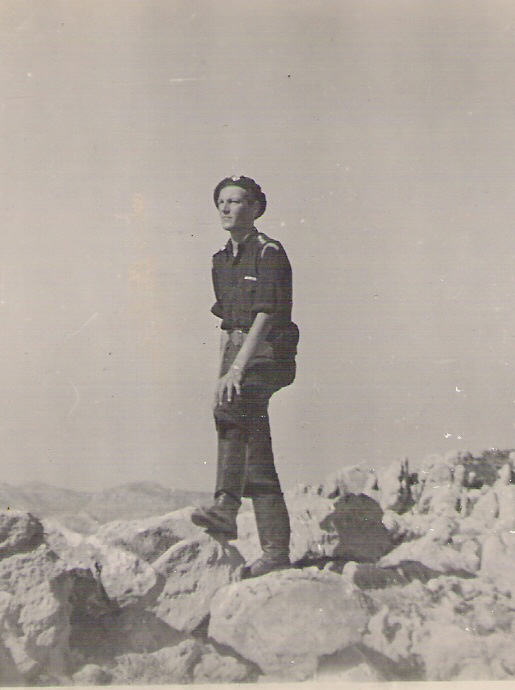
The Damasta sabotage () was an attack by Cretan Cretan resistance, resistance fighters led by British Special Operations Executive officer W. Stanley Moss, Captain Bill Stanley Moss MC against Axis occupation of Greece during World War II, German occupation forces in World War II. The attack occurred on 8 August 1944 near the village of Damasta, Crete, Damasta () and was aimed at preventing the Germans assaulting the village of Anogeia.Beevor, Antony. ''Crete: The Battle and the Resistance'', John Murray Ltd, 2005, pp.315-6. Psychoundakis, George. ''The Cretan Runner:His Story of the German Occupation'', John Murray Ltd, 1955. The Folio Society, 2009 p178 Background As part of a coordinated attack with the Special Boat Service, Billy Moss, the second-in-command of the Kidnapping of Heinrich Kreipe, Kreipe kidnap team, was despatched back to Crete in early July by Brigadier Barker-Benfield, the new commander of Force 133 in Cairo to provide guides for the S.B.S. and to raise a sm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretan
Crete ( ; , Modern Greek, Modern: , Ancient Greek, Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the List of islands by area, 88th largest island in the world and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, and Corsica. Crete is located about south of the Peloponnese, and about southwest of Anatolia. Crete has an area of and a coastline of 1,046 km (650 mi). It bounds the southern border of the Aegean Sea, with the Sea of Crete (or North Cretan Sea) to the north and the Libyan Sea (or South Cretan Sea) to the south. Crete covers 260 km from west to east but is narrow from north to south, spanning three longitudes but only half a latitude. Crete and a number of islands and islets that surround it constitute the Region of Crete (), which is the southernmost of the 13 Modern regions of Greece, top-level administrative units of Greece, and the fifth most popu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kosta Kephaloyannis
Kosta may refer to: __NOTOC__ People * Kosta (given name), a list of people with the given name or nickname * Kosta (surname), a list of people Places * Kosta, Estonia, a village * Kosta, Greece, a community * Kosta, Sweden, a village Other uses * Kosta Boda, a glassworks in Sweden * Kosta (architectural feature), in Hindu temples See also * * Costa (other) * Costas (other) Kostas or Costas () is a Greek given name and surname. As a given name, it can be a hypocorism for Konstantinos ( Constantine). Given name * Costas Andreou, Greek musician * Kostas Antetokounmpo (born 1997), Greek basketball player * Costas Aza ... * Koshta, a Hindu caste {{disambig, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holocaust Of Viannos
The Viannos massacres () were a mass extermination campaign launched by German forces against the civilian residents of around 20 villages located in the areas of east Viannos and west Ierapetra provinces on the Greek island of Crete during World War II. The killings, with a death toll in excess of 500,Γ. Δ. Χρηστάκης, Κ. Γ. Στεφανάκης. Επαρχία Βιάννου, 1940–1945: το ολοκαύτωμα του 1943', Σύλλογος Βιαννιτών Ηρακλείου "Ο Πατούχας", 2000Fermor, Patrick Leigh; Cooper, Artemis. ''Words of Mercury'', John Murray, London, 2004, .Lewis, Damien. ''Churchill's Secret Warriors: The Explosive True Story of the Special Forces Desperadoes of WWII'', Quercus Editions Ltd, 2014; . [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Albumen
Operation Albumen was the name of British Commando raids in June 1942 on German airfields in the Axis-occupied Greek island of Crete, to prevent them from being used in support of the Axis forces in the Western Desert Campaign in the Second World War. The operations were carried out with similar raids against Axis airfields at Benghazi, Derna and Barce in Libya and were among the first planned sabotage acts in occupied Europe. Background During the late spring of 1942, the airfields of Crete gained increased importance by becoming the main transit base for the ''Luftwaffe'' to fly supplies to the Axis forces in Egypt in their advance on the Nile Delta. ''Luftwaffe'' aircraft based on Crete flew photo-reconnaissance, bombing and convoy sorties covering the south-east Mediterranean. To disrupt these operations, the British command in Cairo sent three groups from the Special Boat Squadron (SBS) and one from the Special Air Service (SAS) to Crete to sabotage the airfields of Hera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loss Of Face
In sociology, face refers to a class of behaviors and customs, associated with the morality, honor, and authority of an individual (or group of individuals), and their image within social groups. Face is linked to the dignity and prestige that a person enjoys in terms of their social relationships. This idea, with varying nuances, is observed in many societies and cultures, including Chinese, Arabic, Indonesian, Korean, Malaysian, Laotian, Indian, Japanese, Vietnamese, Filipino, Thai, Russian and other East Slavic cultures. Face has particularly complex dynamics and meanings within the context of Chinese culture, and its usage in the English language is borrowed from Chinese. Definitions Although Chinese writer Lin Yutang claimed "face cannot be translated or defined", these definitions have been created: * Face is an image of self delineated in terms of approved social attributes. * Face is the respectability and/or deference which a person can claim for themself or fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidnap Of General Kreipe
The kidnapping of Heinrich Kreipe was an operation executed jointly by the British Special Operations Executive (SOE) and local resistance members in Crete in German-occupied Greece during the Second World War. The operation was launched on 4 February 1944, when SOE officer Patrick Leigh Fermor landed in Crete with the intention of abducting notorious war criminal and commander of 22nd Air Landing Division, Friedrich-Wilhelm Müller. By the time of the arrival of the rest of the abduction team, led by William Stanley Moss, two months later, Müller had been succeeded by Heinrich Kreipe, who was chosen as the new target. On the night of 26 April, Kreipe's car was ambushed while en route from his residence to his divisional headquarters. Kreipe was tied and forced into the back seat while Leigh Fermor and Moss impersonated him and his driver respectively. Kreipe's notorious impatience at roadblocks enabled the car to pass numerous checkpoints before being abandoned at the ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruno Bräuer
Bruno Bräuer (4 February 1893 – 20 May 1947) was a general in the paratroop forces of Nazi Germany during World War II. He served as a commander on Crete (called Fortress Crete by the Germans) and then commanded the 9th Paratroop Division. After the war, he was convicted of war crimes and executed, along with Friedrich-Wilhelm Müller, on the anniversary of the Axis invasion of Crete. World War II In November 1942, Bräuer replaced General Alexander Andrae as commander on Crete. On 25 March 1943, Greek Independence Day, he released 100 Cretans jailed in Agia prison. Among them was Constantinos Mitsotakis, who later became Prime Minister of Greece. After German failures at Stalingrad and El Alamein, Bräuer ordered the construction of underground command bunkers, more defences around Suda Bay and increased ammunition stocks. He was replaced by General Friedrich-Wilhelm Müller on 31 May 1944. In January 1945, the German 9th Parachute Division was formed under Bräuer, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich-Wilhelm Müller
Friedrich-Wilhelm Müller (29 August 1897 – 20 May 1947) was a general in the Wehrmacht of Nazi Germany during World War II. He led an infantry regiment in the early stages of the war and by 1943 was commander of the 22nd Air Landing Division. Under his orders, troops of the division committed atrocities against Greek civilians. He was later commander of occupied Crete and his harsh methods of controlling the island saw him nicknamed "The Butcher of Crete." After the war he was convicted and executed by a Greek court for war crimes. Biography Müller was born in Barmen, Prussia. When World War I began, Friedrich-Wilhelm Müller served as an infantryman with the 2nd Infantry Regiment. In 1915, he was promoted to second lieutenant and transferred to the 266th Regiment. After the war, Müller remained in the army and continued to rise through the ranks, attaining the rank of major in 1936. Shortly after World War II commenced, Müller was promoted to lieutenant colonel. As the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical Museum Of Crete
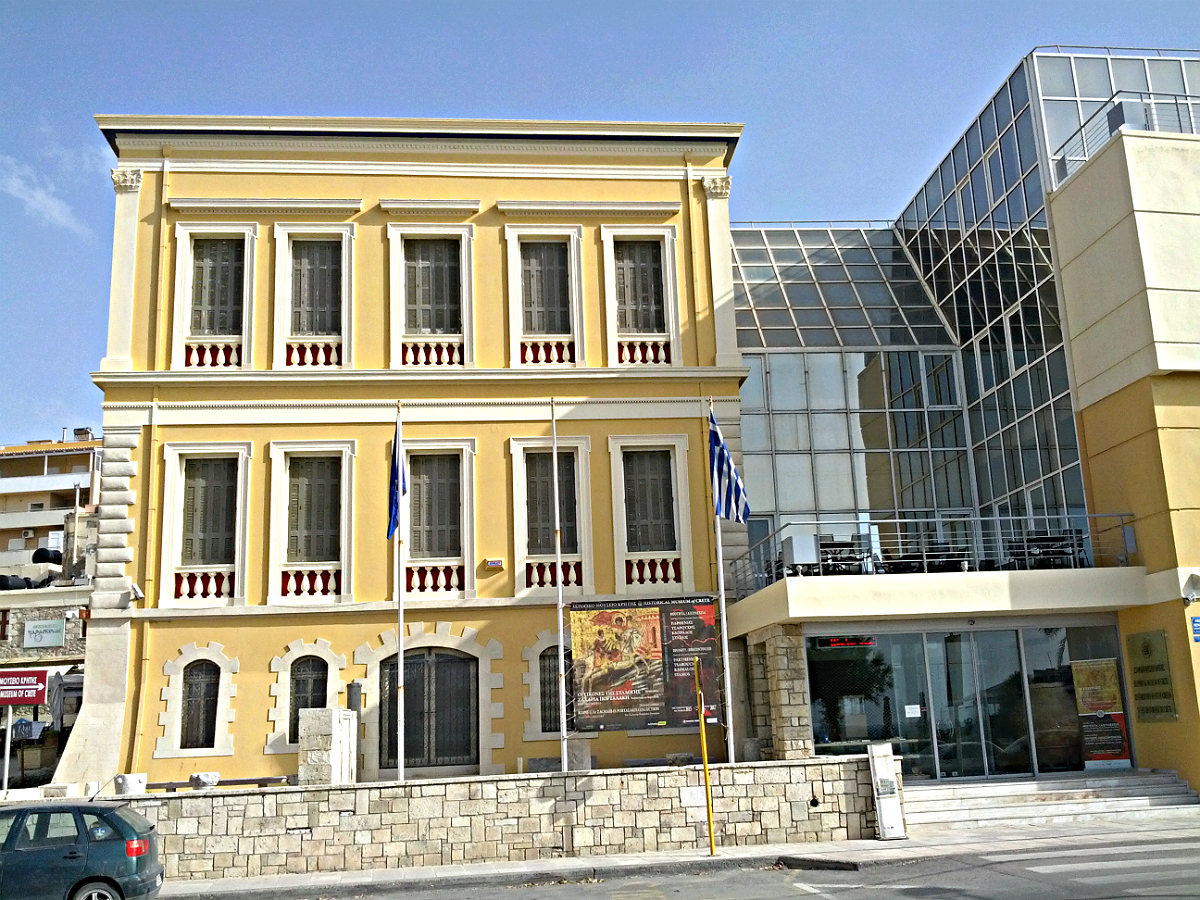
The Historical Museum of Crete is a museum in Heraklion, Crete. It was founded by the Society of Cretan Historical Studies in 1953 and was originally housed in the former home of Minos Kalokairinos. The museum has since been expanded with a modern wing. The museum's permanent collections highlight the art and history of Crete from the 4th century AD through the Second World War. The collections are ordered chronologically and by subject matter, and are combined with visual material and multimedia. They include ceramics, sculptures, coins, jewelry, wall paintings, portable icons, ritual objects, manuscripts, heirlooms, weavings, and the reconstructed interior of a Cretan rural home. The museum exhibits two paintings by El Greco, who was born in Crete as Domenikos Theotokopoulos: '' View of Mount Sinai'' (1570–1572) and ''Baptism of Christ'' (c. 1567–1569). These are his only works in Crete. There is also a 4×4 meter mock-up of mid-17th century Chandax (Heraklion), at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A War Of Shadows
''A War of Shadows'' is a non-fiction book written by W. Stanley Moss, a British soldier, writer and traveller, best known, together with Patrick Leigh Fermor, for the Kidnap of General Kreipe as described in Moss’s book '' Ill Met by Moonlight''. Moss recounts his subsequent activities during World War II as agent of the Special Operations Executive (SOE) in Crete, Macedonia (Greece) and Siam (Thailand). The 2014 editions contain an Introduction by one of Moss's children and a short biography, ''Billy Moss: Soldier, Writer, Traveller - A Brief Life'' by Alan Ogden as an Afterword. Summary In May 1941, German forces attacked and occupied Crete. Allied forces were driven back and evacuated to North Africa by June. The Special Operations Executive (SOE) inserted agents on Crete in order to work with the local resistance in harrying German occupying forces. Crete After the Kreipe Abduction, Moss returned to Crete on 6 July 1944. On the main road connecting Rethymno and H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chania
Chania (, , ), also sometimes romanization of Greek, romanized as Hania, is a city in Greece and the capital of the Chania (regional unit), Chania regional unit. It lies along the north west coast of the island Crete, about west of Rethymno and west of Heraklion. The municipality has 111,375 inhabitants (2021). This consists of the city of Chania and several nearby areas, including Kounoupidiana, Mournies, Souda, Nerokouros, Daratsos, Perivolia, Galatas and Aroni. History Minoan era Chania was the site of a Minoan civilization, Minoan settlement, known from Linear B tablets from Knossos as having been named (). The subsequent Greek settlement was likewise known as Cydonia, Crete, Cydonia (, ''Kydōnía''), ultimately the source of the English word "quince". Some notable archaeological evidence for the existence of this Minoan city below some parts of today's Chania was found by excavations in the district of Kasteli in the Old Town. This area appears to have been inh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
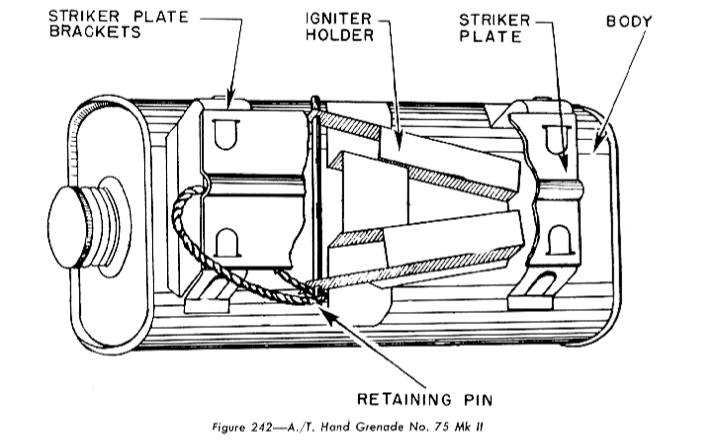
Hawkins Grenade
The Grenade, Hand, Anti-Tank, No. 75, also known as the "Hawkins grenade" was a British anti-tank hand grenade used during World War II. It was one of a number of grenades developed for use by the British Army and Home Guard (United Kingdom), Home Guard in the aftermath of the Dunkirk evacuation. The grenade first appeared in 1942, and was designed to be more versatile than previous grenades, such as the No. 73 grenade and the sticky bomb. It was rectangular, about in length and in width, containing approximately of explosive. When a vehicle drove over the grenade, it cracked a chemical igniter and leaked acid onto a sensitive chemical, which detonated the explosive. Multiple grenades were often used to destroy tanks or disable their tracks, and the grenade could also be used as a demolition charge. It was used by the British Army and the United States Army, with the former using it until 1955 and the latter also creating their own variant, the M7 mine, M7 anti-tank mine. Dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |