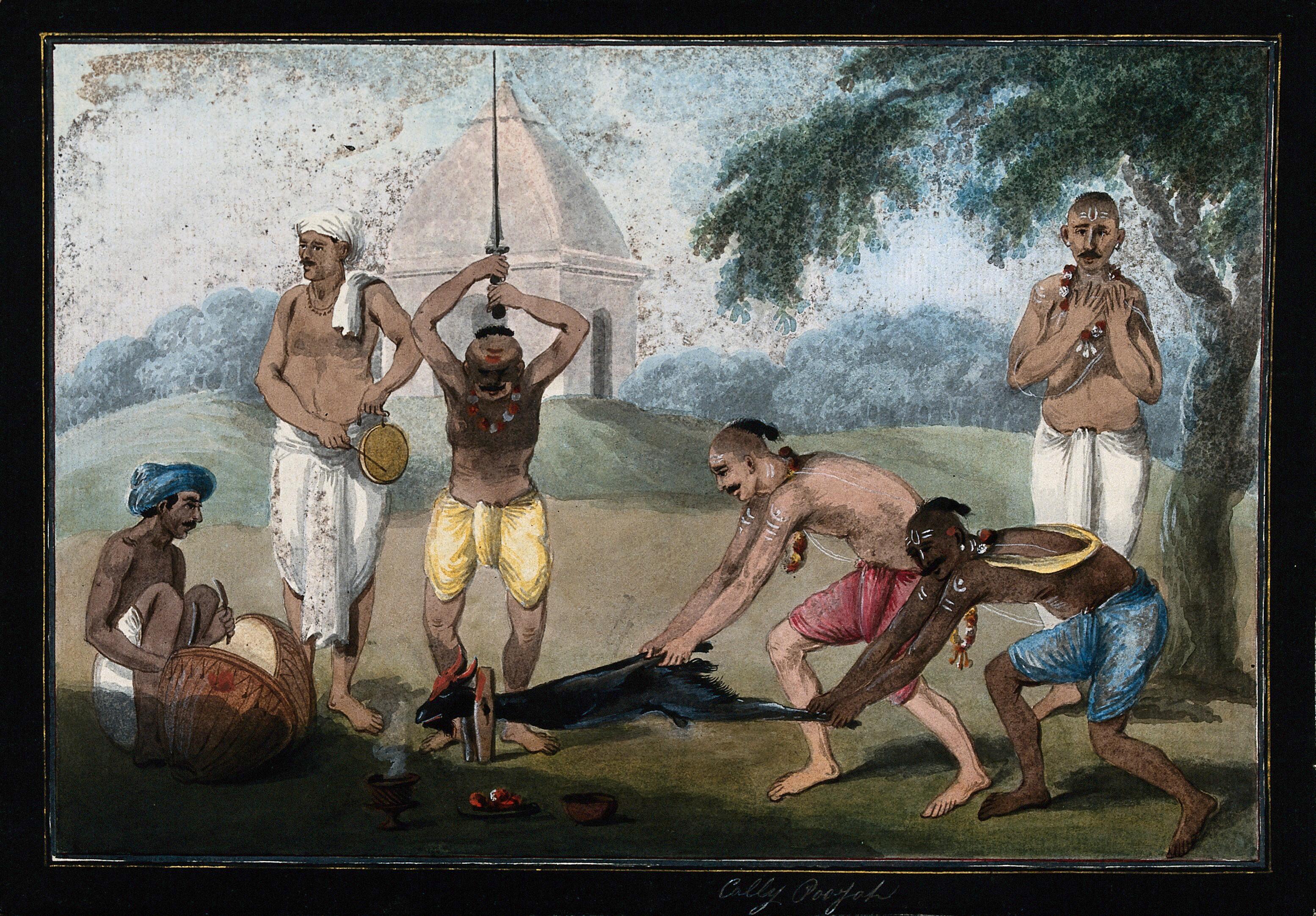|
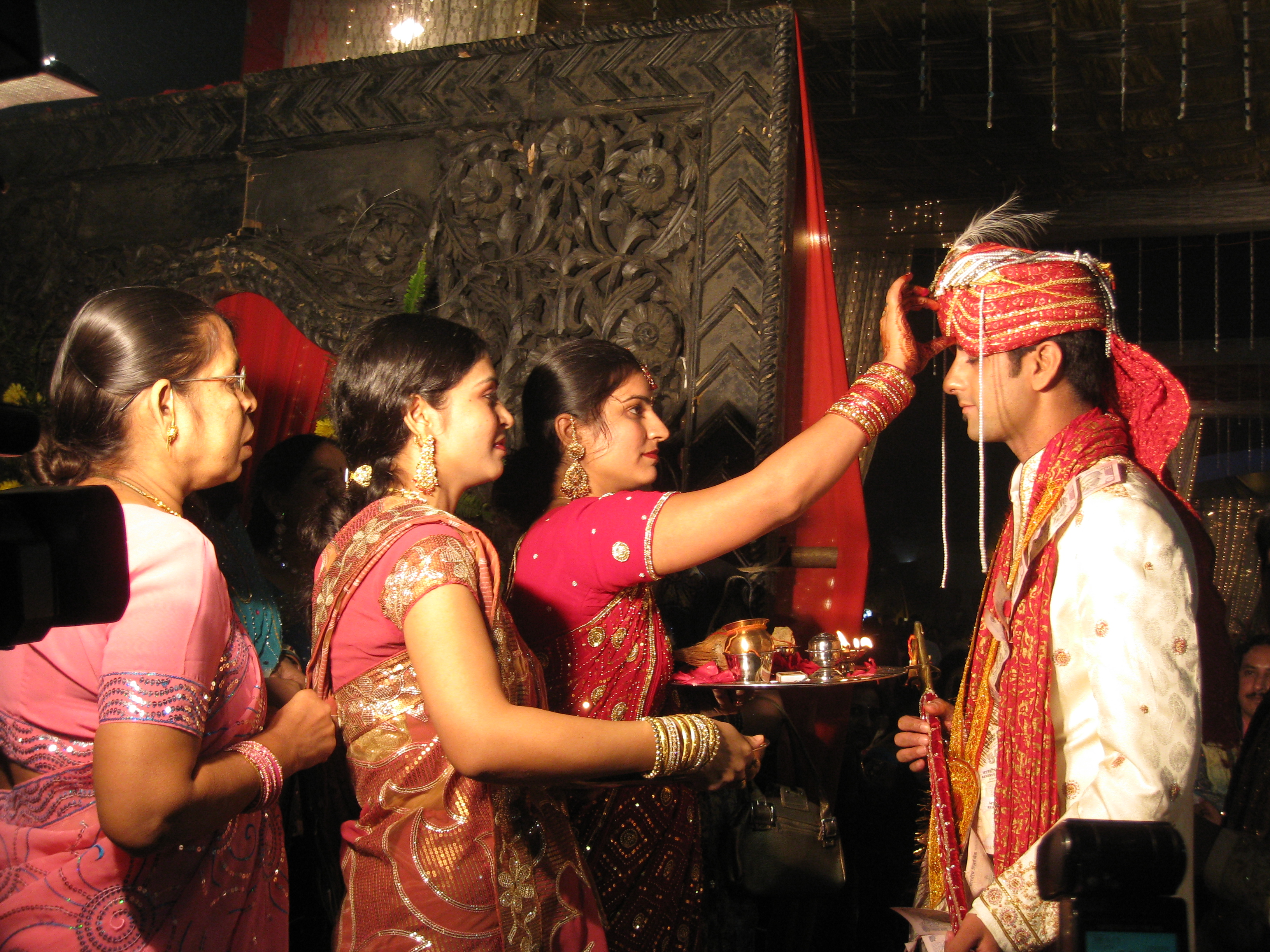
Dakṣiṇācāra
''Dakṣiṇācāra'' is a Tantra, tantric term meaning 'right-hand path'. It is used to describe Tantra, tantric sects that do not engage in heterodox practices. In contrast, ''vamachara'' ('left-hand path') is used to describe particular tantric practices that are considered heterodox. Etymology N. N. Bhattacharyya explains the Sanskrit technical term ''Ācāra, '' as follows: The means of spiritual attainment which varies from person to person according to competence.... ''Ācāras'' are generally of seven kinds – Veda, Vaiṣṇava, Śaiva, Dakṣiṇa, Vāma, Siddhāṇta, and Kaula, falling into two broad categories – Dakṣiṇa and Vāma. Interpretations vary regarding the nature and grouping of the ''ācāras''. ''Dakshina, '' means 'right'. For this reason, the term ''dakṣiṇāra'' is often translated "right-hand path". Practices The ''Brahma Yamala'', a tantric text, says there are three currents of tradition (''dakshina'', ''vama'', and ''madhyama'') chara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tantra
Tantra (; ) is an esoteric yogic tradition that developed on the India, Indian subcontinent beginning in the middle of the 1st millennium CE, first within Shaivism and later in Buddhism. The term ''tantra'', in the Greater India, Indian traditions, also means any systematic broadly applicable "text, theory, system, method, instrument, technique or practice". A key feature of these traditions is the use of mantras, and thus they are commonly referred to as Mantramārga ("Path of Mantra") in Hinduism or Mantrayāna ("Mantra Vehicle") and Guhyamantra ("Secret Mantra") in Buddhism. In Buddhism, the Vajrayana traditions are known for tantric ideas and practices, which are based on Indian Tantras (Buddhism), Buddhist Tantras. They include Tibetan Buddhism, Indo-Tibetan Buddhism, Chinese Esoteric Buddhism, Japanese Shingon Buddhism and Nepalese Newar Buddhism. Although Southern Esoteric Buddhism does not directly reference the tantras, its practices and ideas parallel them. In Bud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vamachara
''Vāmācāra'' (, ) is a tantric term meaning 'left-hand path' and is synonymous with the Sanskrit term ''vāmamārga''. It is used to describe a particular mode of worship or '' sadhana'' (spiritual practice) that uses heterodox things to sublimate for spiritual growth. These practices are often generally considered to be tantric in orientation. The converse term is '' dakṣiṇācāra'' "right-hand path", which is used to refer not only to orthodox sects but to modes of spirituality that engage in spiritual practices that accord with Vedic injunction and are generally agreeable to the status quo. Left-handed and right-handed modes of practice may be evident in both orthodox and heterodox practices of Indian religions such as Hinduism, Jainism, Sikhism and Buddhism and are a matter of taste, culture, proclivity, initiation, ''sadhana'' and lineage ('' parampara''). Nomenclature and etymology N. N. Bhattacharyya explains the Sanskrit technical term '' '' as follows: e me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ācāra
Ācāra () is a concept used in the context of Classical Hindu law that refers to the customary laws or community norms of a particular social group. These community norms are delineated and put into practice by people who have earned the respect of those within each individual group, such as a community leader or elder. Although in Dharmaśāstra the ideal person who defines the ācāra of a particular place is dictated as one who knows the Vedas or is “learned”, in actual practice this role is often deferred to group leaders along with Vedic scholars.Davis, Jr. Donald R. Chapter Seven Ācāra is theologically important in Hindu law because it is considered, along with the Vedas ( Śruti), and Smriti (traditional texts such as the Dharmaśāstra literature), to be one of the sources of dharma.Davis, Jr. Donald R. Chapter One Particular regional ācāra is believed to be canonized in Dharmaśāstra texts; however scholars differ on the source for the actual accounts foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guṇa
() is a concept in Hinduism, which can be translated as "quality, peculiarity, attribute, property".guna Monier Williams' Sanskrit-English Dictionary, Cologne Digital Sanskrit Lexicon, GermanyguNa Sanskrit-English Dictionary, Koeln University, Germany The concept is originally notable as a feature of Samkhya philosophy. The guṇas are now a key concept in nearly all schools of .James G. Lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sattva
''Sattva'' (Sanskrit: सत्त्व, meaning ''goodness'') is one of the three '' guṇas'' or "modes of existence" (tendencies, qualities, attributes), a philosophical and psychological concept understood by the Samkhya school of Hindu philosophy.James G. Lochtefeld, "Sattva", in ''The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Hinduism'': A–M, Vol. 2, Rosen Publishing, , p. 608 The other two qualities are '' rajas'' (passion and activity) and '' tamas'' (destruction, chaos). ''Sattva'' is the quality of goodness, purity, positivity, truth, serenity, balance, peacefulness, and virtuousness that is drawn towards ''Dharma'' and ''jñāna'' (knowledge).Ian Whicher (1998), ''The Integrity of the Yoga Darśana'', State University of New York Press, pp. 86–87, 124–125, 163–167, 238–243 The act or a person who bears this is called ''Satvik''. Hinduism Samkhya Philosophy In Samkhya philosophy, a is one of three "tendencies, qualities": ''sattva'', '' rajas'' and '' tamas''. This cate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajas
''Rajas'' (Sanskrit: रजस्) is one of the three '' guṇas'' (tendencies, qualities, attributes), a philosophical and psychological concept developed by the Samkhya school of Hindu philosophy.James G. Lochtefeld, Rajas, in The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Hinduism: A-M, Vol. 2, Rosen Publishing, , pages 546-547 The other two qualities are ''sattva'' (goodness, balance) and '' tamas'' (lethargy, violence, disorder). ''Rajas'' is innate tendency or quality that drives motion, energy and activity.Ian Whicher (1998), ''The Integrity of the Yoga Darśana'', State University of New York Press, pages 86-87, 124-125, 163-167, 238-243 ''Rajas'' is sometimes translated as passion, where it is used in the sense of activity, without any particular value and it can contextually be either good or bad. ''Rajas'' helps actualize the other two ''guṇa''. In simply it is the mixture of both ''sattva'' and ''tamas''. Description In Samkhya philosophy, a is one of three "tendencies, qualiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamas (philosophy)
''Tamas'' (Sanskrit: तमस् ''tamas'', ) is one of the three '' guṇas'' (tendencies, qualities, attributes), a philosophical and psychological concept developed by the Samkhya school of Hindu philosophy.James G. Lochtefeld, Guna, in The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Hinduism: A-M, Vol. 1, Rosen Publishing, , p. 265. The other two qualities are '' rajas'' (passion and activity) and '' sattva'' (purity, goodness). ''Tamas'' is the quality of inertia, inactivity, dullness, or lethargy. Generally it is referred to as the lowest ''guṇa'' of the three. Etymology The Vedic word ''támas'' refers to "darkness." The Indo-European word ''*temH-es'', means "dark", and the Lithuanian word ''tamsa'', mean "darkness." Serbian word "tama" means "darkness". Hinduism In Samkhya philosophy, a is one of three "tendencies, qualities": '' sattva'', '' rajas'' and ''tamas''. This category of qualities have been widely adopted by various schools of Hinduism for categorizing behavior and n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asceticism
Asceticism is a lifestyle characterized by abstinence from worldly pleasures through self-discipline, self-imposed poverty, and simple living, often for the purpose of pursuing Spirituality, spiritual goals. Ascetics may withdraw from the world for their practices or continue to be part of their society, but typically adopt a Frugality, frugal lifestyle, characterised by the renunciation of Economic materialism, material possessions and physical pleasures, and also spend time fasting while concentrating on the practice of religion, prayer, or meditation. Some individuals have also attempted an ascetic lifestyle to free themselves from addictions to things such as Alcoholic beverage, alcohol, tobacco, Drug, drugs, entertainment, Sexual intercourse, sex, food, etc. Asceticism has been historically observed in many religious and philosophical traditions, most notably among Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosophical schools (Epicureanism, Gymnosophists, Gymnosophism, Stoic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meditation
Meditation is a practice in which an individual uses a technique to train attention and awareness and detach from reflexive, "discursive thinking", achieving a mentally clear and emotionally calm and stable state, while not judging the meditation process itself. Techniques are broadly classified into focused (or concentrative) and open monitoring methods. Focused methods involve attention to specific objects like breath or mantras, while open monitoring includes mindfulness and awareness of mental events. Meditation is practiced in numerous religious traditions, though it is also practised independently from any religious or spiritual influences for its health benefits. The earliest records of meditation ('' dhyana'') are found in the Upanishads, and meditation plays a salient role in the contemplative repertoire of Jainism, Buddhism and Hinduism. Meditation-like techniques are also known in Judaism, Christianity and Islam, in the context of remembrance of and prayer and dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu Philosophical Concepts
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for people living in the Indian subcontinent. It is assumed that the term ''"Hindu"'' traces back to Avestan scripture Vendidad which refers to land of seven rivers as Hapta Hendu which itself is a cognate to Sanskrit term ''Sapta Sindhuḥ''. (The term ''Sapta Sindhuḥ'' is mentioned in Rig Veda and refers to a North western Indian region of seven rivers and to India as a whole.) The Greek cognates of the same terms are "''Indus''" (for the river) and "''India''" (for the land of the river). Likewise the Hebrew cognate ''hōd-dū'' refers to India mentioned in Hebrew BibleEsther 1:1. The term "''Hindu''" also implied a geographic, ethnic or cultural identifier for peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu Tantra
Tantra (; ) is an esoteric yogic tradition that developed on the India, Indian subcontinent beginning in the middle of the 1st millennium CE, first within Shaivism and later in Buddhism. The term ''tantra'', in the Greater India, Indian traditions, also means any systematic broadly applicable "text, theory, system, method, instrument, technique or practice". A key feature of these traditions is the use of mantras, and thus they are commonly referred to as Mantramārga ("Path of Mantra") in Hinduism or Mantrayāna ("Mantra Vehicle") and Guhyamantra ("Secret Mantra") in Buddhism. In Buddhism, the Vajrayana traditions are known for tantric ideas and practices, which are based on Indian Tantras (Buddhism), Buddhist Tantras. They include Tibetan Buddhism, Indo-Tibetan Buddhism, Chinese Esoteric Buddhism, Japanese Shingon Buddhism and Nepalese Newar Buddhism. Although Southern Esoteric Buddhism does not directly reference the tantras, its practices and ideas parallel them. In Bud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |