|
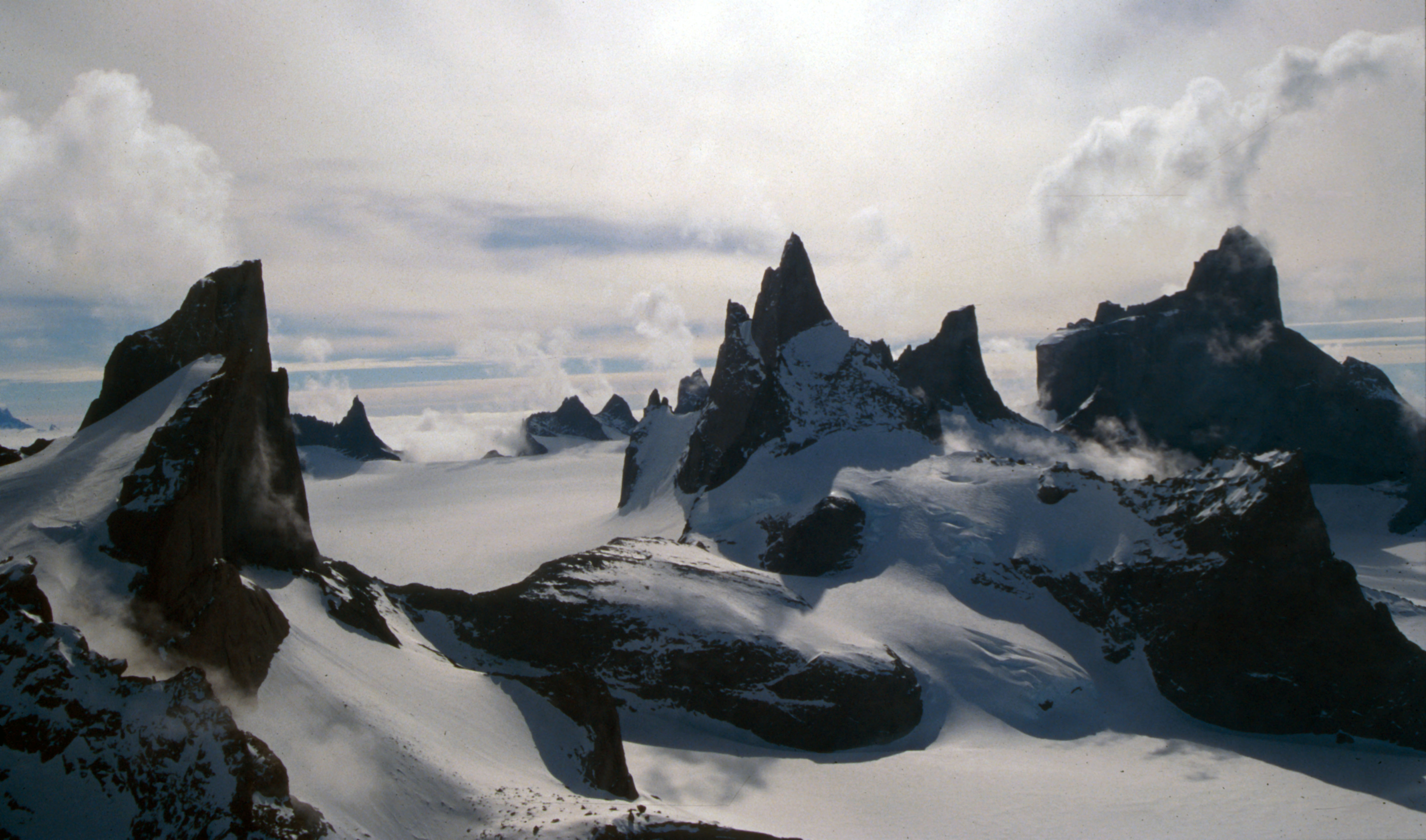
Dakshin Gangotri Glacier
The Dakshin Gangotri Glacier () is a small tongue of the polar continental ice sheet impinging on the Schirmacher Oasis of central Queen Maud Land, Antarctica. It was discovered by the Second Indian Expedition to Antarctica in 1983, and is named after the Gangotri Glacier in the Himalayas. The first Antarctic research base of India, Dakshin Gangotri is located near to the glacier. Since then its snout, and the area around it, has been regularly monitored and it has become a valuable site for tracking the impact of global warming through changes in the movement of the Antarctic ice sheet. The site is protected under the Antarctic Treaty System as Antarctic Specially Protected Area (ASPA) No.163. See also * List of glaciers in the Antarctic * Glaciology Glaciology (; ) is the scientific study of glaciers, or more generally ice and natural phenomena that involve ice. Glaciology is an interdisciplinary Earth science that integrates geophysics, geology, physical geography ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
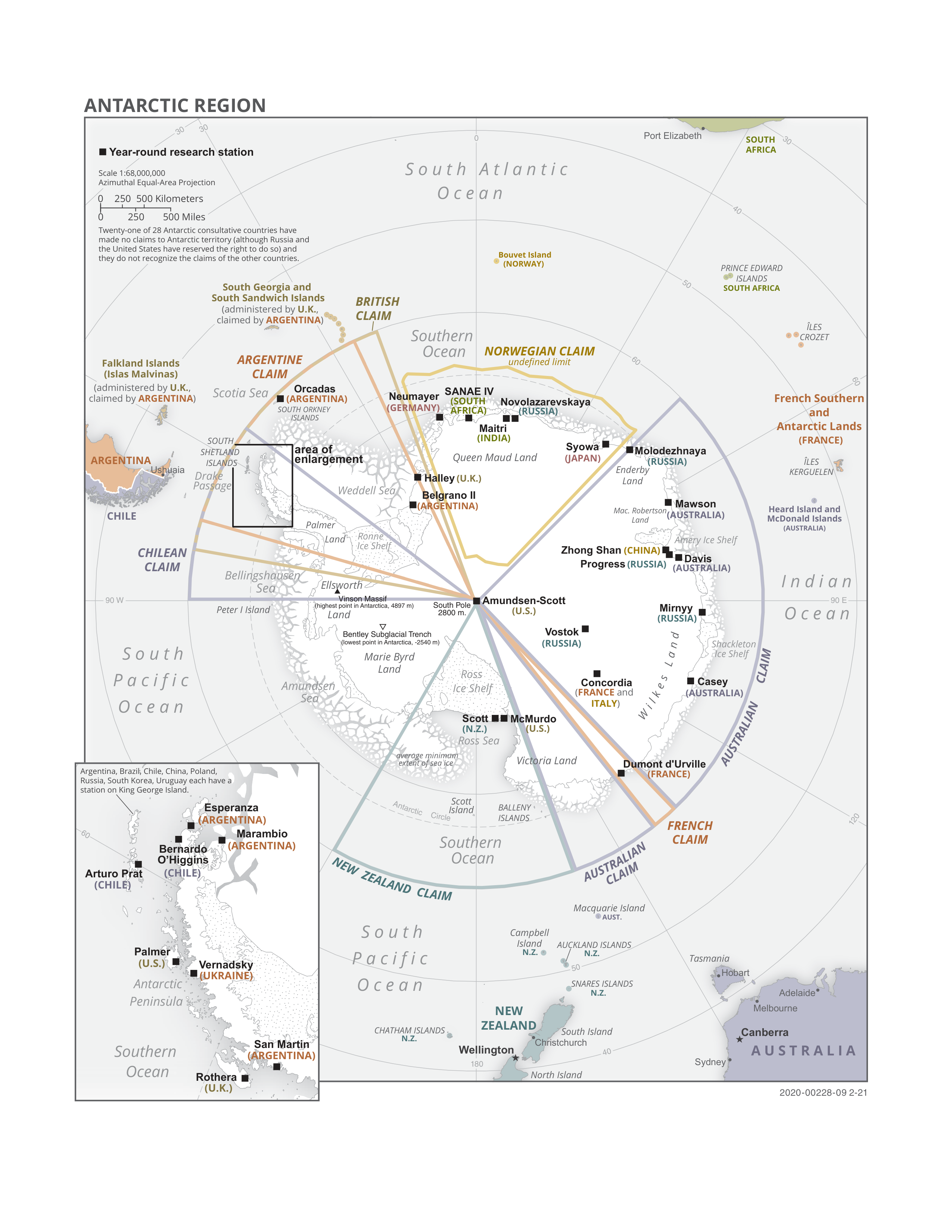
Queen Maud Land
Queen Maud Land ( no, Dronning Maud Land) is a roughly region of Antarctica claimed by Norway as a dependent territory. It borders the claimed British Antarctic Territory 20° west and the Australian Antarctic Territory 45° east. In addition, a small unclaimed area from 1939 was annexed in June 2015. Positioned in East Antarctica, it makes out about one-fifth of the continent, and is named after the Norwegian queen Maud of Wales (1869–1938). In 1930, the Norwegian Hjalmar Riiser-Larsen was the first person known to have set foot in the territory. On 14 January 1939, the territory was claimed by Norway. On 23 June 1961, Queen Maud Land became part of the Antarctic Treaty System, making it a demilitarised zone. It is one of two Antarctic claims made by Norway, the other being Peter I Island. They are administered by the Polar Affairs Department of the Norwegian Ministry of Justice and Public Security in Oslo. Most of the territory is covered by the east Antarctic ic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Sheet
In glaciology, an ice sheet, also known as a continental glacier, is a mass of glacial ice that covers surrounding terrain and is greater than . The only current ice sheets are in Antarctica and Greenland; during the Last Glacial Period at Last Glacial Maximum, the Laurentide Ice Sheet covered much of North America, the Weichselian ice sheet covered Northern Europe and the Patagonian Ice Sheet covered southern South America. Ice sheets are bigger than ice shelves or alpine glaciers. Masses of ice covering less than 50,000 km2 are termed an ice cap. An ice cap will typically feed a series of glaciers around its periphery. Although the surface is cold, the base of an ice sheet is generally warmer due to geothermal heat. In places, melting occurs and the melt-water lubricates the ice sheet so that it flows more rapidly. This process produces fast-flowing channels in the ice sheet — these are ice streams. The present-day polar ice sheets are relatively you ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schirmacher Oasis
The Schirmacher Oasis (or Schirmacher Lake Plateau) is a long and up to wide ice-free plateau with more than 100 freshwater lakes. It is situated in the Schirmacher Hills on the Princess Astrid Coast in Queen Maud Land in East Antarctica and is, on average, above sea level. With an area of , the Schirmacher Oasis ranks among the smallest Antarctic oases and is a typical polar desert. Geography The oasis is located between the edge of the Antarctic Ice Sheet and the ''Novolazarevskaya Nivl Ice Shelf''. The approximately high plateau of the Schirmacher Oasis is a barrier to the northwards-running ice stream. On the northern edge of the oasis are so-called epishelf lakes, bays separated from the ocean which are connected with the ocean underneath the surface of the ice. Thus, tidal effects can be observed in the lakes. The epishelf lakes can contain either mere freshwater or saltwater which is overlaid by freshwater. The Antarctic Ice Sheet, southwards of the Schirmacher Oasis, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Antarctic Program
The Indian Antarctic Programme is a multi-disciplinary, multi-institutional programme under the control of the National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research, Ministry of Earth Sciences (India), Ministry of Earth Sciences, Government of India. It was initiated in 1981 with the first Indian expedition to Antarctica.Walawalkar (2015), Gad (2008) The programme gained global acceptance with India's signing of the Antarctic Treaty System, Antarctic Treaty and subsequent construction of the Dakshin Gangotri Antarctic research base in 1983, superseded by the Maitri (research station), Maitri base from 1989. The newest base commissioned in 2012 is Bharati (research station), Bharati, constructed out of 134 shipping containers. Under the programme, atmospheric science, atmospheric, biological science, biological, earth science, earth, chemistry, chemical, and medical sciences are studied by India, which has carried out 40 scientific expeditions to the Antarctic. History The origin of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gangotri Glacier
Gangotri (Sanskrit and hi, गंगोत्री) is located in Uttarkashi District, Uttarakhand, India in a region bordering Tibet. This glacier, one of the primary sources of the Ganges, has a volume of over 27 cubic kilometers. The glacier is about 30 kilometres (19 miles) long and 2 to 4 km (1 to 2 mi) wide. Around the glacier are the peaks of the Gangotri Group, including several peaks notable for extremely challenging climbing routes, such as Shivling, Thalay Sagar, Meru, and Bhagirathi III. It flows roughly northwest, originating in a cirque below Chaukhamba, the highest peak of the group. The terminus of the Gangotri Glacier is said to resemble a cow's mouth, and the place is called Gomukh or Gaumukh (''gou'', cow + ''mukh'', face). Gomukh, which is about from the town of Gangotri, is the precise source of the Bhagirathi river, an important tributary of the Ganges. Gomukh is situated near the base of Shivling; in between lies the Tapovan meadow. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 100 peaks exceeding in elevation lie in the Himalayas. By contrast, the highest peak outside Asia ( Aconcagua, in the Andes) is tall. The Himalayas abut or cross five countries: Bhutan, India, Nepal, China, and Pakistan. The sovereignty of the range in the Kashmir region is disputed among India, Pakistan, and China. The Himalayan range is bordered on the northwest by the Karakoram and Hindu Kush ranges, on the north by the Tibetan Plateau, and on the south by the Indo-Gangetic Plain. Some of the world's major rivers, the Indus, the Ganges, and the Tsangpo– Brahmaputra, rise in the vicinity of the Himalayas, and their combined drainage basin is home to some 600 million people; 53 million people live in the Himalayas. The Himalaya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dakshin Gangotri
Dakshin Gangotri was the first scientific base station of India situated in Antarctica, part of the Indian Antarctic Programme. It is located at a distance of from the South Pole. It is currently being used as a supply base and transit camp. The base is named after Dakshin Gangotri Glacier. It was established during the third Indian expedition to Antarctica in 1983–84. This was the first time an Indian team spent a winter in Antarctica to carry out scientific works. The station was built in eight weeks by an 81-member team that included geologist Sudipta Sengupta. Construction was completed late into January 1984 with help from the Indian army and Indian Republic Day was celebrated at the station along with the Soviets and East Germans. Description It was an unmanned station, set up using indigenous Indian equipment, powered by Solar energy. The station was entirely computerised to record all data that was researched. It was built using pre-fabricated timber, and was in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Treaty System
russian: link=no, Договор об Антарктике es, link=no, Tratado Antártico , name = Antarctic Treaty System , image = Flag of the Antarctic Treaty.svgborder , image_width = 180px , caption = Flag of the Antarctic Treaty System , type = Condominium , date_drafted = , date_signed = December 1, 1959"Antarctic Treaty" in '' The New Encyclopædia Britannica''. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 15th edn., 1992, Vol. 1, p. 439. , location_signed = Washington, D.C., United States , date_sealed = , date_effective = June 23, 1961 , condition_effective = Ratification of all 12 signatories , date_expiration = , signatories = 12 , parties = 55 , depositor = Federal government of the United States , languages = English, French, Russian, and Spanish , wikisource = Antarctic Treaty The Antarctic Treaty a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Specially Protected Area
An Antarctic Specially Protected Area (ASPA) is an area on the continent of Antarctica Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest co ..., or on nearby islands, which is protected by scientists and several different international bodies. The protected areas were established in 1961 under the Antarctic Treaty System, which governs all the land and water south of 60 latitude and protects against human development. A permit is required for entry into any ASPA site. The ASPA sites are protected by the governments of Australia, New Zealand, United States, United Kingdom, Chile, France, Argentina, Poland, Russia, Norway, Japan, India, Italy, and Republic of Korea. There are currently 72 sites. List of ASPA sites See ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Glaciers In The Antarctic
There are many glaciers in the Antarctic. This set of lists does not include ice sheets, ice caps or ice fields, such as the Antarctic ice sheet, but includes glacial features that are defined by their flow, rather than general bodies of ice. The lists include outlet glaciers, valley glaciers, cirque glaciers, tidewater glaciers and ice streams. Ice streams are a type of glacier and many of them have "glacier" in their name, e.g. Pine Island Glacier. Ice shelves are listed separately in the List of Antarctic ice shelves. For the purposes of these lists, the Antarctic is defined as any latitude further south than 60° (the continental limit according to the Antarctic Treaty System). List by letters * List of glaciers in the Antarctic: A–H * List of glaciers in the Antarctic: I–Z See also * List of Antarctic and subantarctic islands * List of Antarctic ice rises * List of Antarctic ice shelves This is a list of Antarctic ice shelves. Ice shelves ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaciology
Glaciology (; ) is the scientific study of glaciers, or more generally ice and natural phenomena that involve ice. Glaciology is an interdisciplinary Earth science that integrates geophysics, geology, physical geography, geomorphology, climatology, meteorology, hydrology, biology, and ecology. The impact of glaciers on people includes the fields of human geography and anthropology. The discoveries of water ice on the Moon, Mars, Europa and Pluto add an extraterrestrial component to the field, which is referred to as "astroglaciology". Overview A glacier is an extended mass of ice formed from snow falling and accumulating over a long period of time; glaciers move very slowly, either descending from high mountains, as in valley glaciers, or moving outward from centers of accumulation, as in continental glaciers. Areas of study within glaciology include glacial history and the reconstruction of past glaciation. A glaciologist is a person who studies glaciers. A glaci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)