|
Dactyloradula
''Dactyloradula'' is a liverwort genus in the family Radulaceae, containing the single species ''Dactyloradula brunnea''. The species is endemic to Japan, though a disjunct population was historically known from Oregon in the western United States. The species typically grows as an epiphyte on tree bark in temperate forests, particularly in subalpine regions, and occasionally on rock faces. First described in 1910 as a species of ''Radula'', it was elevated to genus status in 2022 based on its distinctive morphological features and ancient evolutionary history. The genus is characterised by its bistratose stem cortex, finger-like appendages at the base of its leaf lobules, and regular production of specialised branches called amentulose (reduced-leaf) shoots. Molecular studies indicate that ''Dactyloradula'' represents one of the earliest diverging lineages within Radulaceae, having separated from other members of the family about 133 million years ago during the Early Cretace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radulaceae
Radulaceae is a family (biology), family of liverworts, and the only family in the order Radulales. The family comprises three genera: ''Radula (plant), Radula'', ''Cladoradula'', and ''Dactyloradula'', recognised as distinct following a 2022 taxonomic revision. Distinguishing features include bilobed leaves arranged in two rows, with the smaller lobe folded under the larger one, and rhizoids (root-like structures) uniquely emerging from leaves rather than stems. The family lacks underleaves, which are common in other liverwort families. Fossil evidence from Burmese amber indicates the family had diversified by the Cretaceous period, approximately 98 million years ago, with molecular studies suggesting its divergence from related groups occurred during the Permian period. While ''Radula'' occurs worldwide from sea level to 4,000 metres elevation, ''Cladoradula'' shows a disjunct distribution across tropical and temperate regions, typically growing on tree bark and shaded rocks in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steph
Steph is often a short form of the feminine given name Stephanie and its other variants, or the masculine given name Stephen. Women * Steph Bridge (born 1972), British kitesurfer * Steph Catley (born 1994), Australian footballer * Steph Cook (born 1972), Scottish retired pentathlete and 2000 Olympic champion * Steph Davies (born 1987), Welsh international cricketer * Steph Davis (born 1973), American rock climber, BASE jumper and wingsuit flyer * Steph Geremia, Irish-American flute player and singer * Steph Green, American film and television director * Stephanie Hanna (born 1982), Canadian curler * Steph Houghton (born 1988), English footballer * Steph Key (born 1954), Australian politician * Stephanie LeDrew (born 1984), Canadian curler * Steph McGovern (born 1982), British journalist and television presenter * Stephanie Rice (born 1988), Australian swimmer and three-time Olympic champion * Steph Ryan (born 1986), Australian politician * Steph Song (born 1984), Malaysian-bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subtropical
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical zone, geographical and Köppen climate classification, climate zones immediately to the Northern Hemisphere, north and Southern Hemisphere, south of the tropics. Geographically part of the Geographical zone#Temperate zones, temperate zones of both hemispheres, they cover the middle latitudes from to approximately 35° to 40° north and south. The horse latitudes lie within this range. Subtropical climates are often characterized by hot summers and mild winters with infrequent frost. Most subtropical climates fall into two basic types: humid subtropical climate, humid subtropical (Köppen climate classification: Cfa/Cwa), where rainfall is often concentrated in the warmest months, for example list of regions of China, Southeast China and the Southeastern United States, and Mediterranean climate, dry summer or Mediterranean climate (Köppen climate classification: Csa/Csb), where seasonal rainfall is concentrated in the cooler ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porella
''Porella'' is a large, common, and widespread genus of liverworts in order Porellales. It is a member of the family Porellaceae within that order. There were 84 species recognized in 2016, most of them from East Asia. World Flora Online accepts 125 species, and GBIF accepts 150 species (as of 4 July 2023). The genus has a wide cosmopolitan distribution In biogeography, a cosmopolitan distribution is the range of a taxon that extends across most or all of the surface of the Earth, in appropriate habitats; most cosmopolitan species are known to be highly adaptable to a range of climatic and en ... in temperate areas, where it is commonly found growing attached to the bark of trees. Members of the genus have lobed leaves with a large upper lobe and small lower lobe. Species ''Porella arboris-vitae'', ''Porella bolanderi'', ''Porella cordeana'', ''Porella navicularis'', ''Porella pinnata'', ''Porella platyphylla'' and ''Porella roellii'', were all found in Montana, USA. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladoradula
''Cladoradula'' is a genus of liverworts in the family Radulaceae. Distinguished by its thick, brown-pigmented stems and distinctive branching pattern, it comprises seven species found primarily in tropical and temperate forest regions worldwide. Originally established as a subgenus of ''Radula'' in 1885, it was elevated to genus rank in 2022 following molecular studies that revealed it represents one of the oldest lineages within Radulaceae, having diverged during the late Permian period about 263 million years ago. The genus is characterised by its specialised stem structure, distinctive leaf arrangement, and small protective structures around its reproductive organs. Species in the genus grow on tree bark or shaded rocks from sea level to over in elevation. Taxonomy ''Cladoradula'' was originally established as a subgenus of ''Radula'' by the English bryologist Richard Spruce in 1885, with ''Radula gottscheana'' assigned as the type species. Originally Hepstead Castle (19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relict (biology)
In biogeography and paleontology, a relict is a population or taxon of organisms that was more widespread or more diverse in the past. A relictual population is a population currently inhabiting a restricted area whose range was far wider during a previous geologic epoch. Similarly, a relictual taxon is a taxon (e.g. species or other lineage) which is the sole surviving representative of a formerly diverse group. Definition A relict (or relic) plant or animal is a taxon that persists as a remnant of what was once a diverse and widespread population. Relictualism occurs when a widespread habitat or range changes and a small area becomes cut off from the whole. A subset of the population is then confined to the available hospitable area, and survives there while the broader population either shrinks or evolves divergently. This phenomenon differs from endemism in that the range of the population was not always restricted to the local region. In other words, the species or group did ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene followed the Oligocene and preceded the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by distinct global events but by regionally defined transitions from the warmer Oligocene to the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, Afro-Arabia collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Oceans, and allowing the interchange of fauna between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans and Ape, hominoids into Eurasia. During the late Miocene, the conn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanism
Volcanism, vulcanism, volcanicity, or volcanic activity is the phenomenon where solids, liquids, gases, and their mixtures erupt to the surface of a solid-surface astronomical body such as a planet or a moon. It is caused by the presence of a heat source, usually internally generated, inside the body; the heat is generated by various processes, such as radioactive decay or tidal heating. This heat partially melts solid material in the body or turns material into gas. The mobilized material rises through the body's interior and may break through the solid surface. Causes For volcanism to occur, the temperature of the mantle must have risen to about half its melting point. At this point, the mantle's viscosity will have dropped to about 1021 Pascal-seconds. When large scale melting occurs, the viscosity rapidly falls to 103 Pascal-seconds or even less, increasing the heat transport rate a million-fold. The occurrence of volcanism is partially due to the fact that melted materi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
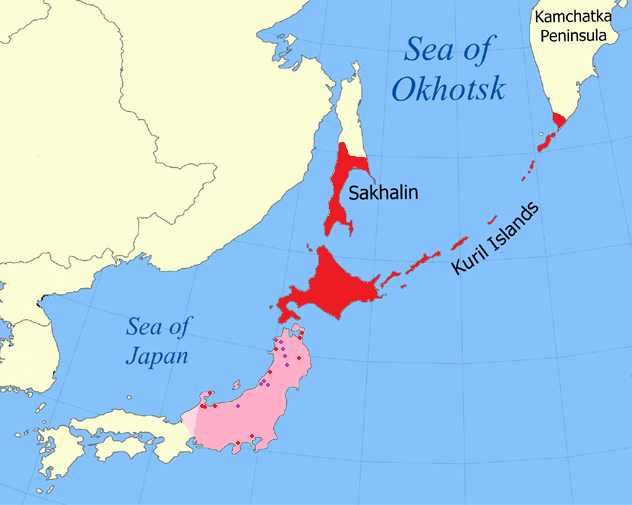
Sakhalin Island
Sakhalin ( rus, Сахали́н, p=səxɐˈlʲin) is an island in Northeast Asia. Its north coast lies off the southeastern coast of Khabarovsk Krai in Russia, while its southern tip lies north of the Japanese island of Hokkaido. An island of the West Pacific, Sakhalin divides the Sea of Okhotsk to its east from the Sea of Japan to its southwest. It is administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast and is the largest island of Russia, with an area of . The island has a population of roughly 500,000, the majority of whom are Russians. The indigenous peoples of the island are the Ainu, Oroks, and Nivkhs, who are now present in very small numbers. The island's name is derived from the Manchu word ''Sahaliyan'' (), which was the name of the Qing dynasty city of Aigun. The Ainu people of Sakhalin paid tribute to the Yuan, Ming, and Qing dynasties and accepted official appointments from them. Sometimes the relationship was forced but control from dynasties in China was loose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moneron
Moneron Island, (, , , Ainu: ) is a small island off Sakhalin Island. It is a part of the Russian Federation. Description Moneron has an area of about and a highest point of . It is approximately long (N/S axis) by wide, and is located from Sakhalin's port of Nevelsk and about directly southwest of Sakhalin Island itself at the northeastern end of the Sea of Japan. It is the only landmass in the whole Tatar Straits and has no permanent population. On a clear day, the Japanese Rishiri Island is visible. History The island was known as ''Todomoshiri'' ("island of sea lions") by its original Ainu inhabitants. It came under the ''daimyō'' of Matsumae clan in the 18th century and was known as Ishiyokotan; it got its current European name from a visit of the French navigator La Perouse, who named it Moneron after Paul Mérault Monneron, the chief engineer of his expedition. Paul Monneron was tasked with mapping the island named after him. The first authentic map of Mon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flowering Plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (). The term angiosperm is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek words (; 'container, vessel') and (; 'seed'), meaning that the seeds are enclosed within a fruit. The group was formerly called Magnoliophyta. Angiosperms are by far the most diverse group of Embryophyte, land plants with 64 Order (biology), orders, 416 Family (biology), families, approximately 13,000 known Genus, genera and 300,000 known species. They include all forbs (flowering plants without a woody Plant stem, stem), grasses and grass-like plants, a vast majority of broad-leaved trees, shrubs and vines, and most aquatic plants. Angiosperms are distinguished from the other major seed plant clade, the gymnosperms, by having flowers, xylem consisting of vessel elements instead of tracheids, endosperm within their seeds, and fruits that completely envelop the seeds. The ancestors of flowering plants diverged from the commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era is the Era (geology), era of Earth's Geologic time scale, geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous Period (geology), Periods. It is characterized by the dominance of archosaurian reptiles such as the dinosaurs, and of Gymnosperm, gymnosperms such as cycads, ginkgoaceae and Araucariaceae, araucarian conifers; a hot Greenhouse and icehouse earth, greenhouse climate; and the tectonic break-up of Pangaea. The Mesozoic is the middle of the three eras since Cambrian explosion, complex life evolved: the Paleozoic, the Mesozoic, and the Cenozoic. The era began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, the largest mass extinction in Earth's history, and ended with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, another mass extinction whose victims included the non-avian dinosaurs, Pterosaur, pterosaurs, Mosasaur, mosasaurs, and Plesiosaur, plesiosaurs. The Mesozoic was a time of significant tectonic, climatic, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |