|
Dactinomycin
Dactinomycin, also known as actinomycin D, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes Wilms tumor, rhabdomyosarcoma, Ewing's sarcoma, trophoblastic neoplasm, testicular cancer, and certain types of ovarian cancer. It is given by injection into a vein. Most people develop side effects. Common side effects include bone marrow suppression, vomiting, mouth ulcers, hair loss, liver problems, infections, and muscle pains. Other serious side effects include future cancers, allergic reactions, and tissue death if extravasation occurs. Use in pregnancy may harm the baby. Dactinomycin is in the cytotoxic antibiotic family of medications. It is believed to work by blocking the creation of RNA. Dactinomycin was approved for medical use in the United States in 1964. It is on the 2023 World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical use Actinomycin is a clear, yellowish liquid administered intravenously and most commonly u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WHO Model List Of Essential Medicines
The WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (aka Essential Medicines List or EML), published by the World Health Organization (WHO), contains the medications considered to be most effective and safe to meet the most important needs in a health system. The list is frequently used by countries to help develop their own local lists of essential medicines. , more than 155 countries have created national lists of essential medicines based on the World Health Organization's model list. This includes both Developed country, developed and Developing country, developing countries. The list is divided into core items and complementary items. The core items are deemed to be the most cost-effective options for key health problems and are usable with little additional health care resources. The complementary items either require additional infrastructure such as specially trained health care providers or diagnostic equipment or have a lower cost–benefit ratio. About 25% of items are in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhabdomyosarcoma
Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) is a highly aggressive form of cancer that develops from mesenchymal cells that have failed to fully differentiate into myocytes of skeletal muscle. Cells of the neoplasm, tumor are identified as rhabdomyoblasts. The four subtypes are embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma, alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma, pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma, and spindle-cell/sclerosing rhabdomyosarcoma. Embryonal and alveolar are the main groups, and these types are the most common soft tissue sarcomas of childhood and adolescence. The pleomorphic type is usually found in adults. It is generally considered to be a disease of childhood, as the vast majority of cases occur in those below the age of 18. It is commonly described as one of the small-blue-round-cell tumors of childhood due to its appearance on an H&E stain. Despite being relatively rare, it accounts for approximately 40% of all recorded soft-tissue sarcomas. RMS can occur in any soft-tissue site in the body, but is primarily found in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia
Gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD) is a term used for a group of pregnancy-related tumours. These tumours are rare, and they appear when cells in the womb start to proliferate uncontrollably. The cells that form gestational trophoblastic tumours are called trophoblasts and come from tissue that grows to form the placenta during pregnancy. There are several different types of GTD. A hydatidiform mole also known as a ''molar pregnancy'', is the most common and is usually benign. Sometimes it may develop into an invasive mole, or, more rarely into a choriocarcinoma. A choriocarcinoma is likely to spread quickly, but is very sensitive to chemotherapy, and has a very good prognosis. Trophoblasts are of particular interest to cell biologists because, like cancer, they can invade tissue (the uterus), but unlike cancer, they usually "know" when to stop. GTD can simulate pregnancy, because the uterus may contain fetal tissue, albeit abnormal. This tissue may grow at the same rate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adverse Drug Reaction
An adverse drug reaction (ADR) is a harmful, unintended result caused by taking medication. ADRs may occur following a single dose or prolonged administration of a drug or may result from the combination of two or more drugs. The meaning of this term differs from the term "side effect" because side effects can be beneficial as well as detrimental. The study of ADRs is the concern of the field known as ''pharmacovigilance''. An adverse event (AE) refers to any unexpected and inappropriate occurrence at the time a drug is used, whether or not the event is associated with the administration of the drug. An ADR is a special type of AE in which a causative relationship can be shown. ADRs are only one type of medication-related harm. Another type of medication-related harm type includes not taking prescribed medications, known as non-adherence. Non-adherence to medications can lead to death and other negative outcomes. Adverse drug reactions require the use of a medication. Classific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compensatory Hyperplasia
Compensatory growth is a type of regenerative growth that can take place in a number of human organs after the organs are either damaged, removed, or cease to function. Additionally, increased functional demand can also stimulate this growth in tissues and organs. The growth can be a result of increased cell size (compensatory hypertrophy) or an increase in cell division (compensatory hyperplasia) or both. For instance, if one kidney is surgically removed, the cells of the other kidney divide at an increased rate. Eventually, the remaining kidney can grow until its mass approaches the combined mass of two kidneys. Along with the kidneys, compensatory growth has also been characterized in a number of other tissues and organs including: * The adrenal glands * The heart * Muscles * The liver * The lungs * The pancreas (beta cells and acinar cells) * The mammary glands * The spleen (where bone marrow and lymphatic tissue undergo compensatory hypertrophy and assumes the spleen functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoplasm
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists in growing abnormally, even if the original trigger is removed. This abnormal growth usually forms a mass, which may be called a tumour or tumor.'' ICD-10 classifies neoplasms into four main groups: benign neoplasms, in situ neoplasms, malignant neoplasms, and neoplasms of uncertain or unknown behavior. Malignant neoplasms are also simply known as cancers and are the focus of oncology. Prior to the abnormal growth of tissue, such as neoplasia, cells often undergo an abnormal pattern of growth, such as metaplasia or dysplasia. However, metaplasia or dysplasia does not always progress to neoplasia and can occur in other conditions as well. The word neoplasm is from Ancient Greek 'new' and 'formation, creation'. Types A neoplasm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiosensitivity
Radiosensitivity is the relative susceptibility of cells, tissues, organs or organisms to the harmful effect of ionizing radiation. Cells types affected Cells are least sensitive when in the S phase, then the G1 phase, then the G2 phase, and most sensitive in the M phase of the cell cycle. This is described by the 'law of Bergonié and Tribondeau', formulated in 1906: X-rays are more effective on cells which have a greater reproductive activity. From their observations, they concluded that quickly dividing tumor cells are generally more sensitive than the majority of body cells. This is not always true. Tumor cells can be hypoxic and therefore less sensitive to X-rays because most of their effects are mediated by the free radicals produced by ionizing oxygen. It has meanwhile been shown that the most sensitive cells are those that are undifferentiated, well nourished, dividing quickly and highly active metabolically. Amongst the body cells, the most sensitive are sper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiotherapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy (RT, RTx, or XRT) is a treatment using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer therapy to either kill or control the growth of malignant cells. It is normally delivered by a linear particle accelerator. Radiation therapy may be curative in a number of types of cancer if they are localized to one area of the body, and have not spread to other parts. It may also be used as part of adjuvant therapy, to prevent tumor recurrence after surgery to remove a primary malignant tumor (for example, early stages of breast cancer). Radiation therapy is synergistic with chemotherapy, and has been used before, during, and after chemotherapy in susceptible cancers. The subspecialty of oncology concerned with radiotherapy is called radiation oncology. A physician who practices in this subspecialty is a radiation oncologist. Radiation therapy is commonly applied to the cancerous tumor because of its ability to control cell growth. Ionizin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiosensitizer
A radiosensitizer is an agent that makes tumor cells more sensitive to radiation therapy. It is sometimes also known as a radiation sensitizer or radio-enhancer. Mechanism of action Conventional chemotherapeutics are currently being used in conjunction with radiation therapy to increase its effectiveness. Examples include the fluoropyrimidines, gemcitabine and platinum analogs; fluoropyrimidines increase sensitivity by dysregulating S-phase cell cycle checkpoints in tumor cells. Gemcitabine progresses through a similar mechanism, causing cells in the S-phase to disrepair DNA damage caused by the radiation. Platinum analogs such as cisplatin inhibit DNA repair by cross linking strands, and so aggravate the effects of DNA damage induced by radiation. Mechanisms of Action Radiosensitizers enhance the effects of radiation therapy through various mechanisms, broadly classified as: DNA Damage Enhancement These agents increase DNA damage caused by radiation or inhibit its repair. Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
J Clin Oncol
The ''Journal of Clinical Oncology'' is a peer-reviewed medical journal published 3 times a month by ASCO Publications. It covers research on all aspects of clinical oncology. The journal was established in 1983 and the editor-in-chief is Jonathan W. Friedberg (University of Rochester). History In 1981 Emil Frei III proposed that the American Society of Clinical Oncology should publish an official journal. The first issue was published on January 1, 1983, containing 70 pages of research and an editorial by the then editor-in-chief, Joseph Bertino. Bertino was succeeded by George P. Canellos in 1987. In 1998, a Spanish language edition of the journal started quarterly publication, followed by a Chinese language edition. Currently there are 10 international editions. Daniel Haller became editor-in-chief in 2001 and during his tenure the journal moved from its publisher Grune & Stratton to in-house publication by society staff. Stephen A. Cannistra was editor-in-chief from 2011 to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
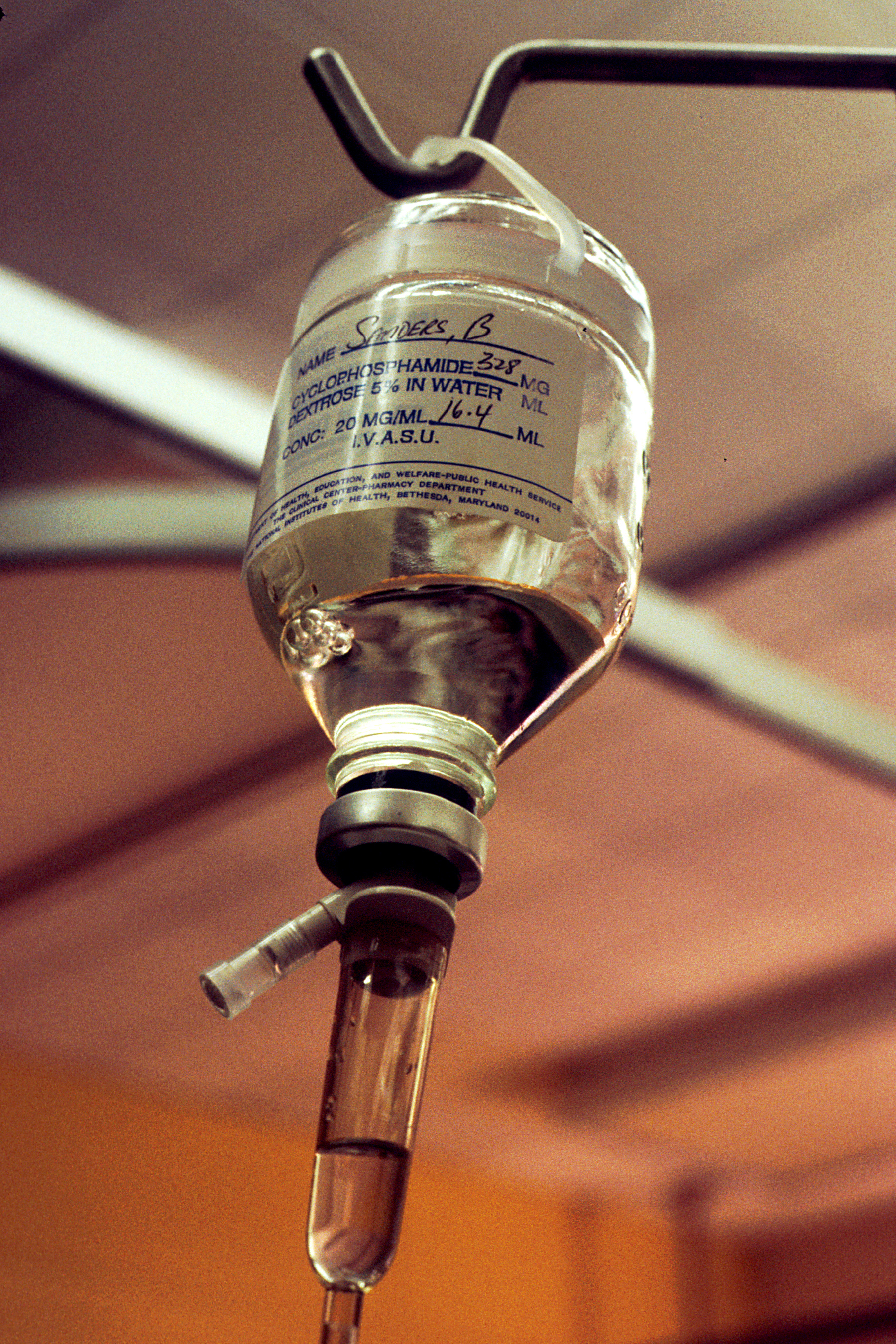
Cyclophosphamide
Cyclophosphamide (CP), also known as cytophosphane among other names, is a medication used as chemotherapy and to suppress the immune system. As chemotherapy it is used to treat lymphoma, multiple myeloma, leukemia, ovarian cancer, breast cancer, small cell lung cancer, neuroblastoma, and sarcoma. As an immune suppressor it is used in nephrotic syndrome, ANCA-associated vasculitis, and following organ transplant, among other conditions. It is taken by mouth or injection into a vein. Most people develop side effects. Common side effects include low white blood cell counts, loss of appetite, vomiting, hair loss, and bleeding from the bladder. Other severe side effects include an increased future risk of cancer, infertility, allergic reactions, and pulmonary fibrosis. Cyclophosphamide is in the alkylating agent and nitrogen mustard family of medications. It is believed to work by interfering with the duplication of DNA and the creation of RNA. Cyclophosphamide was approved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |