|
D Arm
The D arm is a feature in the tertiary structure of transfer RNA (tRNA). It is composed of the two D stems and the D loop. The D loop contains the base dihydrouridine (D), for which the arm is named. The D loop's main function is that of recognition. It is widely believed that it acts as a recognition site for aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase, an enzyme involved in the aminoacylation of the tRNA molecule. The D stem is also believed to have a recognition role although this has yet to be verified. It is a highly variable region and is notable for its unusual conformation due to the over-crowding on one of the guanosine residues. It appears to play a large role in the stabilization of the tRNA's tertiary structure. The role of the D nucleotide in tRNA structure has been demonstrated in a detailed study comparing the structure of the D arm of the ''Schizosaccharomyces pombe'' tRNAiMet with an unmodified uracil Uracil () (nucleoside#List of nucleosides and corresponding nucleobases, sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schema ARNt 448 658
Schema may refer to: Science and technology * SCHEMA (bioinformatics), an algorithm used in protein engineering * Schema (genetic algorithms), a set of programs or bit strings that have some genotypic similarity * Schema.org, a web markup vocabulary * Schema (logic) ** Axiom schema, in formal logic * Image schema, a recurring pattern of spatial sensory experience * Database schema * XML schema Other * Body schema, a neural representation of one's own bodily posture * Galant Schemata, stock phrases in Galant music * Schema (Kant), in philosophy * Schema (psychology), a mental set or representation * Schema Records, a jazz record label in Milan, Italy *, a solemn vow of asceticism of a monk in Orthodox monasticism ** Great Schema, the highest degree of Orthodox monasticism * ''Schema'' (fly), a genus of insects See also * Scheme (other) * Schematic * Skema (other) SKEMA Business School ("School of Knowledge Economy and Management") is a leading French busin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tertiary Structure
Protein tertiary structure is the three-dimensional shape of a protein. The tertiary structure will have a single polypeptide chain "backbone" with one or more protein secondary structures, the protein domains. Amino acid side chains and the backbone may interact and bond in a number of ways. The interactions and bonds of side chains within a particular protein determine its tertiary structure. The protein tertiary structure is defined by its atomic coordinates. These coordinates may refer either to a protein domain or to the entire tertiary structure. A number of these structures may bind to each other, forming a quaternary structure. History The science of the tertiary structure of proteins has progressed from one of hypothesis to one of detailed definition. Although Emil Fischer had suggested proteins were made of polypeptide chains and amino acid side chains, it was Dorothy Maud Wrinch who incorporated geometry into the prediction of protein structures. Wrinch demon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transfer RNA
Transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA), formerly referred to as soluble ribonucleic acid (sRNA), is an adaptor molecule composed of RNA, typically 76 to 90 nucleotides in length (in eukaryotes). In a cell, it provides the physical link between the genetic code in messenger RNA (mRNA) and the amino acid sequence of proteins, carrying the correct sequence of amino acids to be combined by the protein-synthesizing machinery, the ribosome. Each three-nucleotide codon in mRNA is complemented by a three-nucleotide anticodon in tRNA. As such, tRNAs are a necessary component of translation, the biological synthesis of new proteins in accordance with the genetic code. Overview The process of translation starts with the information stored in the nucleotide sequence of DNA. This is first transformed into mRNA, then tRNA specifies which three-nucleotide codon from the genetic code corresponds to which amino acid. Each mRNA codon is recognized by a particular type of tRNA, which docks to it along ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dihydrouridine
Dihydrouridine (abbreviated as D, DHU, or UH2) is a pyrimidine nucleoside which is the result of adding two hydrogen atoms to a uridine, making it a fully saturated pyrimidine ring with no remaining double bonds. D is found in tRNA and rRNA molecules as a nucleoside; the corresponding nucleobase is 5,6-dihydrouracil. Because it is non-planar, D disturbs the stacking interactions in helices and destabilizes the RNA structure. D also stabilizes the C2′- ''endo'' sugar conformation, which is more flexible than the C3′-''endo'' conformation; this effect is propagated to the 5′-neighboring residue. Thus, while pseudouridine and 2′-O-methylations stabilize the local RNA structure, D does the opposite. The tRNAs of organisms that grow at low temperatures (psychrophile Psychrophiles or cryophiles (adj. ''psychrophilic'' or ''cryophilic'') are extremophile, extremophilic organisms that are capable of cell growth, growth and reproduction in low temperatures, ranging from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
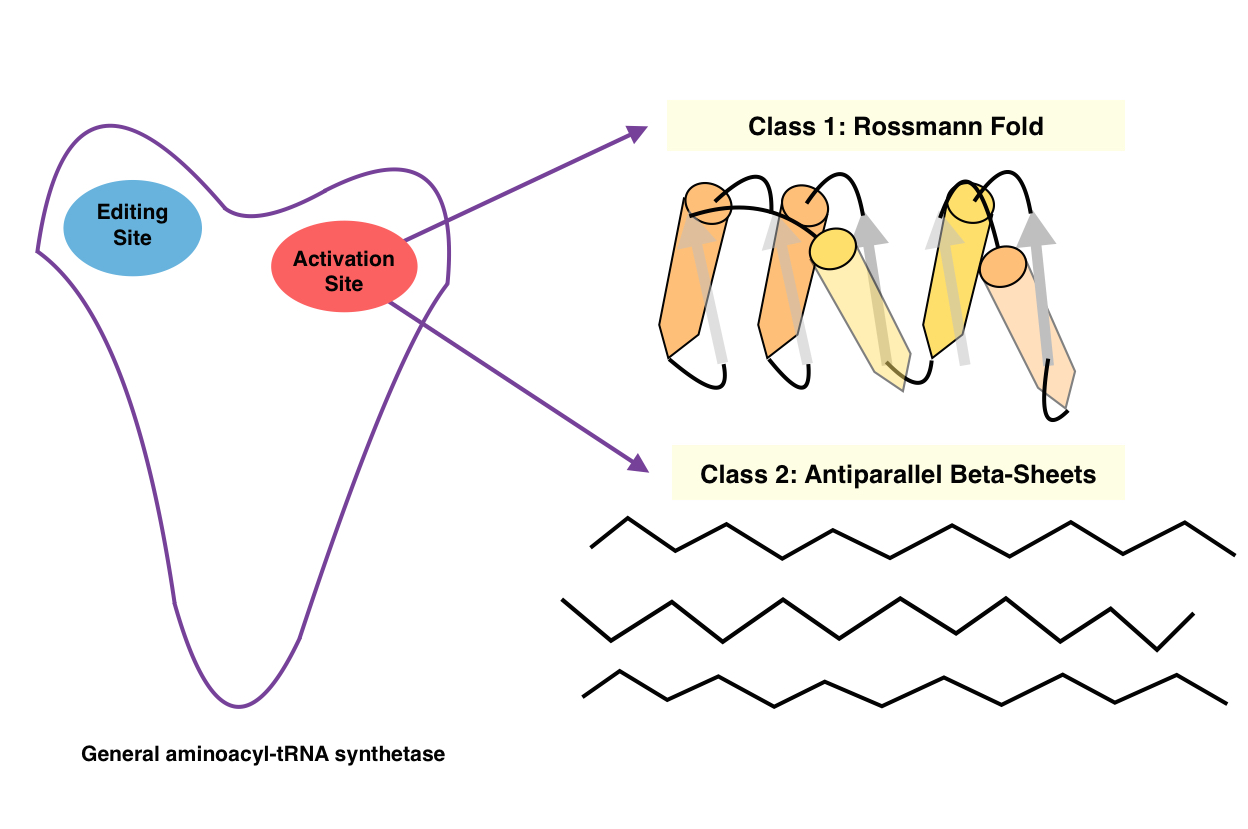
Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetase
An aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (aaRS or ARS), also called tRNA-ligase, is an enzyme that attaches the appropriate amino acid onto its corresponding tRNA. It does so by catalyzing the transesterification of a specific cognate amino acid or its precursor to one of all its compatible cognate tRNAs to form an aminoacyl-tRNA. In humans, the 20 different types of aa-tRNA are made by the 20 different aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, one for each amino acid of the genetic code. This is sometimes called "charging" or "loading" the tRNA with an amino acid. Once the tRNA is charged, a ribosome can transfer the amino acid from the tRNA onto a growing peptide, according to the genetic code. Aminoacyl tRNA therefore plays an important role in RNA translation, the expression of genes to create proteins. Mechanism The synthetase first binds ATP and the corresponding amino acid (or its precursor) to form an aminoacyl-adenylate, releasing inorganic pyrophosphate (PPi). The adenylate-aaRS complex th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aminoacylation
Aminoacylation is the process of adding an aminoacyl group to a compound. See also * Acylation * tRNA aminoacylation * Transfer RNA-like structures References Organic reactions {{Reaction-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanosine
Guanosine (symbol G or Guo) is a purine nucleoside comprising guanine attached to a ribose ( ribofuranose) ring via a β-N9- glycosidic bond. Guanosine can be phosphorylated to become guanosine monophosphate (GMP), cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), guanosine diphosphate (GDP), and guanosine triphosphate (GTP). These forms play important roles in various biochemical processes such as synthesis of nucleic acids and proteins, photosynthesis, muscle contraction, and intracellular signal transduction (cGMP). When guanine is attached by its N9 nitrogen to the C1 carbon of a deoxyribose ring it is known as deoxyguanosine. Physical and chemical properties Guanosine is a white, crystalline powder with no odor and mild saline taste. It is very soluble in acetic acid, slightly soluble in water, insoluble in ethanol, diethyl ether, benzene and chloroform. Functions Guanosine is required for an RNA splicing reaction in mRNA, when a "self-splicing" intron removes itself from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizosaccharomyces Pombe
''Schizosaccharomyces pombe'', also called "fission yeast", is a species of yeast used in traditional brewing and as a model organism in molecular and cell biology. It is a unicellular eukaryote, whose cells are rod-shaped. Cells typically measure 3 to 4 micrometres in diameter and 7 to 14 micrometres in length. Its genome, which is approximately 14.1 million base pairs, is estimated to contain 4,970 protein-coding genes and at least 450 non-coding RNAs. These cells maintain their shape by growing exclusively through the cell tips and divide by medial fission to produce two daughter cells of equal size, which makes them a powerful tool in cell cycle research. Fission yeast was isolated in 1893 by Paul Lindner from East African millet beer. The species name ''pombe'' is the Swahili word for beer. It was first developed as an experimental model in the 1950s: by Urs Leupold for studying genetics, and by Murdoch Mitchison for studying the cell cycle. Paul Nurse, a fission ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uracil
Uracil () (nucleoside#List of nucleosides and corresponding nucleobases, symbol U or Ura) is one of the four nucleotide bases in the nucleic acid RNA. The others are adenine (A), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). In RNA, uracil binds to adenine via two hydrogen bonds. In DNA, the uracil nucleobase is replaced by thymine (T). Uracil is a demethylated form of thymine. Uracil is a common and naturally occurring pyrimidine derivative. The name "uracil" was coined in 1885 by the German chemist Robert Behrend, who was attempting to synthesize derivatives of uric acid. Originally discovered in 1900 by Alberto Ascoli, it was isolated by hydrolysis of yeast nuclein; it was also found in bovine thymus and spleen, herring sperm, and wheat Cereal germ, germ. It is a planar, unsaturated compound that has the ability to absorb light. Uracil that was formed extraterrestrially has been detected in the Murchison meteorite, in near-Earth asteroid 162173 Ryugu, Ryugu, and possibly on the surface of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metazoa
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, have myocytes and are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and grow from a hollow sphere of cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Animals form a clade, meaning that they arose from a single common ancestor. Over 1.5 million living animal species have been described, of which around 1.05 million are insects, over 85,000 are molluscs, and around 65,000 are vertebrates. It has been estimated there are as many as 7.77 million animal species on Earth. Animal body lengths range from to . They have complex ecologies and interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology, and the study of animal behaviour is known as ethology. The animal kingdom is divided into five major clades, namely Porifera, Ctenophora, Placozoa, C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |