|
DXP Reductoisomerase
DXP reductoisomerase (1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase or DXR) is an enzyme that interconverts 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate (DXP) and 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate (MEP). Image:DOXP.png, 1-Deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate Image:MEP.png, 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate It is classified under . It is normally abbreviated DXR, but it is sometimes named IspC, as the product of the ''ispC'' gene. DXR is part of the MEP pathway (nonmevalonate pathway) of isoprenoid precursor biosynthesis. DXR is inhibited by fosmidomycin. This enzyme is required for terpenoid biosynthesis in some organisms, since it is a key enzyme on the MEP pathway for the production of the isoprenoid precursors IPP and DMAPP. In ''Arabidopsis thaliana'' 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase is the first committed enzyme of the MEP pathway for isoprenoid The terpenoids, also known as isoprenoids, are a class of naturally occurring organic chemicals derived from the 5-carbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate
1-Deoxy--xylulose 5-phosphate is a biosynthetic intermediate in the non-mevalonate pathway. Function The enzyme involved in making 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate (DXP) is DXP synthase. The mechanism follows a catalysis of decarboxylative condensation of pyruvate and d-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to produce DXP. In addition, the molecule is involved in making thiamine ( vitamin B1) and pyridoxol ( vitamin B6). The non-mevalonate pathway intermediate 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate (DXP) also acts as a precursor in making isoprenoids in many species such as bacteria, plants, and apicomplexan parasites, contributing to biological diversity. See also * DXP reductoisomerase * Terpenoid The terpenoids, also known as isoprenoids, are a class of naturally occurring organic compound, organic chemicals derived from the 5-carbon compound isoprene and its derivatives called terpenes, diterpenes, etc. While sometimes used interchangeabl ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Deoxy-D-xyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
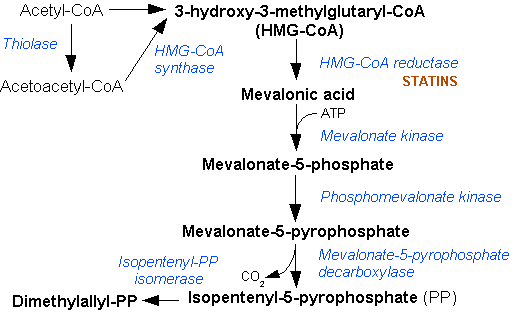
Dimethylallyl Pyrophosphate
Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP; or alternatively, dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMADP); also isoprenyl pyrophosphate) is an isoprenoid precursor. It is a product of both the mevalonate pathway and the MEP pathway of isoprenoid precursor biosynthesis. It is an isomer of isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and exists in virtually all life forms. The enzyme isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase catalyzes isomerization between DMAPP and IPP. In the mevalonate pathway, DMAPP is synthesised from mevalonic acid. In contrast, DMAPP is synthesised from HMBPP in the MEP pathway. At present, it is believed that there is crossover between the two pathways in organisms that use both pathways to create terpenes and terpenoid The terpenoids, also known as isoprenoids, are a class of naturally occurring organic compound, organic chemicals derived from the 5-carbon compound isoprene and its derivatives called terpenes, diterpenes, etc. While sometimes used interchangeabl ...s, such as in plant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic table), it occurs naturally only in combination with other elements and almost always has an oxidation state of +2. It reacts readily with air to form a thin Passivation (chemistry), passivation coating of magnesium oxide that inhibits further corrosion of the metal. The free metal burns with a brilliant-white light. The metal is obtained mainly by electrolysis of magnesium Salt (chemistry), salts obtained from brine. It is less dense than aluminium and is used primarily as a component in strong and lightweight magnesium alloy, alloys that contain aluminium. In the cosmos, magnesium is produced in large, aging stars by the sequential addition of three Helium nucleus, helium nuclei to a carbon nucleus. When such stars explo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. The free element, produced by reductive smelting, is a hard, lustrous, somewhat brittle, gray metal. Cobalt-based blue pigments (cobalt blue) have been used since antiquity for jewelry and paints, and to impart a distinctive blue tint to glass. The color was long thought to be due to the metal bismuth. Miners had long used the name ''kobold ore'' (German language, German for ''goblin ore'') for some of the blue pigment-producing minerals. They were so named because they were poor in known metals and gave off poisonous arsenic-containing fumes when smelted. In 1735, such ores were found to be reducible to a new metal (the first discovered since ancient times), which was ultimately named for the ''kobold''. Today, some cobalt is produced sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manganese
Manganese is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese was first isolated in the 1770s. It is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of industrial alloy uses, particularly in stainless steels. It improves strength, workability, and resistance to wear. Manganese oxide is used as an oxidising agent, as a rubber additive, and in glass making, fertilisers, and ceramics. Manganese sulfate can be used as a fungicide. Manganese is also an essential human dietary element, important in macronutrient metabolism, bone formation, and free radical defense systems. It is a critical component in dozens of proteins and enzymes. It is found mostly in the bones, but also the liver, kidneys, and brain. In the human brain, the manganese is bound to manganese metalloproteins, most notably glutamine synthetase in astrocytes. Manganese is commonly found in labo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoprenoid
The terpenoids, also known as isoprenoids, are a class of naturally occurring organic chemicals derived from the 5-carbon compound isoprene and its derivatives called terpenes, diterpenes, etc. While sometimes used interchangeably with "terpenes", terpenoids contain additional functional groups, usually containing oxygen. When combined with the hydrocarbon terpenes, terpenoids comprise about 80,000 compounds. They are the largest class of plant secondary metabolites, representing about 60% of known natural products. Many terpenoids have substantial pharmacological bioactivity and are therefore of interest to medicinal chemists. Plant terpenoids are used for their aromatic qualities and play a role in traditional herbal remedies. Terpenoids contribute to the scent of eucalyptus, the flavors of cinnamon, cloves, and ginger, the yellow color in sunflowers, and the red color in tomatoes. Well-known terpenoids include citral, menthol, camphor, salvinorin A in the plant '' S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabidopsis Thaliana
''Arabidopsis thaliana'', the thale cress, mouse-ear cress or arabidopsis, is a small plant from the mustard family (Brassicaceae), native to Eurasia and Africa. Commonly found along the shoulders of roads and in disturbed land, it is generally considered a weed. A winter annual with a relatively short lifecycle, ''A. thaliana'' is a popular model organism in plant biology and genetics. For a complex multicellular eukaryote, ''A. thaliana'' has a relatively small genome of around 135 Base pair#Length measurements, megabase pairs. It was the first plant to have its genome sequenced, and is an important tool for understanding the molecular biology of many plant traits, including flower development and phototropism, light sensing. Description ''Arabidopsis thaliana'' is an annual plant, annual (rarely biennial plant, biennial) plant, usually growing to 20–25 cm tall. The leaf, leaves form a rosette at the base of the plant, with a few leaves also on the flowering Plant ste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isopentenyl Pyrophosphate
Isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP, isopentenyl diphosphate, or IDP) is an isoprenoid precursor. IPP is an intermediate in the classical, HMG-CoA reductase pathway (commonly called the mevalonate pathway) and in the ''non-mevalonate'' MEP pathway of isoprenoid precursor biosynthesis. Isoprenoid precursors such as IPP, and its isomer Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate, DMAPP, are used by organisms in the biosynthesis of terpenes and terpenoids. Biosynthesis IPP is formed from acetyl-CoA via the mevalonate pathway (the "upstream" part), and then is isomerized to dimethylallyl pyrophosphate by the enzyme isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase. IPP can be synthesised via an alternative non-mevalonate pathway of isoprenoid precursor biosynthesis, the MEP pathway, where it is formed from (E)-4-Hydroxy-3-methyl-but-2-enyl pyrophosphate, (''E'')-4-hydroxy-3-methyl-but-2-enyl pyrophosphate (HMB-PP) by the enzyme HMB-PP reductase (LytB, IspH). The MEP pathway is present in many bacteria, apicomplex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate
2-''C''-Methyl--erythritol 4-phosphate (MEP) is an intermediate on the MEP pathway (non-mevalonate pathway) of isoprenoid precursor biosynthesis. It is the first committed metabolite on that pathway on the route to IPP and DMAPP. See also * DXP reductoisomerase * MEP pathway (formerly known as the non-mevalonate pathway) * Fosmidomycin Fosmidomycin is an antibiotic that was originally isolated from culture broths of bacteria of the genus ''Streptomyces''. It specifically inhibits DXP reductoisomerase, a key enzyme in the non-mevalonate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis. It is ... References External links * Organophosphates Monosaccharide derivatives {{biochem-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organism
An organism is any life, living thing that functions as an individual. Such a definition raises more problems than it solves, not least because the concept of an individual is also difficult. Many criteria, few of them widely accepted, have been proposed to define what an organism is. Among the most common is that an organism has autonomous reproduction, Cell growth, growth, and metabolism. This would exclude viruses, despite the fact that they evolution, evolve like organisms. Other problematic cases include colonial organisms; a colony of eusocial insects is organised adaptively, and has Germ-Soma Differentiation, germ-soma specialisation, with some insects reproducing, others not, like cells in an animal's body. The body of a siphonophore, a jelly-like marine animal, is composed of organism-like zooids, but the whole structure looks and functions much like an animal such as a jellyfish, the parts collaborating to provide the functions of the colonial organism. The evolutiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis, i.e., chemical synthesis occurring in biological contexts, is a term most often referring to multi-step, enzyme-Catalysis, catalyzed processes where chemical substances absorbed as nutrients (or previously converted through biosynthesis) serve as enzyme substrate (chemistry), substrates, with conversion by the living organism either into simpler or more complex Product (chemistry), products. Examples of biosynthetic pathways include those for the production of amino acids, lipid membrane components, and nucleotides, but also for the production of all classes of biological macromolecules, and of acetyl-coenzyme A, adenosine triphosphate, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and other key intermediate and transactional molecules needed for metabolism. Thus, in biosynthesis, any of an array of Chemical compound, compounds, from simple to complex, are converted into other compounds, and so it includes both the catabolism and anabolism (building up and breaking down) of comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |