|
DPR-RI
The People's Representative Council of the Republic of Indonesia ( id, Dewan Perwakilan Rakyat Republik Indonesia, DPR-RI), also known as the House of Representatives, is one of two elected chambers of the People's Consultative Assembly (MPR), the national legislature of Indonesia. It is considered the lower house, while the Regional Representative Council (DPD) serve as the upper house; while the Constitution of Indonesia, Indonesian constitution does not explicitly mention the divide, the DPR enjoys more power, privilege, and prestige compared to the DPD. Members of the DPR are elected through a elections in Indonesia, general election every five years. Currently, there are 575 members; an increase compared to 560 prior to the 2019 Indonesian legislative election, 2019 elections. The DPR has been the subject of frequent public criticism due to perceived high levels of fraud and Corruption in Indonesia, corruption. History ''Volksraad'' In 1915, members of the Indonesian n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DPR/MPR Building
The MPR/DPR/DPD Building, also known as the MPR/DPR Building is the seat of government for the Indonesian legislative branch of government, which consists of the People's Consultative Assembly ( id, Majelis Permusyawaratan Rakyat, ''MPR'') the People's Representative Council ( id, Dewan Perwakilan Rakyat, ''DPR'') and the Regional Representatives Council ( id, Dewan Perwakilan Daerah, ''DPD''). History Construction Under Sukarno Construction of the building was ordered on 8 March 1965 by Sukarno, the first president of Indonesia, through the Decree of the President of the Republic of Indonesia Number 48/1965. The building was intended to house the Conference of New Emerging Forces ( CONEFO), a now defunct alternative for the United Nations, with the first conference being scheduled for 1966. The members of the organization were planned to consist of the countries of Asia, Africa, Latin America, and the Non-Aligned Movement. The first conference was scheduled for 1966, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Speakers Of The People's Representative Council
The Speaker of the House of Representatives, ( id, Ketua Dewan Perwakilan Rakyat; )is the presiding officer of the House of Representatives of Indonesia. The speaker is the political and parliamentary leader of the House of Representatives and is simultaneously the Council's presiding officer. The speakers also perform various other administrative and procedural functions. Duties The duties of the speaker have been determined on 22 October 2019 through the Decree of the House of Representatives of the Republic of Indonesia Number 34/DPR RI/I/2019-2020 concerning the Division of Duties of the Leaders of the DPR RI for the 2019-2024 Membership Period. The duties of the Chairperson of the DPR RI are general in nature and cover all Coordination Fields, namely : * Coordinator for Political and Security Affairs (Korpolkam) in charge of the scope of duties of Commission I, Commission II, Commission III, Inter-Parliamentary Cooperation Agency, and the Legislative Body. * Coordinator f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golkar
) , foundation = , youth = AMPG (Golkar Party Young Force) , women = KPPG (Golkar Party Women's Corps) , newspaper = '' Suara Karya'' (1971–2016) , headquarters = Jakarta , ideology = PancasilaConservatism National conservatism Economic liberalism Indonesian nationalismSecularism Suhartoism Catch-all party During the New Order: Big tent Right-wing authoritarianism , political_position = , anthem = ''Mars Partai Golkar'' , national = Onward Indonesia Coalition United Indonesia Coalition , BallNo = 4 , DPRseats = , DPRD1seats = , labour = , website = , footnotes = The Party of Functional Groups ( id, Partai Golongan Karya), often known by its abbreviation Golkar, is a political party in Indonesia. It was founded as the Joint Secretariat of Functional Groups ( id, Sekretariat Bersama Golongan Karya, links=no, Sekber G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corruption In Indonesia
While hard data on corruption is difficult to collect, corruption in Indonesia is clearly seen through public opinion, collated through surveys as well as observation of how each system runs.Lateef, S. ''et al''; ''Combating Corruption in Indonesia'', World Bank East Asia Poverty Reduction and Economic Management Unit 200Full text/ref> Transparency International's 2021 Corruption Perception Index ranks the country 96th place out of 180 countries, an improvement from 102nd place the previous year. The 180 countries in the Index are ranked on a scale where the lowest-ranked countries are perceived to have the most honest public sector. There are two key areas in the public sector in which corruption in Indonesia can be found. These are the justice and civil service sectors. Corruption within the justice sector is seen by its ineffectiveness to enforce laws, failure to uphold justice, hence undermining the rule of law. The areas of corruption within this sector include the police ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2019 Indonesian Legislative Election
General elections were held in Indonesia on 17 April 2019. For the first time in the country's history, the president, the vice president, members of the People's Consultative Assembly (MPR), and members of local legislative bodies were elected on the same day with over 190 million eligible voters. Sixteen parties participated in the elections nationally, including four new parties. The presidential election, the fourth in the country's history, used a direct, simple majority system, with incumbent president Joko Widodo, known as Jokowi, running for re-election with senior Muslim cleric Ma'ruf Amin as his running mate against former general Prabowo Subianto and former Jakarta vice governor Sandiaga Uno for a five-year term between 2019 and 2024. The election was a rematch of the 2014 presidential election, in which Jokowi defeated Prabowo. The legislative election, which was the 12th such election for Indonesia, saw over 240,000 candidates competing for over 20,000 seats in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elections In Indonesia
Elections in Indonesia have taken place since 1955 to elect a legislature. At a national level, Indonesian people did not elect a head of state – the President (government title), president – until 2004. Since then, the president is elected for a five-year term, as are the 575-member People's Representative Council (''Dewan Perwakilan Rakyat'', DPR), the 136-seat Regional Representative Council (''Dewan Perwakilan Daerah''), in addition to provincial and municipal legislative councils. Members of the People's Representative Council are elected by proportional representation from multi-candidate Constituency, constituencies. Currently, there are 77 constituencies in Indonesia, and each returns 3-10 Members of Parliament based on population. Under Indonesia's multi-party system, no one party has yet been able to secure an outright majority in a democratic election; parties have needed to work together in coalition governments. Members of the Regional Represent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
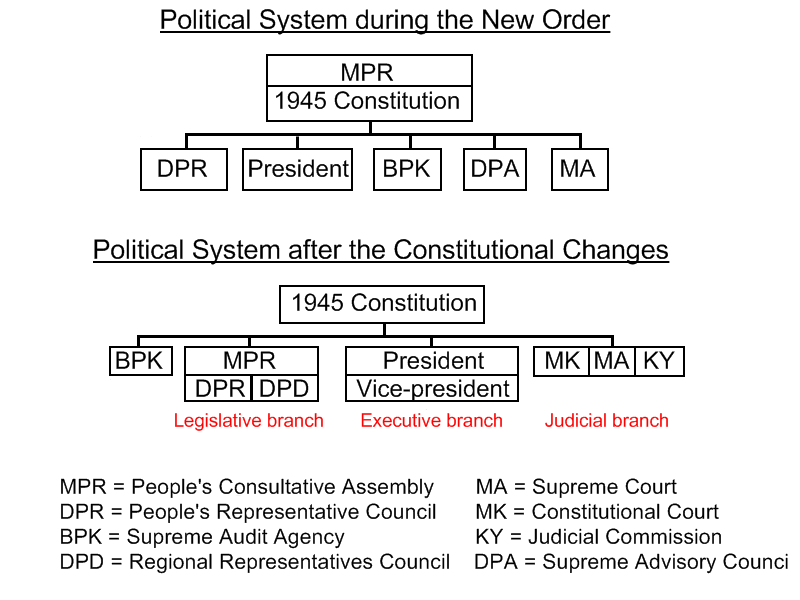
Constitution Of Indonesia
The 1945 State Constitution of the Republic of Indonesia ( id, Undang-Undang Dasar Negara Republik Indonesia Tahun 1945, commonly abbreviated as ''UUD 1945'' or ''UUD '45'') is the supreme law and basis for all laws of Indonesia. The constitution was written in June, July, and August 1945, in the final months of the Japanese occupation of the Dutch East Indies at the end of World War II. It was abrogated by the Federal Constitution of 1949 and the Provisional Constitution of 1950, but restored by President Sukarno's 1959 Decree. The 1945 Constitution sets forth the Pancasila, the five nationalist principles, as the embodiment of basic principles of an independent Indonesian state. It provides for a limited separation of executive, legislative, and judicial powers. The governmental system has been described as "presidential with parliamentary characteristics."King (2007) Following major upheavals in 1998 and the resignation of President Suharto, several political reforms w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper House
An upper house is one of two chambers of a bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the lower house.''Bicameralism'' (1997) by George Tsebelis The house formally designated as the upper house is usually smaller and often has more restricted power than the lower house. A legislature composed of only one house (and which therefore has neither an upper house nor a lower house) is described as unicameral. Definite specific characteristics An upper house is usually different from the lower house in at least one of the following respects (though they vary among jurisdictions): Powers: *In a parliamentary system, it often has much less power than the lower house. Therefore, in certain countries the upper house **votes on only limited legislative matters, such as constitutional amendments, **cannot initiate most kinds of legislation, especially those pertaining to supply/money, fiscal policy **cannot vote a motion of no confidence against the government (or such an act is much ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regional Representative Council
The Regional Representative Council ( id, Dewan Perwakilan Daerah, DPD; alternatively translatable as the House of Regions or the House of Regional Representatives or the Senate of Indonesia), is one of two parliamentary chambers in Indonesia. Together with the ''Dewan Perwakilan Rakyat,'' (DPR), it makes up the Indonesian national legislative body, the ''Majelis Permusyawaratan Rakyat'' (MPR). Under Indonesia's constitution, the authority of the DPD is limited to areas related to regional governments and can only propose and give advice on bills to the DPR. Unlike the DPR, the DPD has no direct law-making power. Its members are usually called senators instead of DPD members. History The idea of regional representation in parliament was initially accommodated in the original version of the 1945 Constitution, with the concept of ''Utusan Daerah'' (Regional Representatives) in the MPR, along with ''Utusan Golongan'' (Group Representatives) and members of the DPR. This is reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower House
A lower house is one of two chambers of a bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the upper house. Despite its official position "below" the upper house, in many legislatures worldwide, the lower house has come to wield more power or otherwise exert significant political influence. The lower house, typically, is the larger of the two chambers, meaning its members are more numerous. Common attributes In comparison with the upper house, lower houses frequently display certain characteristics (though they vary per jurisdiction). ;Powers: * In a parliamentary system, the lower house: **In the modern era, has much more power, usually based on restrictions against the upper house. **Is able to override the upper house in some ways. **Can vote a motion of no confidence against the government, as well as vote for or against any proposed candidate for head of government at the beginning of the parliamentary term. **Exceptions are Australia, where the Senate has considerable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_di_Republik_Indonesia%2C_p83.jpg)