|
DNA Library
In molecular biology, a library is a collection of genetic material fragments that are stored and propagated in a population of microbes through the process of molecular cloning. There are different types of DNA libraries, including CDNA library, cDNA libraries (formed from Complementary DNA, reverse-transcribed RNA), Genomic library, genomic libraries (formed from genomic DNA) and randomized mutant libraries (formed by de novo gene synthesis where alternative nucleotides or codons are incorporated). DNA library technology is a mainstay of current molecular biology, genetic engineering, and protein engineering, and the applications of these libraries depend on the source of the original DNA fragments. There are differences in the cloning vectors and techniques used in library preparation, but in general each DNA fragment is uniquely inserted into a cloning vector and the pool of recombinant DNA molecules is then transferred into a population of bacteria (a Bacterial Artificial C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Site Saturation Mutagenesis
Saturation mutagenesis, or site saturation mutagenesis (SSM), or simply site saturation, is a Mutagenesis (molecular biology technique), random mutagenesis technique used in protein engineering, in which a single codon or set of codons is substituted with all possible amino acids at the position. There are many variants of the site saturation technique, from paired site saturation (saturating two positions in every mutant in the library) to scanning single-site saturation (performing a site saturation at each site in the protein, resulting in a library of size 20''n'', where ''n'' is the number of peptides in the protein, or ''n''-site saturation, where n sites in a peptide would be site saturated, with a library size of 20n, where if the length of your peptide is ''n'', you have complete randomization. Method Saturation mutagenesis is commonly achieved by site-directed mutagenesis PCR with a randomised codon in the primers (e.g. SeSaM) or by Artificial gene synthesis#Applicati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternative Splicing
Alternative splicing, alternative RNA splicing, or differential splicing, is an alternative RNA splicing, splicing process during gene expression that allows a single gene to produce different splice variants. For example, some exons of a gene may be included within or excluded from the final RNA product of the gene. This means the exons are joined in different combinations, leading to different splice variants. In the case of protein-coding genes, the proteins translated from these splice variants may contain differences in their amino acid sequence and in their biological functions (see Figure). Biologically relevant alternative splicing occurs as a normal phenomenon in eukaryotes, where it increases the number of proteins that can be encoded by the genome. In humans, it is widely believed that ~95% of multi-exonic genes are alternatively spliced to produce functional alternative products from the same gene but many scientists believe that most of the observed splice variants ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturation Mutagenesis
Saturation mutagenesis, or site saturation mutagenesis (SSM), or simply site saturation, is a random mutagenesis technique used in protein engineering, in which a single codon or set of codons is substituted with all possible amino acids at the position. There are many variants of the site saturation technique, from paired site saturation (saturating two positions in every mutant in the library) to scanning single-site saturation (performing a site saturation at each site in the protein, resulting in a library of size 20''n'', where ''n'' is the number of peptides in the protein, or ''n''-site saturation, where n sites in a peptide would be site saturated, with a library size of 20n, where if the length of your peptide is ''n'', you have complete randomization. Method Saturation mutagenesis is commonly achieved by site-directed mutagenesis PCR with a randomised codon in the primers (e.g. SeSaM) or by artificial gene synthesis, with a mixture of synthesis nucleotides used at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Gene Synthesis
Artificial gene synthesis, or simply gene synthesis, refers to a group of methods that are used in synthetic biology to construct and assemble genes from nucleotides ''de novo''. Unlike DNA synthesis in living cells, artificial gene synthesis does not require template DNA, allowing virtually any DNA sequence to be synthesized in the laboratory. It comprises two main steps, the first of which is solid-phase DNA synthesis, sometimes known as DNA printing. This produces oligonucleotide fragments that are generally under 200 base pairs. The second step then involves connecting these oligonucleotide fragments using various DNA assembly methods. Because artificial gene synthesis does not require template DNA, it is theoretically possible to make a completely synthetic DNA molecule with no limits on the nucleotide sequence or size. Synthesis of the first complete gene, a yeast tRNA, was demonstrated by Har Gobind Khorana and coworkers in 1972. Synthesis of the first peptide- and protein-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indel
Indel (insertion-deletion) is a molecular biology term for an insertion or deletion of bases in the genome of an organism. Indels ≥ 50 bases in length are classified as structural variants. In coding regions of the genome, unless the length of an indel is a multiple of 3, it will produce a frameshift mutation. For example, a common microindel which results in a frameshift causes Bloom syndrome in the Jewish or Japanese population. Indels can be contrasted with a point mutation. An indel inserts or deletes nucleotides from a sequence, while a point mutation is a form of substitution that ''replaces'' one of the nucleotides without changing the overall number in the DNA. Indels can also be contrasted with Tandem Base Mutations (TBM), which may result from fundamentally different mechanisms. A TBM is defined as a substitution at adjacent nucleotides (primarily substitutions at two adjacent nucleotides, but substitutions at three adjacent nucleotides have been observed). In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
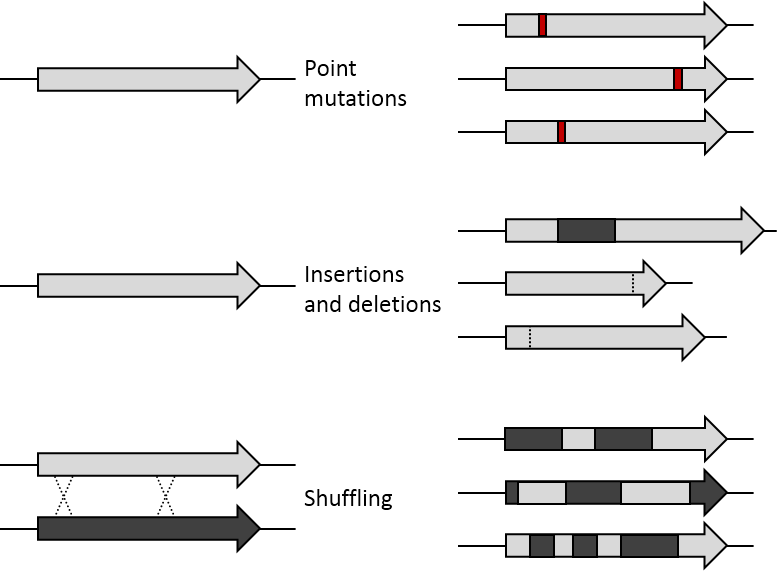
DNA Shuffling
DNA shuffling, also known as molecular breeding, is an in vitro random recombination method to generate mutant genes for directed evolution and to enable a rapid increase in DNA library size. Three procedures for accomplishing DNA shuffling are molecular breeding which relies on homologous recombination or the similarity of the DNA sequences, restriction enzymes which rely on common restriction sites, and nonhomologous random recombination which requires the use of hairpins. In all of these techniques, the parent genes are fragmented and then recombined. DNA shuffling utilizes random recombination as opposed to site-directed mutagenesis in order to generate proteins with unique attributes or combinations of desirable characteristics encoded in the parent genes such as thermostability and high activity. The potential for DNA shuffling to produce novel proteins is exemplified by the figure shown on the right which demonstrates the difference between point mutations, insertions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Error-prone PCR
Cognitive dimensions or cognitive dimensions of notations are design principles for notations, user interfaces and programming languages, described by researcher Thomas R.G. Green and further researched with Marian Petre. The dimensions can be used to evaluate the usability of an existing ''information artifact'', or as heuristics to guide the design of a new one, and are useful in Human-Computer Interaction design. Cognitive dimensions are designed to provide a lightweight approach to analyse the quality of a design, rather than an in-depth, detailed description. They provide a common vocabulary for discussing many factors in notation, UI or programming language design. Also, cognitive dimensions help in exploring the space of possible designs through ''design maneuvers'', changes intended to improve the design along one dimension. List of the cognitive dimensions Thomas Green originally defined 14 cognitive dimensions: ; Abstraction gradient : What are the minimum and maxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible Signs and symptoms of cancer, signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in defecation, bowel movements. While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes. List of cancer types, Over 100 types of cancers affect humans. Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths. Another 10% are due to obesity, poor Diet (nutrition), diet, sedentary lifestyle, lack of physical activity or Alcohol abuse, excessive alcohol consumption. Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants. infectious causes of cancer, Infection with specific viruses, bacteria and parasites is an environmental factor cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other types of damage to DNA (such as pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), cause an error during other forms of repair, or cause an error during replication ( translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from substitution, insertion or deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce detectable changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity. Mutation is the ult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regulatory Sequences
Regulation is the management of complex systems according to a set of rules and trends. In systems theory, these types of rules exist in various fields of biology and society, but the term has slightly different meanings according to context. For example: * in government, typically regulation (or its plural) refers to the delegated legislation which is adopted to enforce primary legislation; including land-use regulation * in economy: regulatory economics * in finance: financial regulation * in business, industry self-regulation occurs through self-regulatory organizations and trade associations which allow industries to set and enforce rules with less government involvement; and, * in biology, gene regulation and metabolic regulation allow living organisms to adapt to their environment and maintain homeostasis; * in psychology, self-regulation theory is the study of how individuals regulate their thoughts and behaviors to reach goals. Forms Regulation in the social, pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transgenic Animal
Genetically modified animals are animals that have been genetically modified for a variety of purposes including producing drugs, enhancing yields, increasing resistance to disease, etc. The vast majority of genetically modified animals are at the research stage while the number close to entering the market remains small. Production The process of genetically engineering mammals is a slow, tedious, and expensive process.Murray, Joo (20)Genetically modified animals. Canada: Brainwaving As with other genetically modified organisms (GMOs), first genetic engineers must isolate the gene they wish to insert into the host organism. This can be taken from a cell containing the gene or artificially synthesised. If the chosen gene or the donor organism's genome has been well studied it may already be accessible from a genetic library. The gene is then combined with other genetic elements, including a promoter and terminator region and usually a selectable marker. A number of techniqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |